Metaphase Technologies ULC-2 User manual

pg. 1 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
ULC
Metaphase
Technologies
Version 7.X
September 2018
USER MANUAL

pg. 2 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
ULC-2 Overview
Metaphase Technologies’ Universal LED Controller (ULC-2) provides independent true
constant-current or voltage control of two LED loads from 0.02 to 4 Amps continuous
(DC) with a maximum output power of 60 Watts per channel. In Pulse (Strobe) Mode, the
ULC-2 is capable of output currents ranging from 0.1 to 40 Amps. Pulsewidths are adjust-
able down to 2 microseconds and external trigger rates up to 50kHz. In Voltage Mode,
ULC-2 output can range from 3V and 50V in 0.1 Volt increments.
The ULC-2 may be remotely controlled over Ethernet using Metaphase Technologies’ Me-
taBOSS Windows software or by third-party programs using the ULC-2’s Ethernet Com-
mands. Additionally, user-adjustments of the ULC-2 are provided by way of a user-friendly
LCD interface. Up to ve preset congurations may be saved and recalled to meet the
changing demands of today’s applications.

pg. 3 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
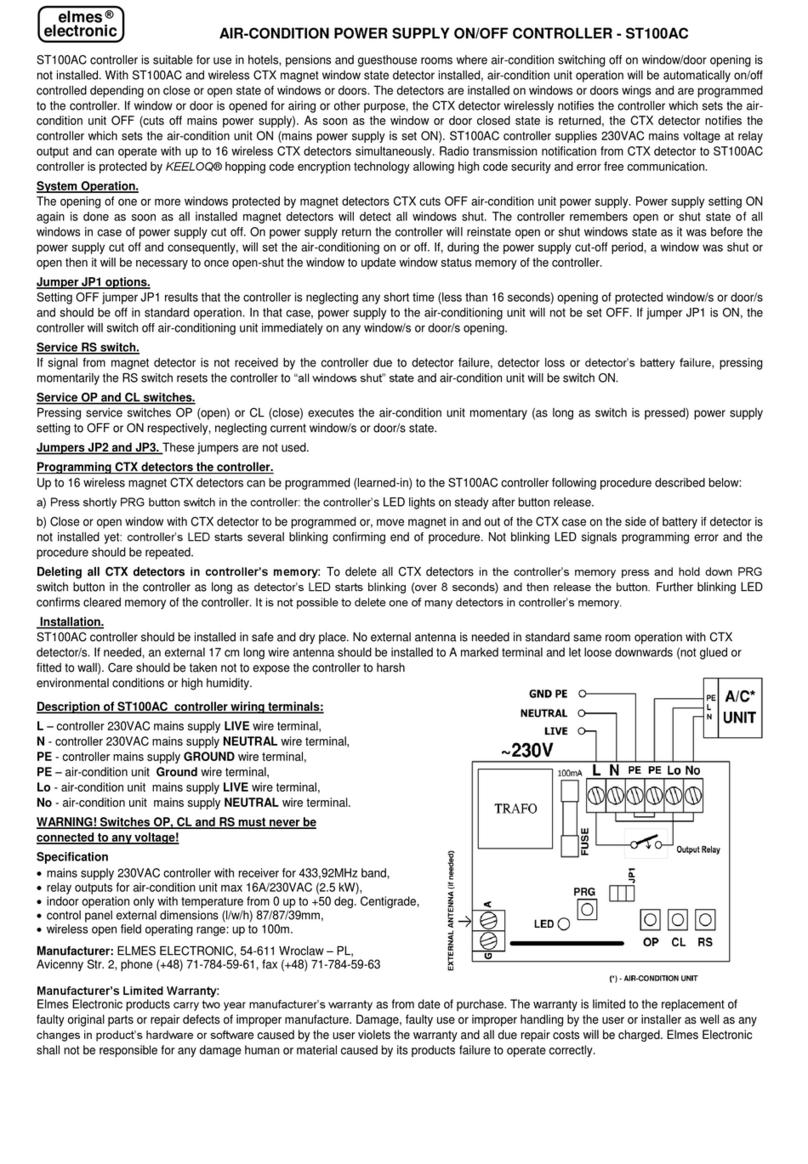
Wiring Connections
Please refer to the diagram below for LED output and trigger input connections.
The ULC-2 is powered by a user-supplied regulated power supply having the following ratings:
• 24VDC +/-10% recommended. Minimum of 9VDC with DC Mode output power derating
(see appendix E).
• 6Amp
• Switching topology (as opposed to linear)
• CE
ULC-2 LED Outputs
• Minimum recommended wire size - 18AWG
• Maximum recommended distance to LED - 10ft (for more info, see Appendix D)
• Un-powered, connect channel 1 & 2 LED loads to the positive and negative LED outputs.
Connecting or disconnecting LED loads while the ULC-2 is powered may damage the ULC-2
controller and/or the LED load.
• To minimize rise-time distortion and guarantee pulsewidth values, keep all LED load wires as
short as possible, and preferably twisted.
ULC-2 Trigger Inputs – (Minimum Recommended Wire Size – 24 AWG)
• For external trigger operation, each channel has its own separate trigger inputs.
Trigger pulses enable the LED output for a period set by the Pulsewidth parameter.
• Twist the + and - input wires together tightly (Twisted pair will pick up less noise)
• Make the trigger input wires as short as possible
• Route the trigger input wires separately from the LED output wires
• Cross wires for other circuits at 90° if necessary. Avoid running them parallel to each other.
(Reduce coupling of large transient noise sources to sensitive circuits)

pg. 4 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
Quick Start
Follow the steps below to quickly setup the Metaphase ULC-2 for basic operation using the
ULC-2 keypad:
1. With external loads disconnected, apply 24V power to the unit.
2. After applying power to the device, the boot-up screen will ash and display the current
software versions. At the bottom left you will nd the current Controller Version followed by the
two Driver Versions:
3. When prompted, choose Yes to enter the Setup Menus.
Though the intended operation of the ULC-2 may be only DC, Voltage or Strobe, the unit should be
congured to safely operate in all three modes in case the operation mode is set improperly at a later
time. Scroll through the various menus using the button located on the ULC-2 front panel.
*If setup prompt is missed at startup, the unit can be prompted to enter the setup menu at any time by
pressing the and buttons simultaneously.
• DC Current Limit – set the maximum DC current for which the LED load is rated. A setting of
200mA is the default. (Range 20 – 4000mA. This parameter applies only to DC Current Mode.)
• Strobe Current Limit – set the maximum peak current for which the LED load is rated for its
associated maximum pulse width. A setting of 1000mA is default. (100-40,000mA Range. This
parameter applies only to Strobe Mode.)
M
M

pg. 5 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
• Pulse width Limit – set the maximum pulse width associated with the maximum peak current.
A low value is safest, but may not
be seen if set too low.(2-60,000µs
range). A setting of 200µs is de
fault.
• Strobe Minimum Period Limit – set the minimum period for which external trigger
pulses will be allowed. A high
value, ex. 60,000 microseconds, is
safest. (20-60,000µs range). A set-
ting of 1000µs is default.
• Voltage Mode Enable – A setting of No-normal is default.
• Voltage Limit – Used to limit the maximum voltage output of the ULC-2. (3-50V range. This
parameter applies only to DC Volt-
age Mode). A setting of 3V is de-
fault.
• Trigger Source – Used to determine Internal or External trigger source. A setting of Internal is
default
• Trigger Polarity - Used to dene which edge of the trigger pulse the system res from.
Rising edge is the default, which is
typical for most users.
• Trigger Controls DC - Used to control DC LED output via trigger signal if set to YES; Default
(Normal) is a setting of NO. If “Trig Controls DC” is set to YES, then the trigger input will control
the DC Current or DC Voltage output. If “Trigger Polarity” is set to “RISING”, then the output
will be ON when a voltage is present at the trigger input. If “Trigger Polarity” is set to “FALLING”,
then the output will be ON when a
voltage is NOT present at the trig-
ger input.”

pg. 6 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
• Repeat the above steps for Channel 2. Scroll through the channels using the button located
on the ULC-2 front panel.
• IP Address- To change the IP Address, select IP Addr Octet from the menu. Using the up and
down arrow, scroll through each Octet 1-4 to change each segment of the IP address.
• Keypad Lock: To prevent changes to the ULC-2 controls, a lock button feature is included
• Keypad Unlock: When locked, press the and buttons similtaneously and select YES to
enter the setup mode.
From there, scroll down to the Unlock Menu and select UNLOCK.
(A locked controller can also be unlocked via MetaBOSS). A setting of unlocked is default
4. Exit the Setup Menus to enter the Run-time Menus.
5. Disconnect power to the ULC-2 device and connect an external LED load.
6. Re-apply power to the ULC-2. Set the DC Current, DC Voltage, and Strobe to application/light
preferences.
M
C

pg. 7 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
User-interface Menus
A. Setup Menus
The setup menus below appear only when the ULC-2 is powered on. Each menu described below ap-
plies to two channels independently. The menus include:
Trigger Source (Internal or External)
This menu allows the setting of the source of trigger when in Strobe mode. In normal operation, Exter-
nal trigger is selected, but for setup and testing purposes, users may elect to use internal trigger in an
effort to verify wiring connections and operation.
When set to External trigger, the ULC-2 will ignore external trigger input events received faster than
what is set by Strobe Minimum Period.
For Internal trigger, the frequency of the strobing output is set by Strobe Minimum Period. For both
types of trigger, the output Strobe Pulsewidth is determined by the Strobe Pulsewidth parameter.
Continuous (DC) Current Limit
This “Limit” menu provides the user a way to set the upper bound of the LED output DC Current up to
4 A current found in the “Run time” menus. For example, if the DC Current Limit is set to 1.6 Amps, the
DC current can be adjusted from 20mA to 1.6 Amps. Such a limit assures adjustments never exceed the
limits of the LED load. This limit applies only to DC Current Mode of operation. In DC Voltage Mode, the
ouput current may exceed 4A depending upon the load.
Voltage (DC) Limit
This “Limit” menu provides the user a way to set the upper bound of the LED output DC Voltage (found
in the Runtime menu) between 3 and 50 volts. For example, if the DC Voltage Limit is set to 24 volts,
the DC Voltage can be adjusted from 3 volts 24 volts. Such a limit assures adjustments never exceed the
limits of the LED load. This limit applies only to DC Voltage Mode of operation. In DC Current Mode, the
output voltage may exceed 60V depending upon the load.
Strobe (Pulse) Current Limit
This “Limit” menu provides the user a way to set the upper bound of the LED output Strobe current up
to 40 amps found in the “Run time” menus. For example, if the Strobe Current Limit is set to 9 Amps,
the Strobe current can be adjusted from 100mA to 9 Amps. Such a limit assures adjustments never ex-
ceed the limits of the LED load.
Strobe Pulsewidth Limit
This “Limit” menu provides the user a way to set the maximum LED output Strobe Pulsewidth found
in the “Run time” menus. For example, if the Strobe Pulsewidth Limit is set to 100 microseconds, the
Strobe Pulsewidth can be adjusted from 2 to 100 microseconds. Such a limit assures adjustments never
exceed the limit of the LED load.

pg. 8 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
User-interface Menus
Strobe Minimum Period Limit
This “Limit” menu provides the user a way to set the Minimum Period of the external strobe triggers
found in the “Runtime” menus. For example, if the Minimum Period Limit is set to 100 microseconds,
the Minimum Period can be adjusted from a maximum of 60 milliseconds down to a minimum of 100
microseconds. Such a limit assures adjustments never exceed the limits of the LED load.
Restore to Default
This allows for the device to be restored to original factory settings, but does not change the IP address.
First, reboot the device until the version menu is displayed.
When the above is displayed, hold the Down Arrow button to restore default settings.
The device should now be restored to the original settings and prompt you to enter setup mode.
Jump to Setup
Hold down the and buttons simultaneously to return to the Setup Menu at any time.
Resetting IP Address
In the unlikely event that, the software is corrupted, preventing IP address changes within the Setup
menu, the IP Address can be reset to 172.16.1.1 by pressing & simultaneously immediately after
power up. Alternatively, for applications where the controller does not have buttons on the front face,
the IP address can be reset to 172.16.1.1 by power cycling the controller four times, leaving it in pow-
ered on for 5 to 6 seconds each time. Exceeding the 6 seconds will reset the counter and subsequently
require four more power cycles.
M
M

pg. 9 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
Runtime Menus
These menus are shown after the setup menus. Each menu described below applies to two channels inde-
pendently. The menus include:
Mode - The Mode menu controls whether the ULC-2 output is continuous DC current, DC voltage, or
Strobed.
DC Current - The DC current menu controls the ULC- 2 out put from 20mA to the Current Limit value
set in the Setup menus. This menu ap-
pears only when the mode is set to DC
Current.
DC Voltage - The DC Voltage menu controls the ULC-2 output from 3V to the Voltage DC Limit value
set in the Setup menus. This menu appears only when the mode is set to DC Voltage.
Strobe Pulse Current - The Pulse current menu controls the ULC-2 output from .1 Amps to the
Pulse Current Limit value set in the Setup menus. This menu appears only when the mode is set to Strobe.
Strobe Pulsewidth - The Strobe Pulsewidth menu controls the ULC-2 output from 2 microseconds
to the Strobe Pulsewidth Limit value set in the Setup menus. This menu
appears only when the mode is set to Strobe.
Strobe Minimum Period - The Strobe Minimum Period menu controls the ULC-2 output from 60
msec down to the minimum value set by Strobe Minimum Period Limit
value set in the Setup menus. This menu appears only when the mode is
set to Strobe. The ULC-2 controller ignores trigger inputs faster than the
Strobe Minimum Period.

pg. 10 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
Runtime Menus
Strobe Trigger Delay
The Strobe Trigger Delay menu controls the delay between a trigger input and the ULC-2’s subsequent
pulse output from 60 msec down to the minimum. There exists a minimum delay of 6 usec (typical) by
default. This menu appears only when the mode is set to Strobe.
One-shot Internal Trigger
This menu allows the user to simulate one cycle of strobe output triggered by the internal trigger. Dur-
ing setup, this feature helps the user determine the appropriate values of pulse width, period, and strobe
current for their specic application. This menu appears only when the mode is set to Strobe.
Save/Recall (5 Presets)
This menu allows all Setup and Runtime settings to be stored in up to 5 presets. Each preset allows pa-
rameter settings for both Channels 1 & 2.
To use one of the presets, select what mode the device will be operating under (Strobe, DC Current, or
DC Voltage) and change settings as desired. After going through all settings, you will nd the Preset Display:
To save the options chosen select the preset number you would like with the button
After choosing which preset to use, select the down arrow to save.
To recall a saved setting, select the desired preset number and hit the up arrow .
This will recall your pre-dened settings as desired.
C

pg. 11 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
MetaBOSS Windows Control Software
Metaphase provides Windows software to control ULC-2 controller from a remote PC. Please follow the
instructions below for setting up the MetaBOSS software:
MetaBOSS Installation & Operation
•Go to https://www.metaphase-tech.com/controllers/ulc-2 to download a copy of the latest MetaBOSS software.
•Unzip the file into a folder of your choosing (typically c:\Metaboss)
•Microsoft .Net Framework 4.0 or later must be installed on the PC. The free upgrade may be found at
http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?id=17851
•The ULC-2 Controller has a default IP address of 172.16.1.1. The PC running MetaBOSS must
be on the same subnet. i.e. – the PC must have an address beginning with 172.16. As required, set the IP address of
the host PC to a 172.16 address (such as 172.16.0.100). The subnet mask should be set to 255.255.0.0 on a 172.16
network and 255.255.255.00 on a 192.168 network.
•Connect the ULC-2 and host PC, using standard CAT-5 patch cables, to an Ethernet switch. Alternatively, connect
the host PC directly to the ULC-2 using a “cross-over” CAT-5 cable.
•Double-click the MetaBOSS.exe application within the installed folder.
•ULC-2 parameters should be displayed automatically upon startup
[APPENDIX A]

pg. 12 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
ULC-2 Ethernet Command List
For users that do not want to use the MetaBOSS Software or the ULC-2 keypad, Metaphase provides
an Ethernet command list that can be embedded into users’ custom programs. All commands are UDP.
The default IP address of the ULC-2 is 172.16.1.1, but can be changed as described elsewhere in this
manual.
The ULC-2 port is 5000 (i.e. the destination port) and can listen for messages originating from any port
should port 5000 not be available on the Windows PC. Use the link below to access the complete com-
mand list on Metaphase Technologies’ website, located in the “file cabinet” at the bottom of the page:
https://www.metaphase-tech.com/controllers/ulc-2
The Ethernet commands are of the following format:
Incoming and Outgoing Message Structure:
<2-byte length> <1-byte channel> <1-byte command> <1-byte reserved> <3-bytes of data>
Message Example: 00 08 01 BF 00 00 9A 5B
all data is in Hex (the space between bytes are added here just for readability
and should not be included in the message)
• Length is 00 08 the length is always 00 08
• Channel is 00 channel is either 00 or 01
• Command is BF command for setting Pulse current
• Reserved is 00 reserved is always 00
• Data is 00 9A 5B Pulse current is 39,515mA (9A5B hex is 39515 decimal)
[APPENDIX B]

pg. 13 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
ULC-2 Trigger Input Equivalent Schematic
[APPENDIX C]

pg. 14 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
Wiring Connections and Noise Considerations
In general, the LED load should be 10’ or less away from the ULC-2 and the wire should be 18AWG or larger. This will work
well in most cases where the pulsewidth is 40us or more, the pulse current is 40A or less, and the nominal forward voltage of
the LED is 25V or less. One exception is LED loads which include signicant amount of internal equivalent series resistance. In
such cases, the internal LED resistance should be added to the LED wiring resistance in the formulas below.
If the pulsewidth is less than 40us, the pulse rise time due to lead wire inductance may become unacceptable since the rise
time may become a signicant percentage of the pulsewidth. Setting the pulse period to at least 20 times the pulsewidth will
help since it will allow the ULC-2 to apply a higher voltage in order to charge the inductance more quickly without dissipat-
ing too much power. Otherwise, shortening the distance to the LED will reduce the inductance and shorten the rise time to
produce better pulse.
For demanding applications with pulsewidths less than 20us, the pulse rinse time in microseconds can be predicted with the
following formula:
For example, if d = 10ft and i = 40A, we expect a rise time of nearly 5us which would be half of a 10us pulse. This formula is
based upon the following assumptions:
1. As a rule of thumb, the inductance of a straight wire is about 12nH per foot and does not
depend very much on the wire size.
2. The total length of the wire is 2 times the distance between the ULC-2 and the LED.
3. For pulsewidths less than 20 times the pulse period, the ULC-2 develops about 2V across the
lead wire inductance.
4. There is no inductance internal to the LED load.
For demanding applications where the LED must be located further than 10’ away from the ULC-2, or the wire size must be
smaller, or the LED includes a signicant amount of internal resistance, use this formula to calculate the permissible voltage
drop in the LED wiring:
Then, the following formula may be used to calculate the LED wiring voltage drop depending upon the distance to the LED
and the size of the wire used:
t_rise = 0.012 * i * d
Where:
t_rise is the rise time in microseconds
i is the pulse current in Amps
dis the distance from the ULC to the LED in feet
Vd < 50 - (r_LED * i) - (1.3 * Vf)
Where:
Vd is the voltage drop across the LED wiring in Volts
r_LED is the internal equivalent series resistance of the LED in ohms
Vf is the nominal forward voltage of the LED load at rated current in Volts
i is the pulse current in Amps
Vd = 2 * d * r * i
1000
Where:
Vd is the voltage drop across the LED wiring in Volts
dis the distance from the ULC to the LED in feet
r is the resistance of the LED wiring in ohms/kft
(ohms per 1000 ft)
i is the LED current in Amps
For reference, the following table shows the wiring
resistance for a range of different wire sizes:
Wire Size
(AWG)
Resistance
(ohms/kft)
24 26.2
22 16.5
20 10.4
18 6.51
14 2.58
12 1.62
[APPENDIX D]

pg. 15 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
Specications
General
[APPENDIX E]
Channels: 2 Channels, Independantly Controllable
Supply Voltage: 24VDC (+/- 10% switching power supply recommended),
6 amps
Trigger Input:
Optically Isolated Yes
Voltage: 3V to 30V
Current: 6mA typical, 10mA max
Rate: 50kHz maximum
Pulsewidth 2us minimum
Edge/Polarity Rising or Falling Edge (Strobe Mode)
High or Low Level On (DC Current and DC Voltage Modes)
Ethernet Control: UDP messaging listening on port 5000 for any incoming
source port
IP Address: User selectable. Defaults to 172.16.1.1
Operating Modes: Strobe (Pulse), DC Current, DC Voltage
ROHS Compliance: Yes
Expected Lifetime: 75,000 hours
Mounting: DIN Rail (vertical preferred for maximum power output)
Dimensions: 7.40in x 4.72in x 2.27in
(187.96mm x 120.65mm x 57.658mm)
Weight: 1.5lbs
Operating Ambient Temperature 35C (95F) maximum
Operating Humidity 0% to 90% RH non-condensing
Enclosure IP Rating None

pg. 16 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
Current: 20mA to 4A
Voltage: 3V to 60V
Continuous Power: 60W maximum per channel
Voltage: 3V to 50V
Current: 20mA to 4A
Continuous Power: 60W maximum per channel
DC Current Mode Output
DC Voltage Mode Output
Specications [continued]
[APPENDIX E]
Strobe Mode Output
Voltage: 0V to 60V
Current: 100mA to 40A
Pulsewidth: 2us to 60ms
Period: 0 to 50kHz (innite to 20us period)
Trigger Delay (delay between trigger event and start of out-
put pulse):
6µs (typical) to 60ms
Combined Current, Pulsewidth, and Period Limitations: pw <= 0.01 / i (single pulse limit)
T >= 319*(pw*i)*(pw*Max(i - 4,0)+0.0011) (FET average
power limit)
T > pw + 15us (retrigger time limit)
T >= 20 (f<= 50kHz, trigger frequency limit)
where:
pw = pulsewidth in seconds
i = pulse current in Amps
T = pulse (or trigger) period in seconds
f = pulse (or trigger) frequency in Hz

pg. 17 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
Single Pulse Limit in Strobe (Pulse) Mode
The ULC-2 works by discharging a capacitor into the load at a constant current. At 4A or less, the capacitor
can be recharged as fast as it is discharged allowing the pulsewidth to be up to the maximum of 60ms
regardless of the exact current. Above 4A, the pulsewidth and current are constrained by the following
equation. The ULC-2 will automatically limit the pulsewidth or current to satisfy this equation.
pw <= 0.01 / i
where: pw = pulsewidth in seconds
i = current in Amps
The relationship in this equation is shown in the following diagram:
For example, the ULC-2 will not allow output pulsewidths greater than 500 microseconds if the output
pulse current is set to 20A.
[APPENDIX F]

pg. 18 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
Trigger Frequency Limit in Strobe (Pulse) Mode
The output pulse frequency of ULC-2 is limited by the maximum allowed average power dissipation in the
output FET, the minimum idle time after a pulse ends before triggering the next pulse, and an absolute
maximum of 50kHz. The equations for these limits are shown in the Strobe Mode Output Specications
on page 16. The ULC-2 will automatically limit the output frequency (trigger period) to satisfy these limits.
The result of these equations are shown in the following diagram:
[APPENDIX F cont..]
10
100
1000
10000
100000
1 10 100 1000 10000 100000
frequency (Hz)
pulsewidth (us)
Frequency vs. Pulsewidth
0.1
1
4
10
40
For example, with a pulse current of 10A and a pulsewidth of 100us, the ULC-2 will not allow a pulse
frequency of more than 1.844kHz (542us period).

pg. 19 metaphase-tech.com
Metaphase
Technologies
ULC-2
ULC-2
Metaphase Technologies, Inc.
metaphase-tech.com
211 Sinclair Road, ste 100
Bristol, PA 19007 - USA
ph: 215.639.8699
fax: 215.639.0877
MT15009R1
Table of contents
Other Metaphase Technologies Controllers manuals
Popular Controllers manuals by other brands

Honeywell
Honeywell ControLinks R7999C manual

Homematic IP
Homematic IP HmIP-DRBLI4 Installation and operating manual

Doctorseyes
Doctorseyes PLC-4 instruction manual

United Automation
United Automation INFRESCO-S-4kW user manual

YASKAWA
YASKAWA A1000 Series quick start guide

Micropelt
Micropelt iTRV quick start