NAVAIR 17-20AQ-347
1
SECTION 1
INTRODUCTION AND DESCRIPTION
1.1 This procedure describes the calibration of the Wavetek 1271 Digital Multimeter with or without OPT12 or 20. The
instrument being calibrated is referred to herein as the TI (Test Instrument).
1.2 All comments concerning this procedure should be directed to the Measurement Science Department, Corona Division,
Naval Surface Warfare Center, P.O. Box 5000, Corona, CA 92878-5000.
1.3 This procedure includes tests of essential performance parameters only. Any malfunction noticed during calibration,
whether specifically tested for or not, should be corrected.
1.4 The TI is not calibrated to 1 MHz above 10 V and not calibrated over 500 V. It is calibrated using the manufacturer’s
12 month specifications. This is an NSWC Measurement Science Department (MSD) assigned tolerance.
1.5 It should be noted that the specifications cited below, in Table 1, are for the Fluke 8505/8506 series digital multimeters
(unless noted otherwise). Since the Fluke specifications were the “procurement specifications” for the Wavetek 1271 (TI), a
SPECIAL CALIBRATION tag shall be affixed to the TI, upon completion of calibration, indicating that the TI was calibrated to
the (12 month) Fluke 8505/8506 specifications. This is an NSWC/MSD assigned specification.
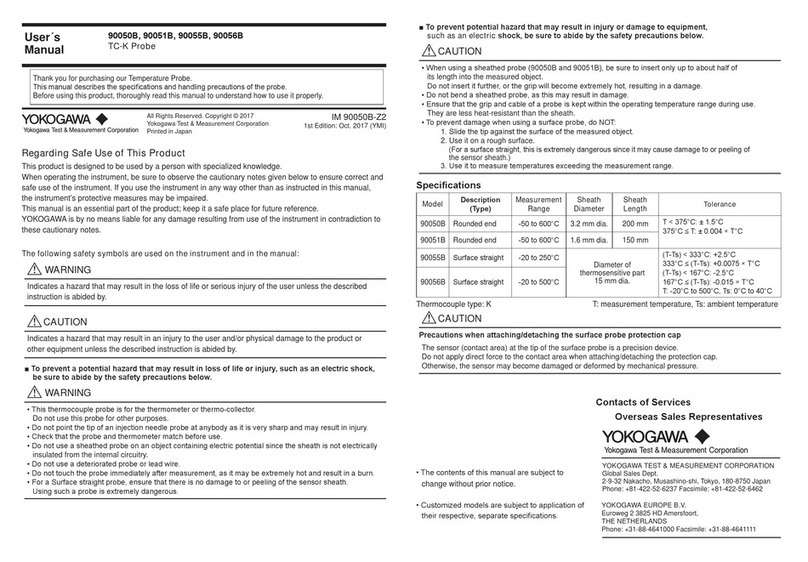
Table 1. Calibration Description
TI
Characteristics Performance
Specifications Test
Method
Direct voltage Ranges: 100 mV, 1, 10, 100 and 1000 V dc
Tolerances:
100 mV: ±(0.00403% iv + 90 counts)
1 V: ±(0.0024% iv + 9 counts)
10 V: ±(0.0019% iv + 9 counts)
100, 100 V: ±(0.00297% iv + 9 counts)
Tested with a voltage
measurement system
containing a voltage divider,
reference divider, and DC
voltage standard.
Resistance Ranges: 10, 100 Ω, 1, 10, 100 kΩ, 1, 10,
100 MΩ
Tolerances:
10 Ω: ±(100 ppm + 20 counts)
100 Ω: ±(60 ppm + 1.4 counts)
1, 10, 100 kΩ, 1 MΩ:
±(60 ppm + 0.8 counts)
10 MΩ: ±(398 ppm + 0.8 counts)
100 MΩ: ±(1004 ppm + 1 count)
Compared with a known
resistance.
AC RMS Voltage Tolerances:
100 mV range:
10 to 40 Hz: ±0.152% iv
40 to 20 kHz: ±(0.035% iv + 5 μV)
20 to 50 kHz: ±0.0825% iv
50 to 100 kHz: ±0.308% iv
Compared with known direct
voltages by thermal voltage
conversion.
10 V range:
10 to 40 Hz: ±0.152% iv
40 to 20 kHz: ±0.025% iv
20 to 50 kHz: ±0.0825% iv
50 to 100 kHz: ±0.308% iv
100 to 200 kHz: ±0.689% iv
200 to 500 kHz: ±2.04% iv
500 kHz to 1 MHz: ±4.49% iv