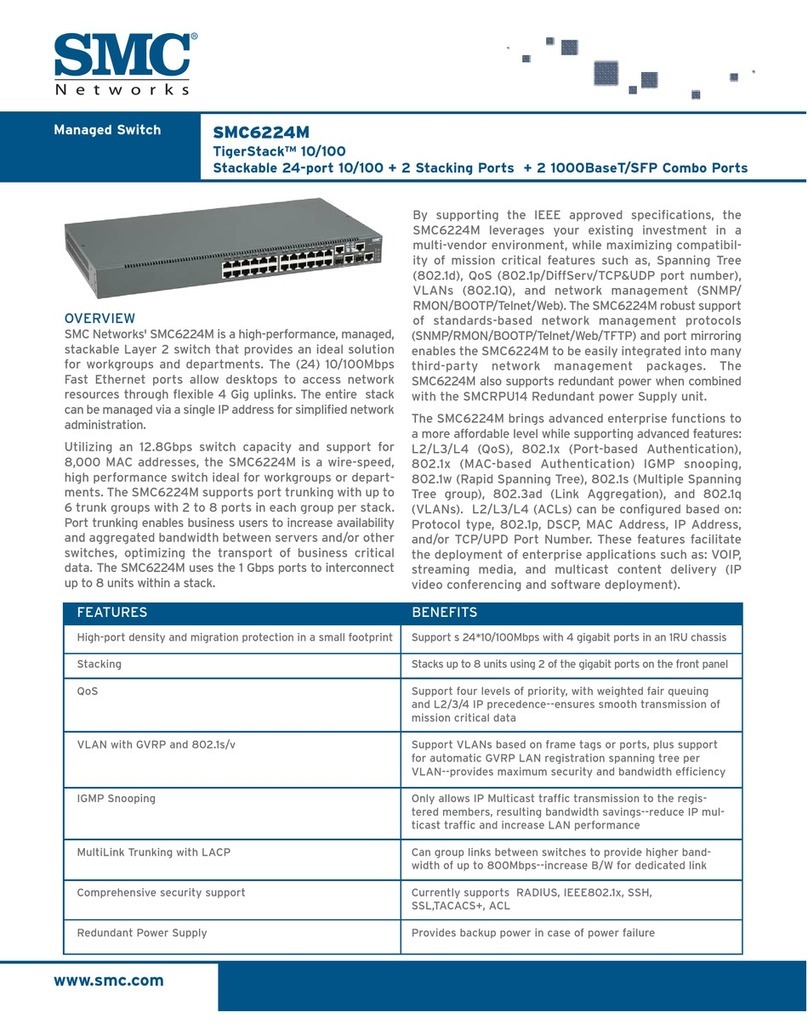
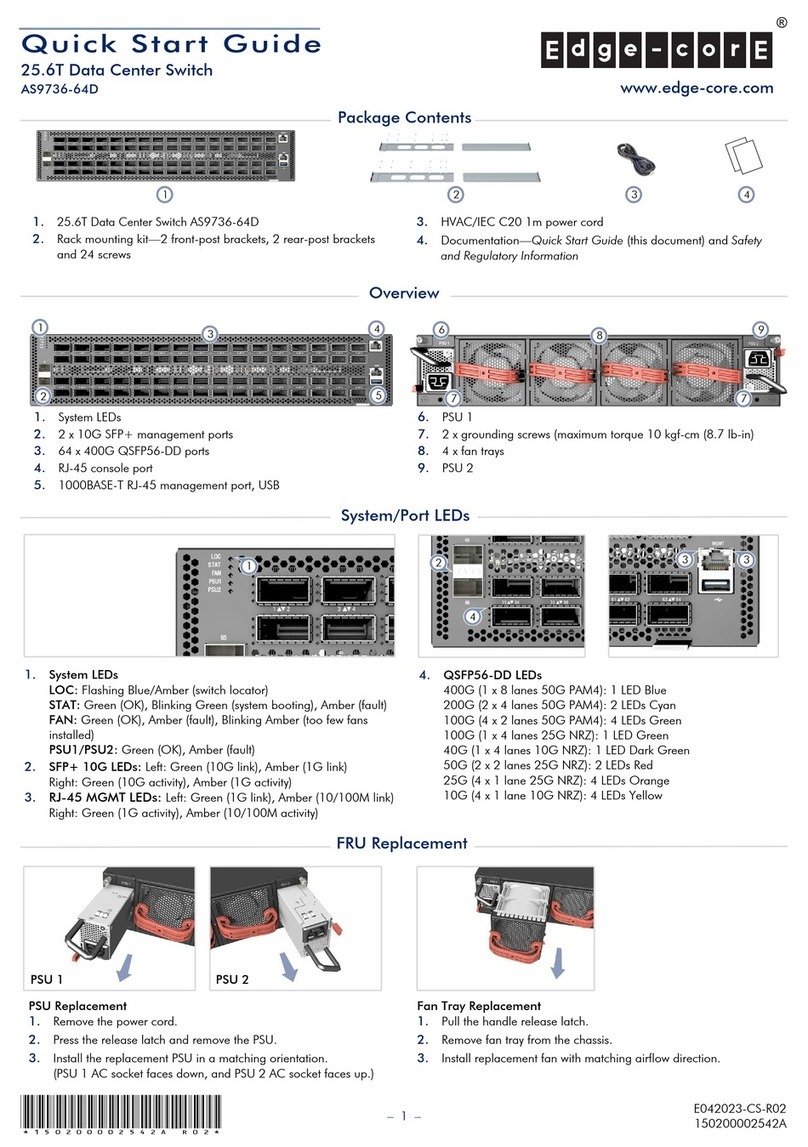
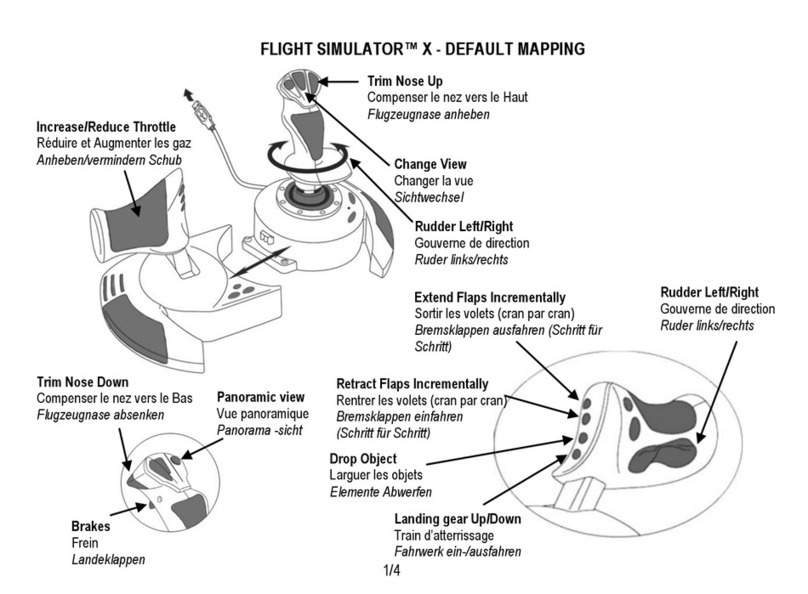
MS 104/5 ML46758, Rev. 01 June 2002
Table 1: DIP Switch Setting (Continued)
UP Set Port 2to operate at 10 Mbps.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 3
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
10/100 2
DOWN Set Port 2to operate at 100 Mbps.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 3
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
UP Set Port 3to operate at 10 Mbps.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 4
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
10/100 3
DOWN Set Port 3to operate at 100 Mbps.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 4
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
UP Set Port 4to operate at 10 Mbps.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 3
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
10/100 4
DOWN Set Port 4to operate at 100 Mbps.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 3
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
UP Set Port 5to operate at 10 Mbps.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 4
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
10/100 5
DOWN Set Port 5to operate at 100 Mbps.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 4
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
UP Set Port 2to operate in Half-Duplex mode.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 3
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
FD/HD 2
DOWN Set Port 2to operate in Full-Duplex mode.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 3
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
UP Set Port 3to operate in Half-Duplex mode.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 3
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
FD/HD 3
DOWN Set Port 3to operate in Full-Duplex mode.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 3
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
UP Set Port 4to operate in Half-Duplex mode.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 3
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
FD/HD 4
DOWN Set Port 4to operate in Full-Duplex mode.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 3
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
UP Set Port 5to operate in Half-Duplex mode.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 3
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
FD/HD 5
DOWN Set Port 5to operate in Full-Duplex mode.
(Effective only if Auto-negotiation DIP switch toggle 3
position is down, i.e., if auto-negotiation is disabled.)
10