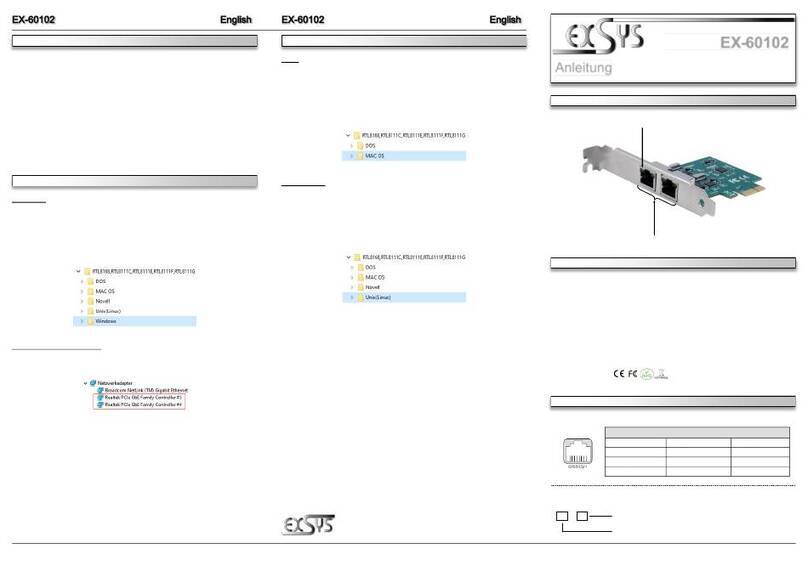
Multi-Interface PCI Serial Cards
vi
WARRANTY
Effective for products of B+B SmartWorx shipped on or after May 1, 2013, B+B
SmartWorx warrants that each such product shall be free from defects in material and
workmanship for its lifetime. This limited lifetime warranty is applicable solely to the
original user and is not transferable.
This warranty is expressly conditioned upon proper storage, installation, connection,
operation and maintenance of products in accordance with their written specifications.
Pursuant to the warranty, within the warranty period, B+B SmartWorx, at its option
will:
1. Replace the product with a functional equivalent;
2. Repair the product; or
3. Provide a partial refund of purchase price based on a depreciated value.
Products of other manufacturers sold by B+B SmartWorx are not subject to any
warranty or indemnity offered by B+B SmartWorx, but may be subject to the
warranties of the other manufacturers.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, under no circumstances shall B+B SmartWorx have any
warranty obligations or any other liability for: (i) any defects resulting from wear and tear,
accident, improper use by the buyer or use by any third party except in accordance with the
written instructions or advice of the B+B SmartWorx or the manufacturer of the products,
including without limitation surge and overvoltage conditions that exceed specified ratings, (ii)
any products which have been adjusted, modified or repaired by any party other than B+B
SmartWorx or (iii) any descriptions, illustrations, figures as to performance, drawings and
particulars of weights and dimensions contained in the B+B SmartWorx’ catalogs, price lists,
marketing materials or elsewhere since they are merely intended to represent a general idea of
the products and do not form part of this price quote and do not constitute a warranty of any
kind, whether express or implied, as to any of the B+B SmartWorx’ products.
THE REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT OF THE DEFECTIVE ITEMS IN ACCORDANCE WITH
THE EXPRESS WARRANTY SET FORTH ABOVE IS B+B SMARTWORX’ SOLE
OBLIGATION UNDER THIS WARRANTY. THE WARRANTY CONTAINED IN THIS SECTION
SHALL EXTEND TO THE ORIGINAL USER ONLY, IS IN LIEU OF ANY AND ALL OTHER
WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, AND ALL SUCH WARRANTIES AND INDEMNITIES
ARE EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION (I) THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND OF MERCHANTABILITY
AND (II) ANY WARRANTY THAT THE PRODUCTS ARE DO NOT INFRINGE OR VIOLATE
THE INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS OF ANY THIRD PARTY. IN NO EVENT SHALL
B+B SMARTWORX BE LIABLE FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF USE OR OF DATA
INTERRUPTION OF BUSINESS, LOST PROFITS OR GOODWILL OR OTHER SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL, EXEMPLARY OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES. B+B SMARTWORX SHALL
DISREGARD AND NOT BE BOUND BY ANY REPRESENTATIONS, WARRANTIES OR
INDEMNITIES MADE BY ANY OTHER PERSON, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION
EMPLOYEES, DISTRIBUTORS, RESELLERS OR DEALERS OF B+B SMARTWORX WHICH
ARE INCONSISTENT WITH THE WARRANTY, SET FORTH ABOVE.