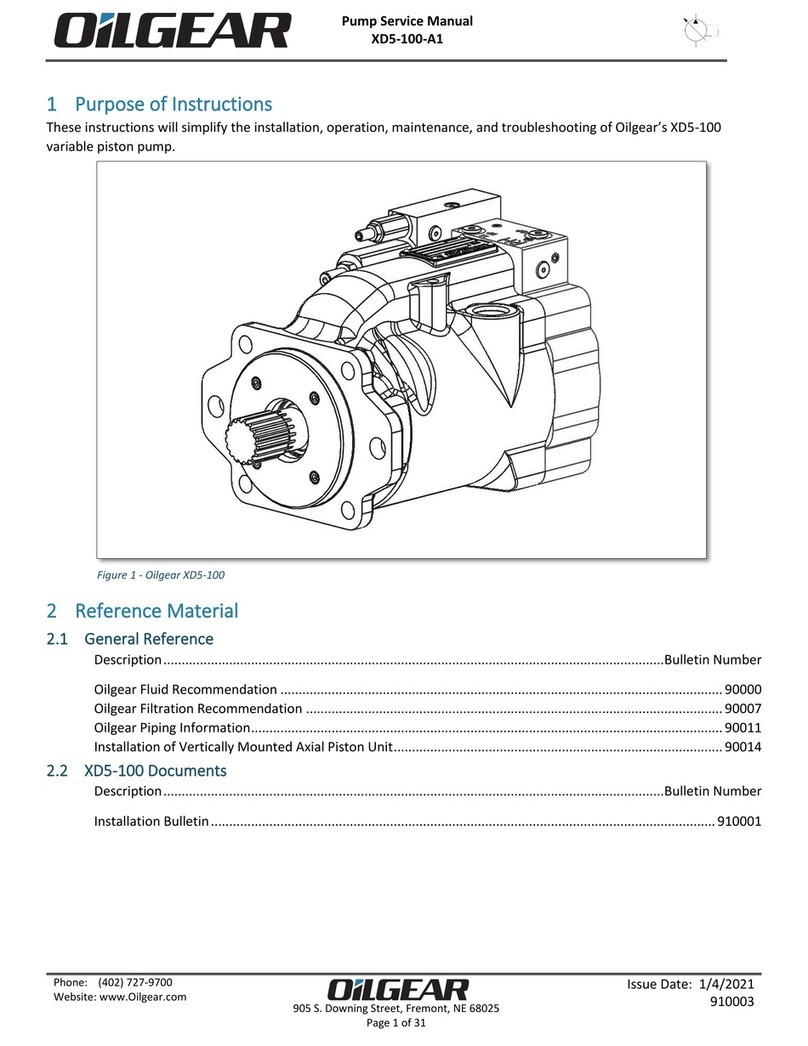
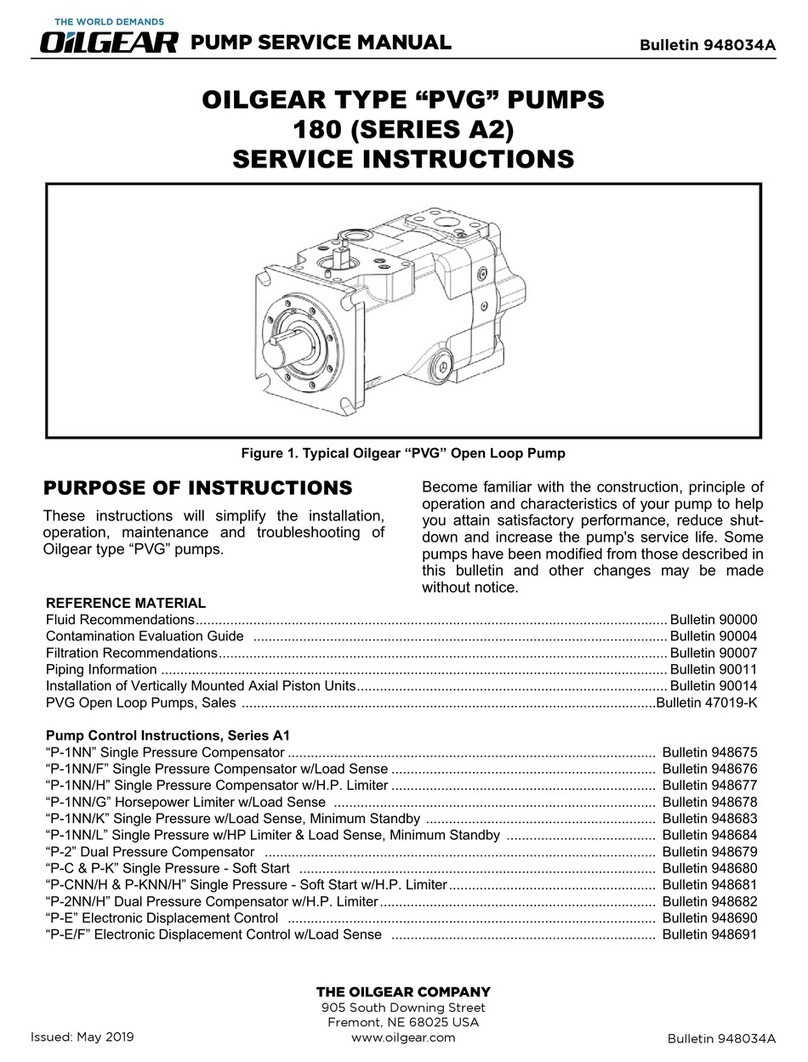
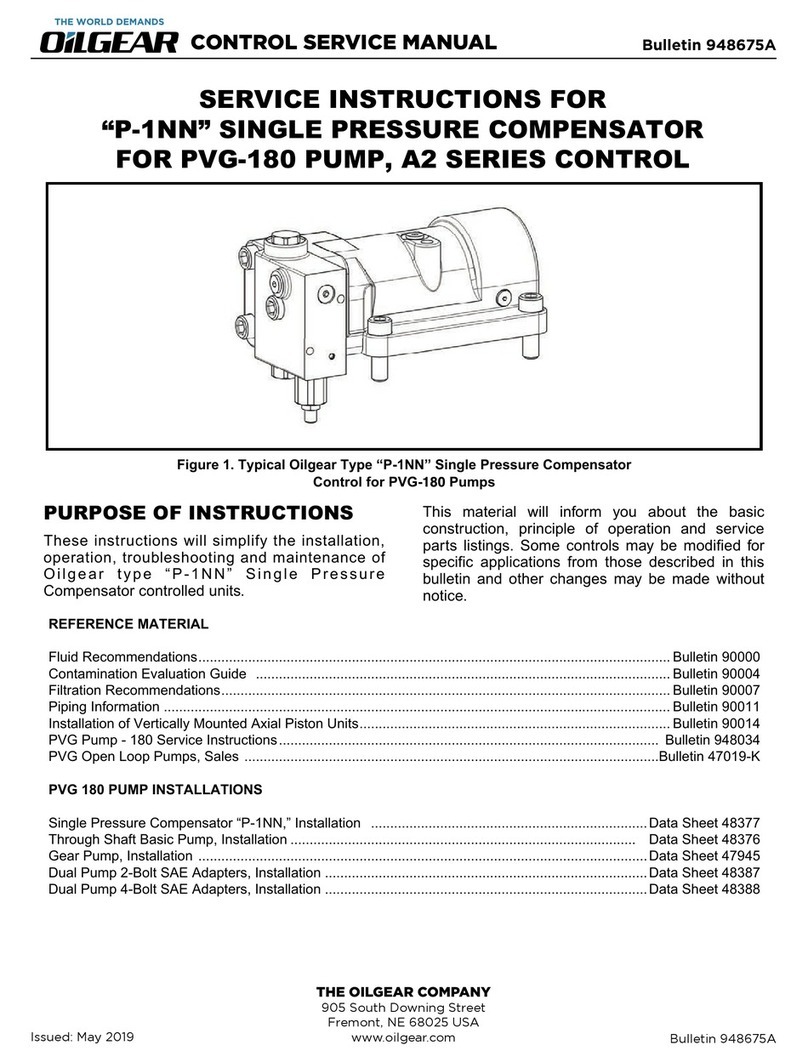
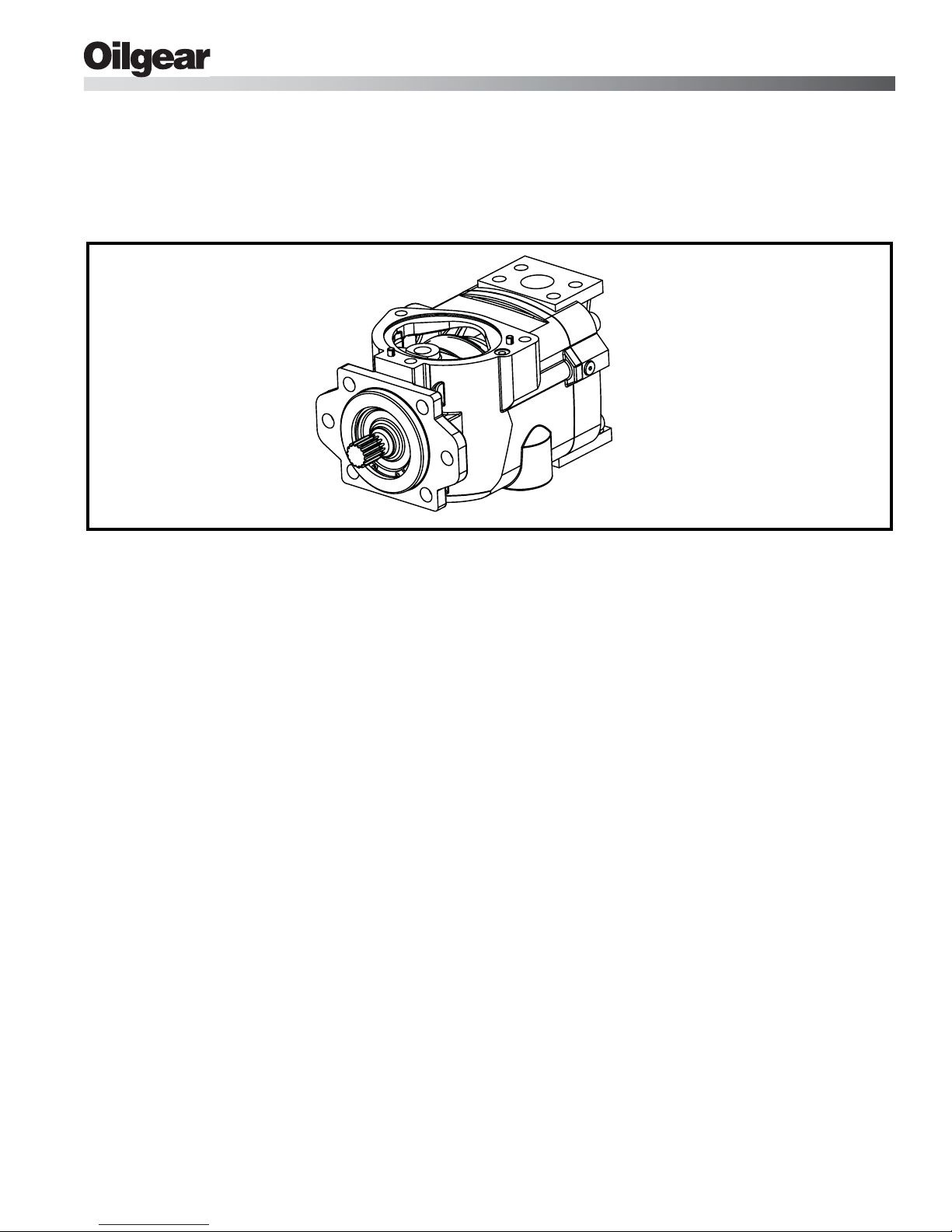
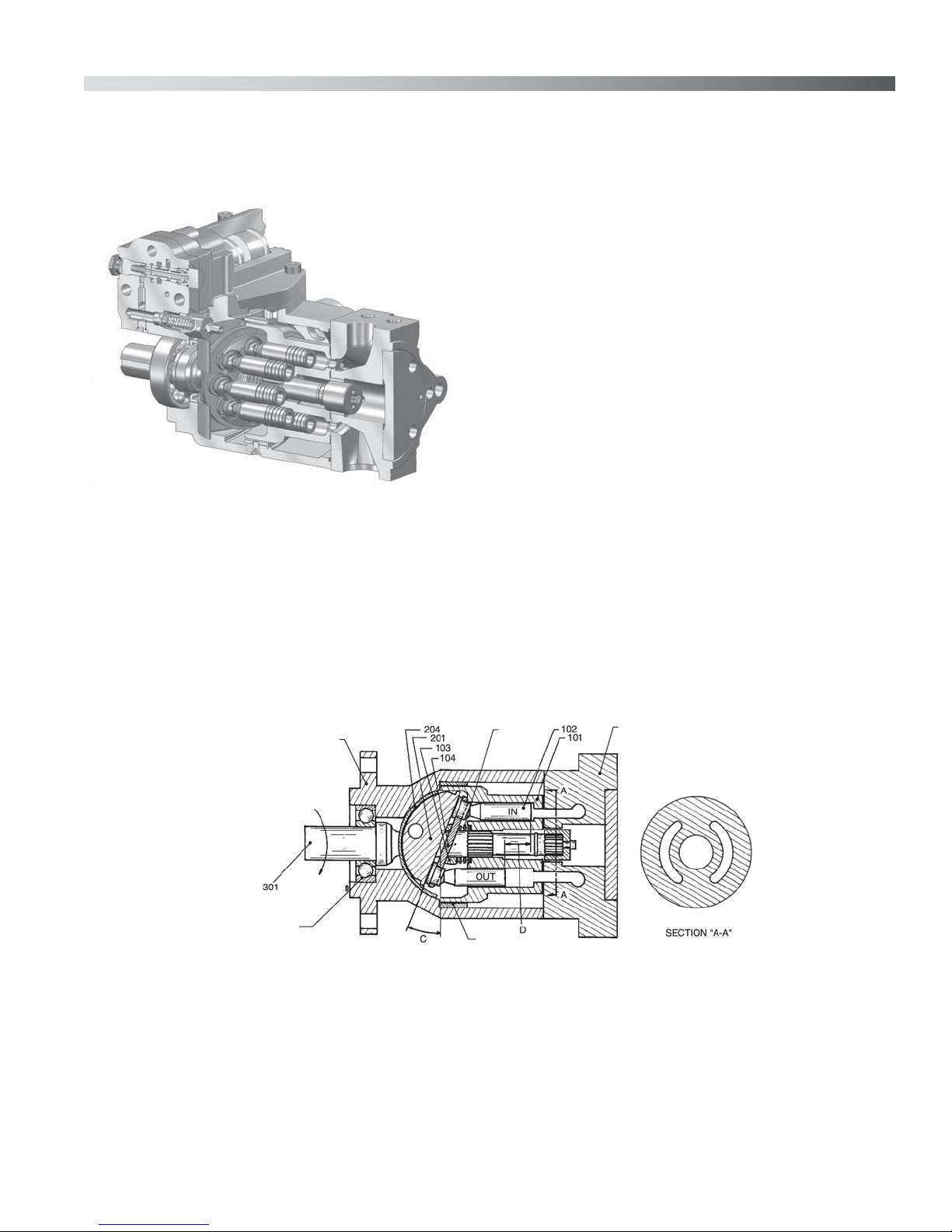
Bulletin 947023 THE OILGEAR COMPANY 3
Hydraulic hoses and tubing must be
inspected on a daily basis for leaks, cuts,
abrasions, damage and improper
clearance along any mounting frame for
hidden damage before the unit is put into
service. Replace damaged hoses or hoses
you suspect are damaged before the
system is returned to service! Hoses must
be replaced every two years. Failure to
properly inspect and maintain the system
may result in serious injury.
Hydraulic systems are hot. DO NOT
TOUCH! Serious personal injury may
result from hot oil. When you have
completed working on the hydraulic
system, thoroughly clean any spilled oil
from the equipment. Do not spill any
hydraulic fluids on the ground. Clean any
hydraulic fluids from your skin as soon as
you have completed maintenance and
repairs. Dispose of used oil and system
filters as required by law.
Use correct hoses, fittings, and adapters
with the correct SAE rating when
replacing hoses to prevent possible
serious injury. Always replace hoses,
fittings, and adapters with replacements
that have a proper, suitable, working
pressure rating. Replacement hoses must
be of the correct length and must comply
with the hose manufacturer’s and
Oilgear’s installation guidelines and
recommendations.
Hydraulic hoses have the SAE ratings
marked on the hose to assist you in
selecting the correct hose. The same
manufacturer must supply any replacement
hydraulic hoses and fitting assemblies. As
an example: Brand “X” hose and brand “Y”
fitting will not normally be compatible. No
“Twist” is allowed in the hydraulic hoses.
“Twist” may result in premature hose
failure. This can cause serious injury.
Please contact Oilgear for assistance when
required.
Hydraulic cylinders can be holding a
function in a certain position when the
pump is OFF. An example of this is a
function being held in the lift or partial lift
position by the cylinders. If a hydraulic
line is removed or the hydraulic circuits or
controls are being worked on, gravity may
allow the function being held in position to
drop. All workers and personnel must
remain clear of these areas when working
on or operating the hydraulic system.
Block and secure all devices and
functions which apply before beginning
work or operation. Failure to comply with
this can result in serious injury or death.
Any hydraulic pipe which is replaced must
conform to SAE J1065 specifications. If
incorrect hydraulic pipe is installed, the
hydraulic system may fail, causing
serious injury. Damaged or leaking
fittings, pipes or hoses must be replaced
before the system is returned to service.
DO NOT heat hydraulic pipe. The carbon
content of this steel tube is such that if
heated for bending, and either water or air
quenched, the pipe may lose its ductility
and thereby be subject to failure under
high pressure conditions. Serious injury
can result. Damaged or leaking pipes must
be replaced before the system is returned
to service. Please contact Oilgear if you
require assistance or have questions.
All hydraulic pressure must be relieved
from the hydraulic system prior to removing
any components from the system. To
relieve the hydraulic pressure from the
hydraulic system, turn off the motor and
operate the control panel with the key in the
ON position. Failure to comply can result in
serious injury. If you have any questions
concerning relieving the hydraulic pressure
from the system, please contact Oilgear.
!WARNING
!WARNING
!WARNING
!WARNING
!WARNING
!WARNING
!WARNING
!WARNING
Safety First