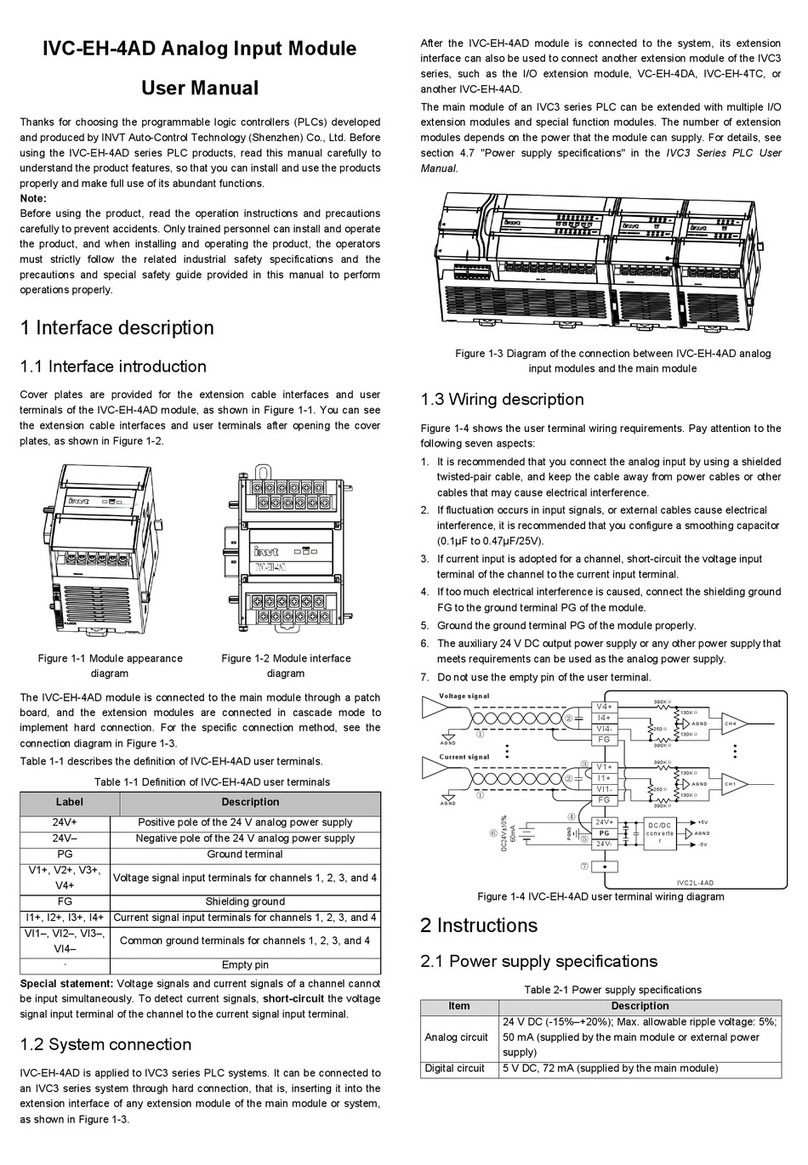
NI 9232 User manual

OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS AND SPECIFICATIONS
NI 9232
3-Channel, ±30 V, 24-Bit Software Selectable IEPE
and AC/DC Analog Input Module
ni.com/manuals
DeutschFrançais

NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications 2 ni.com
This document describes how to use the National Instruments 9232
and includes specifications and terminal assignments for the
NI 9232. For information about installing, configuring, and
programming the system, refer to the system documentation. Visit
ni.com/info and enter the following Info Codes:
•cseriesdoc—for information about C Series and system
documentation.
•compatibility—for information about chassis and carrier
compatibility for the modules youare using.
•rdsoftwareversion—for information about which software
youneed for the modules youare using.
Note The safety guidelines and specifications in this
document are specific to the NI 9232. The other
components in the system might not meet the same safety
ratings and specifications. Refer to the documentation for
each component in the system to determine the safety
ratings and specifications for the entire system. Visit
ni.com/info and enter cseriesdoc for information
about C Series documentation.

© National Instruments Corp. 3 NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications
Safety Guidelines
Operate the NI 9232 only as described in these operating
instructions.
Hot Surface This icon denotes that the component may be
hot. Touching this component may result in bodily injury.
Caution Do not operate the NI 9232 in a manner not
specified in these operating instructions. Product misuse
can result in a hazard. Youcan compromise the safety
protection built into the product if the product is damaged
in any way. If the product is damaged, return it to National
Instruments for repair.
Safety Guidelines for Hazardous Locations
The NI 9232 is suitable for use in Class I, Division 2, Groups A, B,
C, D, T4 hazardous locations; Class I, Zone 2, AEx nA IIC T4, and
Ex nA IIC T4 hazardous locations; and nonhazardous locations
only. Follow these guidelines if youare installing the NI 9232 in a
potentially explosive environment. Not following these guidelines
may result in serious injury or death.

NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications 4 ni.com
Caution Do not disconnect I/O-side wires or connectors
unless power has been switched off or the area is known
to be nonhazardous.
Caution Do not remove modules unless power has been
switched off or the area is known to be nonhazardous.
Caution Substitution of components may impair
suitability for Class I, Division 2.
Caution For Division 2 and Zone 2 applications, install
the system in an enclosure rated to at least IP 54 as
defined by IEC 60529 and EN 60529.
Caution For Division 2 and Zone 2 applications,
connected IEPE sensors must be within the following
limit:
Capacitance..........................0.08 F max
Caution For Division 2 and Zone 2 applications,
connected low impedance sources must include a
protection device installed between the source and the
AI terminals. The protection device must prevent the AI+
to AI– voltage from exceeding 42 V if there is a transient
overvoltage condition.

© National Instruments Corp. 5 NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications
Special Conditions for Hazardous Locations Use in Europe
This equipment has been evaluated as Ex nA IIC T4 equipment
under DEMKO Certificate No. 07 ATEX 0626664X. Each module
is marked II 3G and is suitable for use in Zone 2 hazardous
locations, in ambient temperatures of –40 °C Ta 70 °C. If you
are using the NI 9232 in Gas Group IIC hazardous locations, you
must use the device in an NI chassis that has been evaluated as
Ex nC IIC T4, EEx nC IIC T4, Ex nA IIC T4, or Ex nL IIC T4
equipment.
Electromagnetic Compatibility Guidelines
This product was tested and complies with the regulatory
requirements and limits for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
as stated in the product specifications. These requirements and
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference when the product is operated in its intended
operational electromagnetic environment.
This product is intended for use in industrial locations. There is no
guarantee that harmful interference will not occur in a particular
installation, when the product is connected to a test object, or if the
product is used in residential areas. To minimize the potential for
the product to cause interference to radio and television reception

NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications 6 ni.com
or to experience unacceptable performance degradation, install and
use this product in strict accordance with the instructions in the
product documentation.
Furthermore, any changes or modifications to the product not
expressly approved by National Instruments could void your
authority to operate it under your local regulatory rules.
Caution To ensure the specified EMC performance,
operate this product only with double-shielded, twisted
pair cables and shielded accessories.
Caution To ensure the specified EMC performance,
install snap-on, ferrite beads (National Instruments part
number 611461-01) in accordance with the product
installation instructions.
Caution Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) can damage this
product. To prevent damage, use industry-standard ESD
prevention measures during installation, maintenance,
and operation.

© National Instruments Corp. 7 NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications
Special Guidelines for Marine Applications
Some products are Lloyd’s Register (LR) Type Approved for
marine (shipboard) applications. To verify Lloyd’s Register
certification for a product, visit ni.com/certification and
search for the LR certificate, or look for the Lloyd’s Register mark
on the product label.
Caution In order to meet the EMC requirements for
marine applications, install the product in a shielded
enclosure with shielded and/or filtered power and
input/output ports. In addition, take precautions when
designing, selecting, and installing measurement probes
and cables to ensure that the desired EMC performance is
attained.
Cable Requirements for EMC Compliance
Select and install cables for the NI 9232 in accordance with the
following requirements:
• Connect the cable shield to the chassis ground (grounding
screw of the chassis) as shown in Figure 1.
• Install a clamp-on ferrite bead (National Instruments part
number 611461-01) on the input cables for each channel that you
are connecting to on the NI 9232. Refer to Figure 1 for a diagram.

NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications 8 ni.com
Figure 1. NI 9232 Cable Connections
• Clamp-on ferrite beads must be installed on the cable as close
to the module as possible.
NI 9232
Shield
AI0+
AI0–
Ferrite
Shield
AI1+
AI1–
Ferrite
Shield
AI2+
AI2–
Ferrite
Signal
Source
Signal
Source
Signal
Source

© National Instruments Corp. 9 NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications
Connecting the NI 9232
The NI 9232 has three 2-terminal detachable screw-terminal
connectors that provide connections to three simultaneously
sampled analog input channels.
Figure 2. NI 9232 Terminal Assignments
AI0+
AI0–
AI1+
AI1–
AI2+
AI2–
0
1
0
1
0
1

NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications 10 ni.com
Each channel has a 2-terminal screw-terminal connector to which
youcan connect a signal source. Youcan also enable excitation
current on a per-channel basis to power Integrated Electronics
Piezoelectric (IEPE) sensors. Refer to the NI 9232 Circuitry
section for more information. The AI+ terminal of the connector
provides the DC excitation, when enabled, and the positive input
signal connection. The AI– terminal provides the excitation return
path and the signal ground reference.
Connecting Signal Sources to the NI 9232
Youcan connect ground-referenced or floating signal sources to
the NI 9232.
If youmake a ground-referenced connection between the signal
source and the NI 9232, make sure the voltage on the AI+ and AI–
connections are in the channel-to-earth safety voltage range to
ensure proper operation of the NI 9232. Refer to the Specifications
section for more information about operating voltages and
overvoltage protection. Refer to Figures 3 and 4 for illustrations of
connecting grounded and floating signal sources to the NI 9232.

© National Instruments Corp. 11 NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications
Figure 3. Connecting a Grounded Signal Source to the NI 9232
Figure 4. Connecting a Floating Signal Source to the NI 9232
NI 9232
AI+
AI–
+
–
Signal
Source
Common
Mode
Voltage
NI 9232
AI+
AI–
+
–
Signal
Source

NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications 12 ni.com
The NI 9232 can also provide an IEPE excitation current for each
channel to measure IEPE sensors. Typical IEPE sensors have a
case that is electrically isolated from the IEPE electronics, so
connecting the sensor to the NI 9232 results in a floating
connection even though the case of the sensor is grounded.
NI 9232 Circuitry
The NI 9232 analog input channels are referenced to an isolated
ground through a 50 resistor. Each channel is protected from
overvoltages. The input signal on each channel is buffered,
conditioned, and then sampled by an isolated 24-bit Delta-Sigma
ADC. Youcan configure each channel in software for AC or DC
coupling. For channels set to AC coupling, youcan turn the IEPE
excitation current on or off. Refer to the software help for
information about configuring channels on the NI 9232.

© National Instruments Corp. 13 NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications
Figure 5. NI 9232 Input Circuitry for One Channel
The NI 9232 also has TEDS circuitry. For more information about
TEDS, go to ni.com/info and enter rdteds.
Wiring for High-Vibration Applications
If an application is subject to high vibration, National Instruments
recommends that youeither use ferrules to terminate wires to the
detachable screw-terminal connector or use the NI 9971 backshell
kit to protect the connections. Refer to Figure 6 for an illustration
4 mA IEPE On/Off
Amplifier
and
Prefilter
Isolated
ADC
+
–
AC/DC Coupling
AI+
AI–
NI 9232
Common
Mode
Bias
Current
Current
Limited
Resistor
50 Ω

© National Instruments Corp. 15 NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications
Note Yo umust use 2-wire ferrules to create a secure
connection when connecting more than one wire to a
single terminal on the NI 9232.
Understanding NI 9232 Filtering
The NI 9232 uses a combination of analog and digital filtering
to provide an accurate representation of in-band signals while
rejecting out-of-band signals. The filters discriminate between
signals based on the frequency range, or bandwidth, of the signal.
The three important bandwidths to consider are the passband, the
stopband, and the alias-free bandwidth.
The NI 9232 represents signals within the passband, as quantified
primarily by passband flatness and phase nonlinearity. All signals
that appear in the alias-free bandwidth are either unaliased signals
or signals that have been filtered by at least the amount of the
stopband rejection.
Passband
The signals within the passband have frequency-dependent gain or
attenuation. The small amount of variation in gain with respect to
frequency is called the passband flatness. The digital filters of the
NI 9232 adjust the frequency range of the passband to match the

NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications 16 ni.com
data rate. Therefore, the amount of gain or attenuation at a given
frequency depends on the data rate. Figure 8 shows typical
passband flatness for the NI 9232.
Figure 8. NI 9232 Typical Passband Flatness
Frequency/Data Rate
0.50.4
0.10
0.04
0.06
0.08
–0.04
–0.02
0.00
0.02
–0.10
–0.08
–0.06
0.30.20.10
Gain (dB)

© National Instruments Corp. 17 NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications
Stopband
The digital filter significantly attenuates all signals above the
stopband frequency. The primary goal of the digital filter is to
prevent aliasing. Therefore, the stopband frequency scales
precisely with the data rate. The stopband rejection is the minimum
amount of attenuation applied by the digital filter to all signals with
frequencies within the stopband.
Alias-Free Bandwidth
Any signal that appears in the alias-free bandwidth of the NI 9232
is not an aliased artifact of signals at a higher frequency. The
alias-free bandwidth is defined by the ability of the digital filter to
reject frequencies above the stopband frequency, and it is equal to
the data rate minus the stopband frequency.

NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications 18 ni.com
Understanding NI 9232 Data Rates
The frequency of a master timebase ( fM) controls the data rate ( fs)
of the NI 9232. The NI 9232 includes an internal master timebase
with a frequency of 13.1072 MHz. When using the internal master
timebase, the result is data rates of 102.4 kS/s, 51.2 kS/s, 25.6 kS/s,
17.067 kS/s, and so on down to 0.98 kS/s, depending on the
decimation rate and the value of the clock divider. However, the
data rate must remain within the appropriate data rate range. Refer
to the Specifications section for more information about the data
rate range.
The following equation provides the available data rates of the
NI 9232:
fs=
where fsis the data rate
fMis the master timebase
mis decimation rate (64, 128, or 256)
nis clock divider from 1 to 26
fM
2mn
----------------------

© National Instruments Corp. 19 NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications
There are multiple combinations of clock divider and decimation
rate that yield the same data rate. The software always picks the
highest decimation rate for the selected data rate. Refer to Table 1
for the available data rates with the internal master timebase.
Table 1. Available Data Rates with the Internal Timebase
fs
(kS/s)
Decimation
Rate
fs
(kS/s)
Decimation
Rate
fs
(kS/s)
Decimation
Rate
102.40 64 9.31 64 4.88 64
51.20 128 8.53 256 4.65 128
34.13 64 7.88 64 4.45 64
25.60 256 7.31 128 4.27 256
20.48 64 6.83 64 4.10 64
17.07 128 6.40 256 3.94 128
14.63 64 6.02 64 3.66 256
12.80 256 5.69 128 3.41 128
11.38 64 5.39 64 3.20 256
10.24 128 5.12 256 3.01 128

NI 9232 Operating Instructions and Specifications 20 ni.com
2.84 256 1.97 256 1.22 256
2.69 128 1.83 256 1.16 256
2.56 256 1.71 256 1.11 256
2.44 128 1.60 256 1.07 256
2.33 256 1.51 256 1.02 256
2.23 128 1.42 256 0.98 256
2.13 256 1.35 256 — —
2.05 128 1.28 256 — —
Table 1. Available Data Rates with the Internal Timebase (Continued)
fs
(kS/s)
Decimation
Rate
fs
(kS/s)
Decimation
Rate
fs
(kS/s)
Decimation
Rate
Table of contents
Other NI I/O System manuals