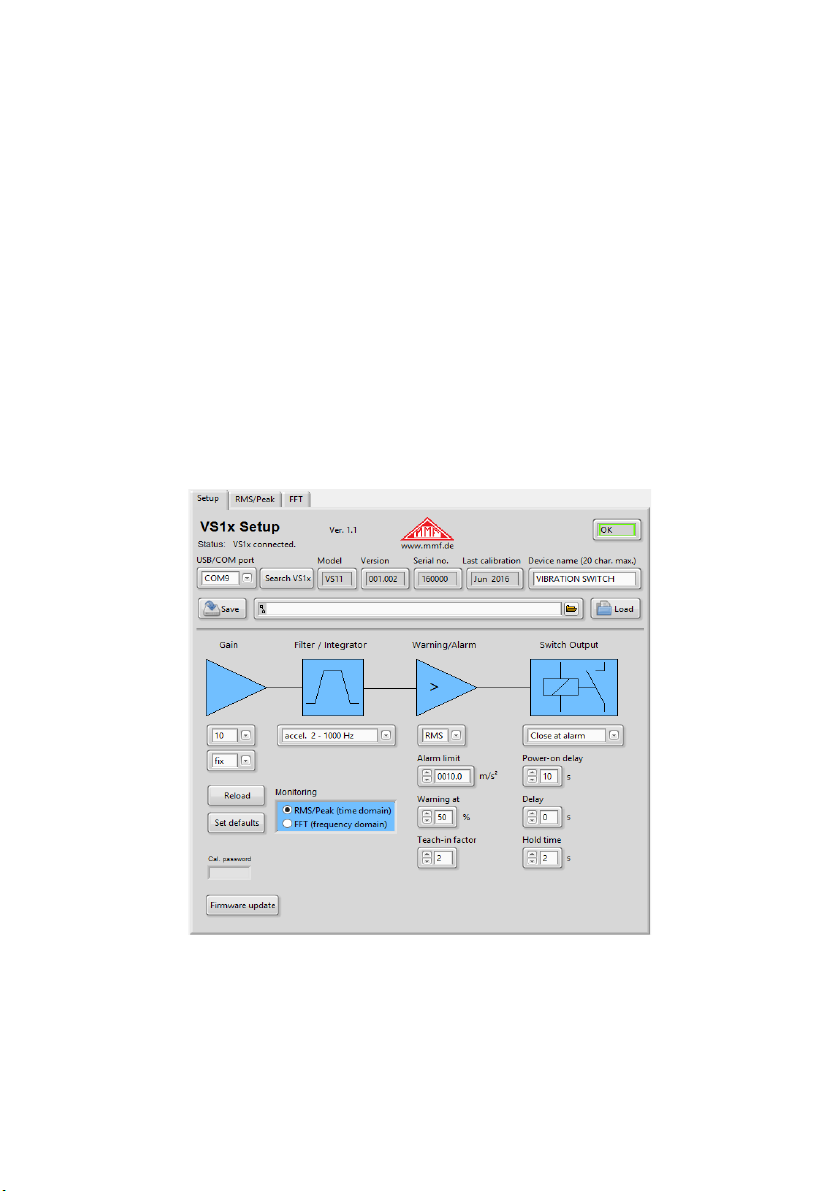
4.2.4. Filters and Integrators
VS / 2 can monitor vibration acceleration or vibration velocity. A range of high
and low pass filters are available for selection. The widest frequency range is 0. Hz
to 0 kHz for acceleration, and 2 to 000 Hz for velocity. The frequency range is
adjusted via a drop-down menu. The three vibration velocity ranges can be found at
the end of the menu. For information on customary frequency ranges in monitoring
rotating machinery, see Chapter 9..
Setting the filters and integrators is only relevant when monitoring in the time do-
main (RMS and peak). In the FFT mode they are deactivated.
4.2.5. Warning and Alarm Limits
You can select the monitoring value from the “RMS/Peak” menu. RMS values are
typically used for measuring vibration, and peak values for single impacts.
The alarm limit determines the switching threshold of the relay output. It is entered
in m/s² for acceleration or mm/s for velocity. The permissible value range is 0. to
500.0.
The warning limit is entered as a percentage of the alarm value.
Values ranging from 0 to 99% are permissible. The warning limit can be used to
indicate pre-alarm status via the LEDs before the alarm is triggered (see Chapter
4.3.).
The “teach-in-factor” is an automatic measuring function for the alarm limit (see
Chapter 7.). It determines how far the alarm limit is set above the currently mea-
sured maximum value. The teach-in warning limit is always set at 50%.
It is only necessary to preset the monitoring variables and the alarm limit when mea-
suring in the time domain (RMS and peak). In FFT mode the alarm limit is set in the
FFT window (see Chapter 6.).
4.2.6. Switching O tp t
The VS / 2 contains a PhotoMOS relay switch. The switching function can be
specified in the options menu. The relay opens (n.c.) or closes (n.o.) in response to a
warning or alarm signal.
The power-on delay is the delay between switching on the power and activation of
the monitoring function. It helps prevent false alarm signals after switching on the
device caused by the transient response of the signal processing.
The delay range is 0 to 99 seconds.
The power-on delay is the delay between the alarm threshold being exceeded and
the relay switching. At zero the relay reacts immediately.
If a minimum time duration should apply to exceeding the alarm limit, a switching
delay of up to 99 seconds can be entered.
The “Hold time” is the time when the amplitude falls below the alarm limit until the
relay returns to normal status. This setting can be useful if a minimum alert duration
is required. The range is from 0 to 9 seconds.
8