Front panel
Controls
The same set of controls is provided for both filters.
A. Cutoff frequency, from 8 Hz to 18 kHz.
B. Resonance. Goes up to self-oscillation.
C. Amount of gain and distortion or wavefolding applied
to the input signal. A gain of 0dB is achieved with the
knob at 11 o’clock. This knob also acts as an offset con-
trol for the DRIVE CV input (3).
D. Response of the drive circuit, continuously variable
between round soft-clipping, and a two-stage wavefolder.
E. Filter input level indicator LED.
F. Filter response. Continuously variable between
low-pass , band-pass , and high-pass .
G. Filter routing. This knob controls the signal routing
(single, parallel or series) between the two filters.
H. Attenuverters for the two filters’ frequency and reso-
nance CV inputs, and for the ROUTING CV input.
I. Filter cutoff coupling. When this button is pressed and
illuminated, filter 2’s cutoff frequency is set relatively to
filter 1’s cutoff frequency: for example, when filter 2’s
FREQUENCY knob is at 12 o’clock, both filters share the
same cutoff frequency. With the knob past (or before) 12
o’clock, filter 2’s cutoff frequency will follow filter 1’s,
but transposed up (or down).
Inputs and Outputs
1. CV inputs for filter mode, cutoff frequency, resonance
and filter routing.
2. V/OCT input. Controls the cutoff frequency according
to the 1 V/octave scale.
3. Drive CV input. If no patch cable is inserted in this
input, a 2V voltage is applied to the drive circuit. This is
why a moderate, but non-null, gain is obtained when the
DRIVE knob [C] is fully turned counter-clockwise.
4. DC-coupled signal input.
5. Individual filter output.
6. Main output. Carries a blend of filter 1 and filter 2’s
outputs, depending on the ROUTING knob and CV.
B
E
A
1
2
3
4
5 6
C
D
F G
DRIVE
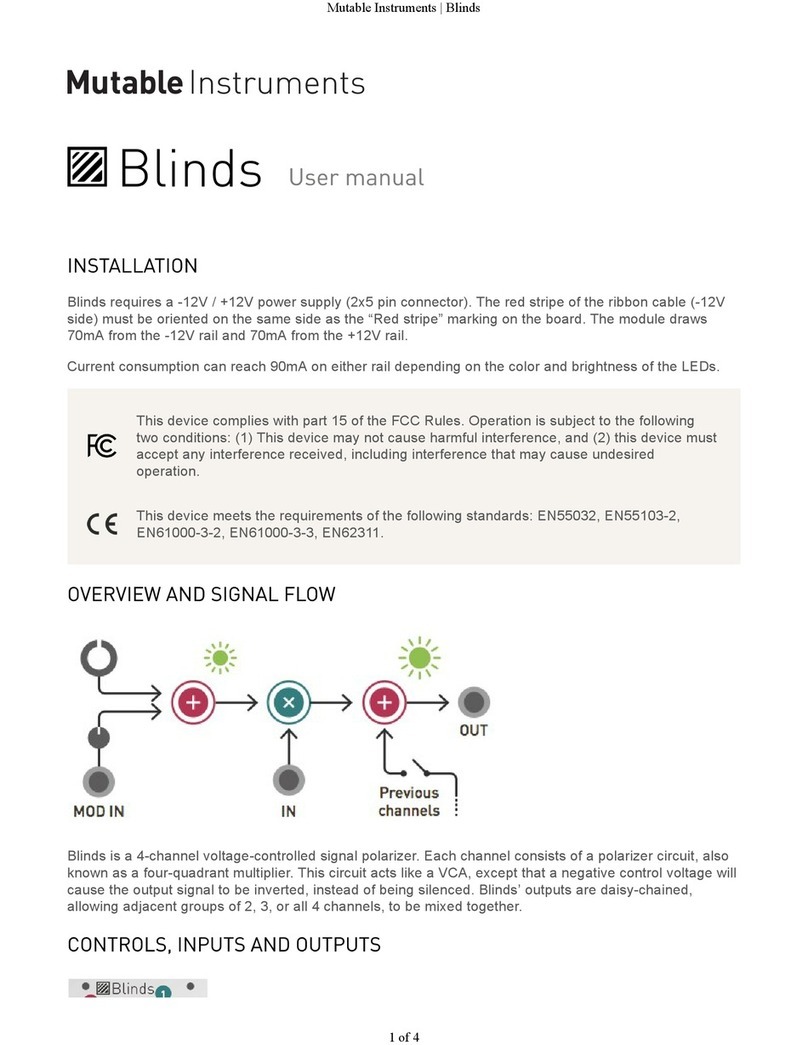
About Blades
Blades is a dual analog 12dB/octave multimode filter
with complete voltage control over a variety of filter
responses and signal paths, and a drive circuit with lots
of character.
It encourages the exploration of the gray, muddy and
foggy areas that generations of rotary switches and
toggle buttons have occulted.
Installation
Blades requires a -12V / +12V power supply (2x5 pin
connector). The red stripe of the ribbon cable (-12V side)
must be oriented on the same side as the “Red stripe”
marking on the board.
The module draws 140mA from the -12V rail and 150mA
from the +12V rail.
Online manual and help
The full manual can be found online at
mutable-instruments.net/modules/blades/manual
For help and discussions, head to
mutable-instruments.net/forum
I
H