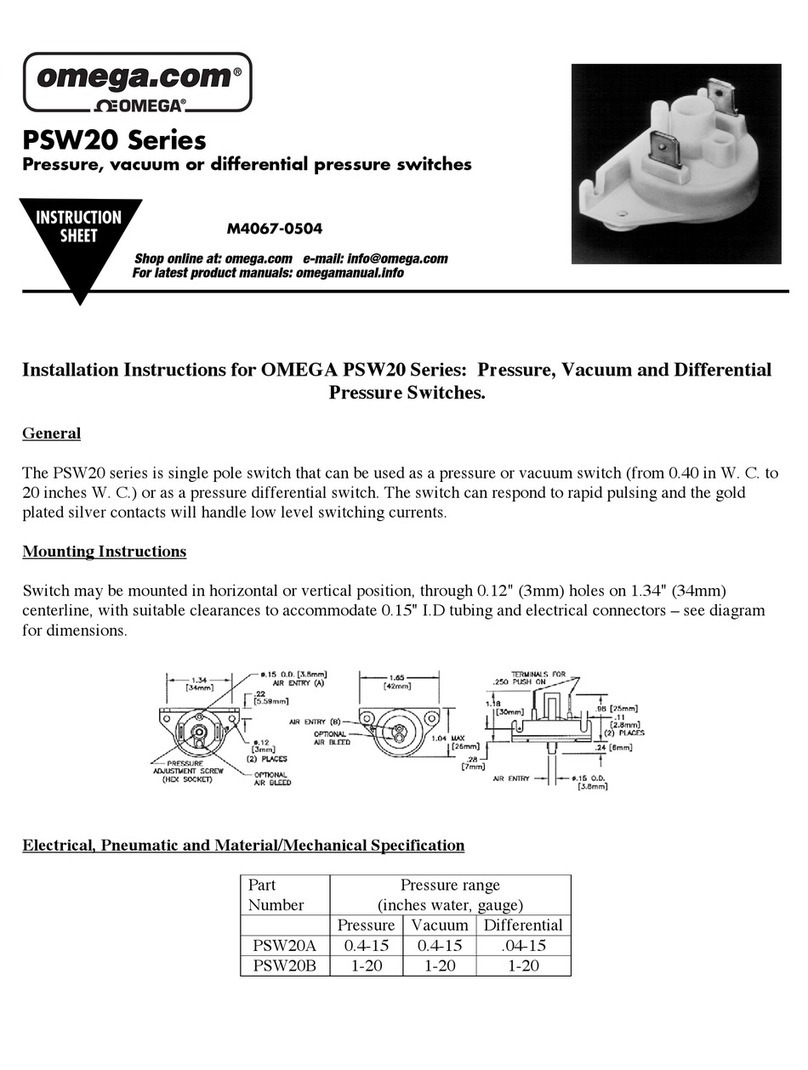
10
SPECIFICATIONS(capacitance)StepTwo
CapacitanceSwitch(LVC‐152series):Thecapacitancelevelswitchgeneratesapulse‐waveradiofrequency
signalfromthecapacitanceelectrodelocatedinthesensingtipofeachsensor.Whenliquidcomesinto
contactwiththesensingtip,thecapacitanceasmeasuredbythesensorchangesbasedonthedielectric
constantoftheliquid.Theguardcircuitrejectsthenegativeeffectsofcoatingbuildupontheprobeby
eliminatingthecoatingsignalpathbetweentheactiveandreferenceelectrodes.
AvoidinstallingtheLVC‐152seriesinmetalfittingsandkeepthesensor6”awayfrommetalobjects.Itis
possibleforalargemetalobjecttoinfluencethesensor’soperation.
LVC‐152‐R
LVC‐152‐G‐R
Thesensor’soperationmayvarybasedonthedielectricpropertiesofvariousapplicationliquids.The
LVC‐152seriessensorisfactory‐calibratedtobeusedwithliquidswithadielectricvaluebetween20and
80.Liquidswithadielectricconstantlessthan20willnotbedetectedbyanLVC‐152seriessensor.
TableofCommonDielectricConstants:NOTE:Liquidswithadielectricconstantlessthan20willnotbe
detectedbyanLVC‐152serieslevelswitch.
Acetone .......................21
Acetoaldehyde .........22.2
Acetyl methyl hexyl
ketone .........................28
Alcohol ..............16 to 31
Ammonia ...........15 to 25
Acetic acid .......4.1 to 6.2
Butyl chloride ............9.6
Barium chloride ...9 to 11
Benzene .....................2.3
Benzine ......................2.3
Barium nitrate ............5.6
Bromine .....................3.1
Chlorobenzene ...4.7 to 6
Chlorotoluene ............4.7
Chloroform ......4.5 to 5.0
Chlorine, liquid .........2.0
Carbon tetrachloride .2.2
Cyan ..........................2.6
Cyclohexane methanol
...................................3.7
D.I. Water ..................20
Ethyl toluene .............2.2
Ethyl alcohol ..............23
Ethylene glycol ..........37
Ethylene oxide ...........14
Ethylene dichloride
...........................11 to 17
Ethylene chloride ....10.5
Ethyl acetate .............6.4
Ethyl salicylate .........8.6
Ethyl stearate ............2.9
Ethyl silicote ............ 4.1
Formic acid ............... 59
Ferric oleate .............. 2.6
Freon ........................ 2.2
Glycerine ................... 47
Glycol ........................ 30
Glycol nitrite ............. 27
Gasoline ............2 to 2.2
Hydrochloric acid .... 4.6
Isobutyric acid .......... 2.7
Isobutyl methyl ketone
.................................... 13
Jet fuel ...................... 1.7
Lead carbonate .......... 18
Lead nitrate ............... 38
Methyl salicylate ...... 9.0
Methanol ..................... 33
Methyl alcohol .. 33 to 38
Margarine, liquid
.......................... 2.8 to 3.2
Methyl acetate ............7.3
N-butyl formate ..........2.4
Nitrobenzene ..... 26 to 35
Nitrotoluene ................ 25
Naphthalene ..... 2.3 to 2.5
Oils, vegetable .................
Oils, mineral ....2.3 to 2.4
Oils, petroleum.................
Oleic acid ....................2.5
Propane, liquid
......................... 1.8 to 1.9
Potassium nitrate5.0 to 5.9
Potassium chloride ...5.0
Stearic acid ................2.3
Toluene .....................2.4
Trichloroethylene .....3.4
Trichloroacetic acid ..4.5
Terephthalic acid
..........................1.5 to 1.7
Thinner ......................3.7
Urea ...........................3.5
Vinyl chloride ....2.8 to 6
Vinyl alcohol ..1.8 to 2.0
Water, 20°C ...............80
Water, 100°C .............48