Next Wave Automation Piranha FX User manual

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 1
Operations Manual
3d Printer Module

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 2
Next Wave 3D Software
Table of Contents
Introduction
Pg. 3
Safety Warnings
Pg. 4
Setup of the 3D Printing Head on the Piranha Fx
Pg. 4
Leveling the 3D Platform
Pg. 9
Installing Next Wave 3D (NW3D)
Pg. 12
Setting Up your Machine’s Workspace
Pg. 12
NW3D –Importing and Manipulating a 3D Model
Pg. 14
Setting Printing Parameters
Pg. 14
Advanced Print Parameters
Pg. 23
Printing and Viewing your Model(s) Toolpaths
Pg. 25
Running a Print Job
Pg. 27
NW3D Print Head
Pg. 30
Appendix
Pg. 32
Comment [S1]:

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 3
Introduction
Next Wave 3D is a modular 3D Printing Solution that allows users to
mix and match a variety of 3D printing components to create a 3D printed
model. While there are a multitude of 3D Printers available from all around
the world, Next Wave 3D allows a user to print sophisticated 3D models
using their Piranha Fx.
The Next Wave 3D System consists of the following...
3D Printing Software
Spindle Mounted 3D Print Head
3D Print Head Heater Control and Extruder Motor Driver unit
Machine Controller with Parallel Port type interface
Features of the Next Wave 3D Software
Imports many 3D File Formats
3ds
3d Studio
gts
GNU Triangulated Surface
lwo
Lightwave
obj
Wavefront
ply
Standard Triangle Format
Stl
Standard Tessellation Language
Layer by Layer View
Outputs standard Gcode for most Machine Controllers
Built-In Parametric Modeling of Gears, and Lithopane Images
Optimized Toolpaths
Water Tight Solid mending of meshes

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 4

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 5
***Safety Warnings***
Read this manual completely before making your first 3D Print
Burn Hazard:
The NW3D Print Head is capable of reaching temperatures in excess
of 300°C (575°F). Allow the Print Head to completely cool before servicing.
This may take 15 minutes or more. If in doubt, wear protective gloves.
The exit temperature of the Extruded Plastic will be at the Temperature of
the Nozzle. Do not touch the melted plastic as it may stick to your skin and
cause burns.
Fire Hazard:
Do not place flammable materials near the Print Head. Do not spray
flammable materials such as Hair Spray onto the Print Area when the Print
Head is hot.
Electric Shock Hazard:
The Cartridge Heater used in the NW3D Print Head runs at Mains
Voltage (either 110v in the USA or 220v in most other Countries). Do not
open the control box, service the Print Head, or move the Control Box
unless the main power cord is disconnected. Do not place the Control box
in an area that may be affected by moisture.
Mechanical Hazard:
Do not place fingers, loose clothing, or hair near the Print Head when
the machine is operating.
Setup of the 3D Printing Head on the Piranha Fx
Make sure power is turned off to the Piranha FX Controller,
Heating Element, and Piranha Hub

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 6
Invert the router cradle by removing the 4 bolts from the back of
the router cradle. Turning the router cradle upside down, and
reattach the 4 bolts. Then place the router in the clamp.
Insert 3D printing head into router collet and tighten the collet
nut.

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 7
Connect hub to controller using 20 pin ribbon cable.
Connect power adapter to the hub.
Power on the controller.
Power on the hub.
Attach the 3D printing head to the heating element.
Power on the heating element.
Wait for the temperature to reach 225 degrees.
REMEMBER: NEVER ADJUST THE 3D PRINTING HEAD WHILE THE
HEATING ELEMENT IS ON!

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 8
Attaching the filament
Make sure that all previous filament is ran through the 3D printing
head before adding more
To do this, you need to access the A axis (fourth axis)
There are two ways to access the A axis
The easiest is to use the “feed” button located on the home
screen of the LCD.
This option slowly jogs the A axis in small increments

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 9
oSimply hold the feed button for 1 second at a time
The other option is to switch access from the Z axis to the A
axis on the LCD home screen
Add the filament through the opening on the side of the printing
head
Jog it through in small increments, as shown in previous steps.
To replace the filament, cut off the end of the filament that is
currently being fed through the 3D printing head

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 10
Then, gently sand the edge of the new filament that will be
added, just enough to make it smooth and straight.
Make sure that you feed the previous filament in a few more
times
Add the new filament following the “Add Filament” steps above
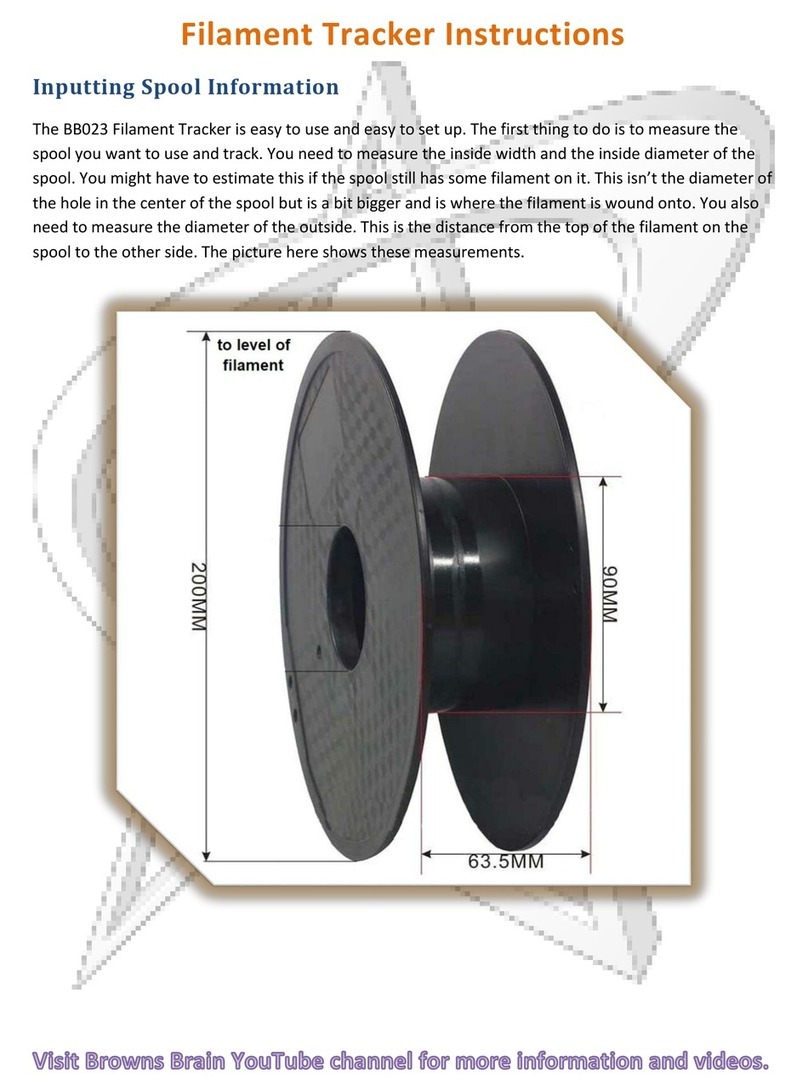
Leveling the 3D Building Platform (glass panel)
The 3D building platform comes ready to use and should be level. The following
guide will assist you in checking the plate to make sure it is level, and the steps to
take if it is not.
You will find bolts in all four corners of the building platform.
These bolts are attached to industrial t-slot nuts
With the bolts and t-slot nut on the build platform, slide the t-slot
nuts into the t channel of the CNC Piranha
Position it roughly in the center of the base and tighten down the
bolts
Position the 3D printing head over the top of the glass at the far
end of the Y Coordinate
Run the 3D printing head towards the front of the Piranha

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 11
Note any difference in the space between the glass and the 3D
printing head
Raise the 3D printing head, and move it out of the way to gain
access to the glass
Pull the glass up and apply masking tape to level out the
difference you saw between the 3D printing head and the glass
Repeat this process until there are no significant differences
Please note that .001-.01 is not a significant difference
Once leveled, re-insert the glass
Apply painters tape to any area that will be used for 3D printing
After the tape is applied, use denatured alcohol to remove the
film on the top of the painters tape
Running the 3D Printer
Move the 3D printing head to the point of origin
Zero the X and Y axis
Move the Z axis slowly down, until a piece of paper can barely fit
under the nozzle of the 3d head and the Glass surface

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 12
Zero all axis’
The system is now ready to run your program.
Load the TAP file onto a USB flash drive.
oNOTE: A SanDisk flash drive is recommended.
Insert USB drive into the Piranha Pendant (refer to Piranha
Manual for detailed instructions)
Select the USB tab Select target file
Press Run.

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 13
1. Installing Next Wave 3D (NW3D)
NW3D Requires:
Windows Operating System (Vista, XP, 7, 8, 10)
2GB Ram
OpenGL capable Graphics Card.
Installing NW3D:
Double click on the downloaded Next Wave 3D-Setup.exe to begin
the install.
Follow the prompts associated with the Installation of the
Software.
Registration for the Software See Apendix.
That's it! You can now run the Next Wave 3D Software.
2. Setting Up your Machine’s Workspace
NW3D is an add-on to your existing CNC Machine. Several
parameters should be set before you make your first print. The Work
Envelope of your machine should be set so that you can get Visual
Feedback of the scale and location of the print job. You will also need to set
and calibrate your machines 4th axis to deposit the correct amount of
plastic if you are using the optional NW3D Motion Controller. These
requirements are handled through an Initialization Script that is located in
your MyDocuments/Next Wave 3D/Config/default.gsc file. This file contains
several Scripts containing both standard and custom NW3D Gcodes. These
Gcodes set up both the general NW3D Software as well as more specific
commands for the optional NW3D Motion Controller. The Initialization
Script is edited by going into the Setup Tab and clicking on the Set Print
Parameters.

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 14
3. NW3D –Importing and Manipulating a 3D Model
NW3D supports a wide range of 3D File Formats for Printing. Each
Model can be Scaled, Translated, or Rotated anywhere in your 3D Printers
work envelope.
Importing your 3D Model:
Click the Add 3D Model Button
The Model is automatically placed at the 0,0 Origin.

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 15
If this is the first model added to the Print Job, it will automatically be
selected. If there are multiple Models for this Print Job, any model may be
selected by right clicking on the Model once. A selected Model will turn
Blue while an unselected Model will be Yellow. If only one Model is
available, it will always be selected regardless of color. The model's
features will be displayed each time a model is selected.
At this point, you can visually Rotate and Zoom around the Model by
using the Mouse buttons. Dragging the Left mouse button will Rotate the
display while using the Mouse Wheel will Zoom the display. To Snap the
View to a specific Model, select the model first with the Right mouse
button (it will turn Blue), and then Double-click the Left mouse button to
target the model. To return to the Table View, make sure that no Model is
selected (Right click anywhere in table space), and double click the Left
mouse button.
If a Model is selected, it can be Scaled, Rotated, Translated, and
Repaired. By default, many 3D File formats are expected to be saved in
Millimeters (STL for example). To Scale the Model and make it either Larger
or Smaller, enter a value for the Scale Factor and press the Enter key. There
are several pre-defined Scale buttons that allow you to instantly scale the
Model from:
Multiply by 10
Multiply by 1
Multiply by 1
To Translate a Model and move it around the 3D workspace, enter
new values for the 3 X, Y and Z Position entry boxes. The entries represent
the X, Y and Z axes respectively. In any of these boxes, pressing the Enter
key will invoke the Model translation. The Position can depict the Lower
Left Corner of the Bounding Box of the Model or it can represent the Center
of the Model depending on the Position Alignment control. When Corner is
selected, the Model will be placed by its Lower Left corner. Likewise, if
Center is checked then the Model will be positioned according to its Center.
If a model is selected (by clicking on it with the Right mouse button), you
can also Drag the model around your Work Envelope by holding the Right
mouse button down while dragging.

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 16
Advanced Model Fix Option: Most 3D model formats for 3D printing are
expected to yield a "water tight" 3D Solid object. This is not always the case
and from time to time you may find yourself with a model that will have
broken layers due to a leaky model. You can try to fix these models using
the automatic mesh mending utility built into NW3D. This utility will
guarantee a water tight model but may also distort the model if the model
has large holes in it (models made up of Surfaces rather than a Solid). Three
options are available for fixing the model: Rough, Smooth, and Sharp. The
Rough option will create a Block representation of the model. The Smooth
option will round off all sharp corners in the model. The Sharp option will
preserve the Sharp corners that exist in the model. In all cases, NW3D will
create a new model and append .fixed to the model's filename and reload
the fixed model.
4. NW3D –Setting Printing Parameters
In order to print properly, certain variables associated with the
NW3D Software need to be set according to your machines capabilities.
Clicking the Set Print Parameters button in the Setup Tab will bring up the
Print Parameters setup dialog window.

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 17
A full set of Parameters can be saved in a single Configuration for
later use. By default, the last used set of parameters will be set the next
time you run the NW3D Software. Selecting a specific Config from the Drop
Down entry box will load the parameters for this Config and allow
Editing/Saving of these Config settings.
Type a unique name in the Config entry box to start a new set of
Printing Parameters. After you have set all of the parameters for the new
Config, press the Save Config button to store these parameters for later
print jobs. You may also select a Config and permanently remove it by
clicking the Delete Config button.
The Configuration group is also where you set the master Inch/MM
setting for your Config. The values for all parameters will default to MM or
Inch units depending on this selection. The output Gcode file from NW3D
will also have its Units (G20 or G21) set according to this setting.
Layer Parameters:

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 18
Nozzle Diameter: This is the Diameter of the exit Nozzle of your 3D Print
Head. If you are using the NW3D Print Head, the standard Nozzle is 0.016 in
or 0.4 mm.
Layer Thickness: This will set the thickness of each individual layer. For
best results, it should be no more than the Nozzle Diameter above. A
smaller thickness will yield a smoother, higher resolution part at the
expense of a longer print time. A value of approximately 2/3 the Nozzle
Diameter is a good place to start.
Toy Car @ 0.010 In. Layer Height Same Car @ 0.005 In. Layer
Height
Foundation:
The Foundation is an area under the Model(s) that support the print
a small distance above the printing platform. It is typically used for printing
materials that have a high degree of shrinkage such as ABS or to prepare a
Level surface for the part. The Foundation consists of a thicker Base Layer
and thinner Top Surface Mesh layer.
Thickness: Here you will set the Height of the Foundation's Base Layer.
The Foundation is usually a heavier/thicker layer and a value of
approximately 1.5 times the Nozzle Diameter is usually sufficient.
Base Density: The Base layer of the Foundation does not need to be a
full solid layer to perform its function. It is common to make the

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 19
Foundation Base a Mesh to save time and material. The Base Density is a
value from 1 –100% with a typical useful range of 10-25%.
Feedrate: Here you set the Feedrate that will be posted to the output
Gcode file for the Base layer. The Top surface layer will use the same
feedrate as the Print layers. For the best ratio of speed and quality, a
feedrate of 30 is recommended.
Top Density: The density of the Top Surface layer of the Foundation.
This should be a much denser mesh layer than the Base Layer. A density of
50-75% should suffice. Lower densities will make it easier to remove the
Model from the Foundation but may not completely support the Model(s)
in all areas.
Top Thickness: This sets the thickness of the Top Surface area of the
Foundation. It should generally be less than the Layer Thickness to promote
adhesion to the Foundation's base layer. ½ to 2/3 of the Layer Thickness is
typical.
Make Foundation: Check this box to enable the creation of the
Foundation. If you are printing directly to your machines table surface and
do not require a Foundation, leave this unchecked.
Foundation Settings Printed Foundation

Next Wave Automation 3d Print Manual Page 20
Shell:
The Shell is the outside surface of a 3D Printed Model. A typical 3D
Print will consist of a Shell and its Fill.
Straight Shell Contour Shell
Wall Thickness: This is the number of passes that make up the outer
Shell. Usually 2 or 3 passes will create a decent and hard outer surface.
Contour or Straight: The Top and Bottom of the Model's Shell will
always be a solid area. Selecting Contour will create this Solid Surface area
using a series of offset contours. Selecting Straight will create this area
using a series of straight line segments.
Feedrate: This is the feedrate that will post out to the output Gcode file
for your machine. You will want to keep this value within your machine’s
capabilities. A faster feedrate will get the job done quicker, but might
sacrifice quality on loose machines. Typical values range from 50-200 Inch
per Minute (20 –160 MM per Second).
Print Inside/Out: Selecting this option will organize the Print to make
the Shell from the Inside Out. This is the default setting. Some Models
might benefit from Outside/In depending on the Overhang areas of the
Model itself. Experimentation is recommended.
Adhesive Overlap: The percentage that each filament will overlap a
previously deposited filament. A value of 0% will have no overlap. A value
of 50% will have a 50% coverage over the previously printed filament.
Typically, 10% will suffice but Models with steeper overhangs may benefit
from a larger value.
Table of contents