MC14028B
http://onsemi.com
7
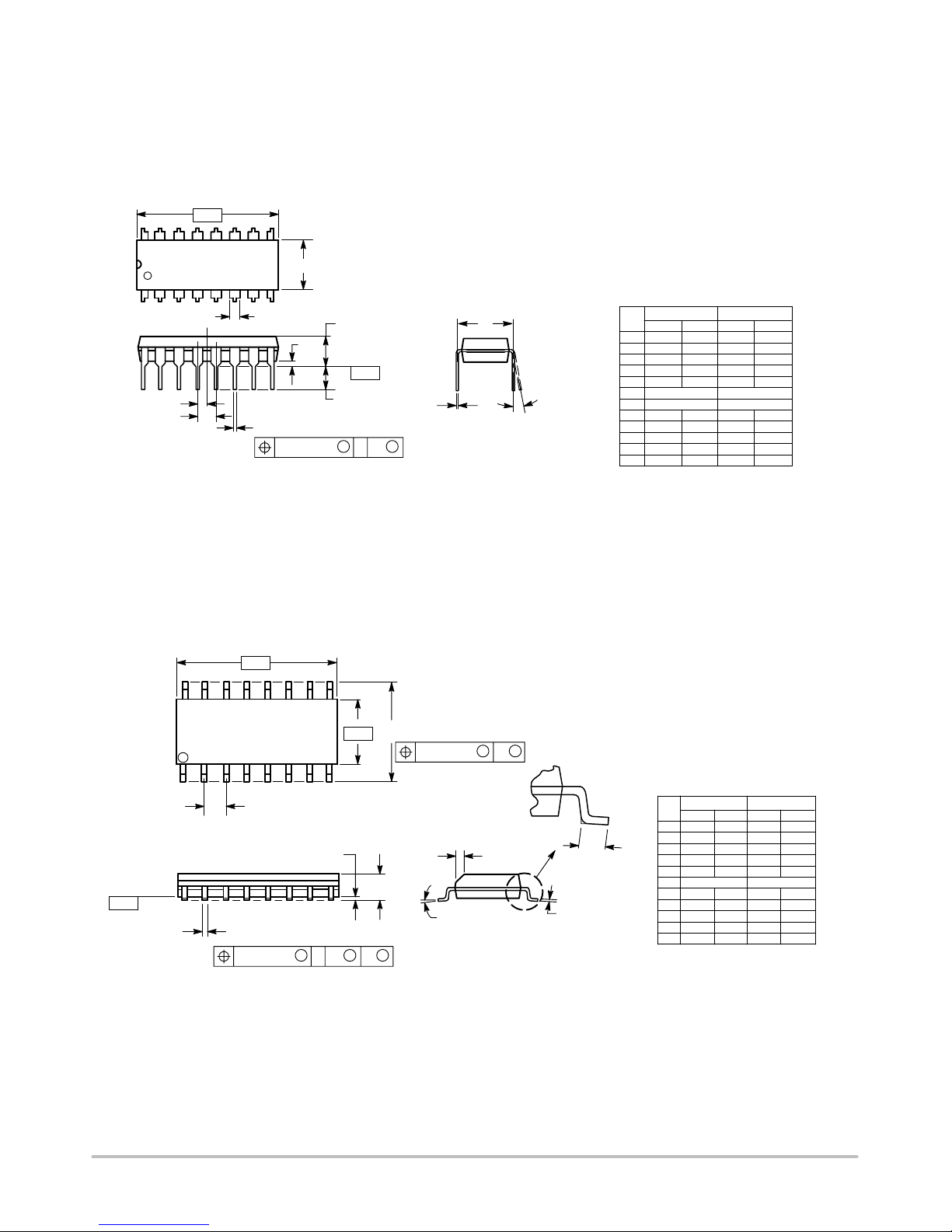
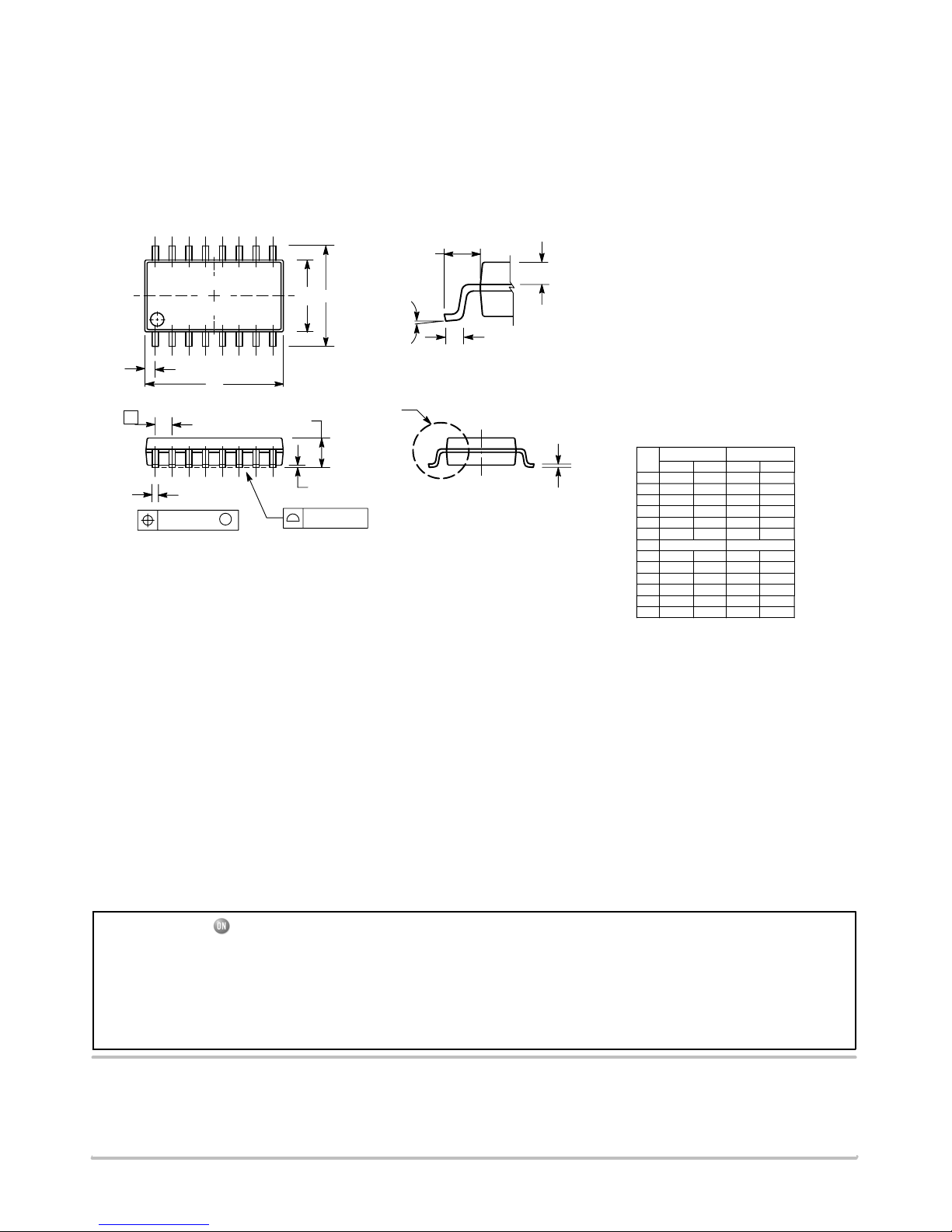
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
SOEIAJ−16
CASE 966−01
ISSUE A
HE
A1
DIM MIN MAX MIN MAX
INCHES
−−− 2.05 −−− 0.081
MILLIMETERS
0.05 0.20 0.002 0.008
0.35 0.50 0.014 0.020
0.10 0.20 0.007 0.011
9.90 10.50 0.390 0.413
5.10 5.45 0.201 0.215
1.27 BSC 0.050 BSC
7.40 8.20 0.291 0.323
0.50 0.85 0.020 0.033
1.10 1.50 0.043 0.059
0
0.70 0.90 0.028 0.035
−−− 0.78 −−− 0.031
A1
HE
Q1
LE
_10 _0
_10 _
LEQ1
_
NOTES:
1. DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER ANSI
Y14.5M, 1982.
2. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: MILLIMETER.
3. DIMENSIONS D AND E DO NOT INCLUDE
MOLD FLASH OR PROTRUSIONS AND ARE
MEASURED AT THE PARTING LINE. MOLD FLASH
OR PROTRUSIONS SHALL NOT EXCEED 0.15
(0.006) PER SIDE.
4. TERMINAL NUMBERS ARE SHOWN FOR
REFERENCE ONLY.
5. THE LEAD WIDTH DIMENSION (b) DOES NOT
INCLUDE DAMBAR PROTRUSION. ALLOWABLE
DAMBAR PROTRUSION SHALL BE 0.08 (0.003)
TOTAL IN EXCESS OF THE LEAD WIDTH
DIMENSION AT MAXIMUM MATERIAL CONDITION.
DAMBAR CANNOT BE LOCATED ON THE LOWER
RADIUS OR THE FOOT. MINIMUM SPACE
BETWEEN PROTRUSIONS AND ADJACENT LEAD
TO BE 0.46 ( 0.018).
M
L
DETAIL P
VIEW P
c
A
b
e
M
0.13 (0.005) 0.10 (0.004)
1
16 9
8
D
Z
E
A
b
c
D
E
e
L
M
Z
ON Semiconductor and are registered trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC (SCILLC). SCILLC reserves the right to make changes without further notice
to any products herein. SCILLC makes no warranty, representation or guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does SCILLC assume any liability
arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation special, consequential or incidental damages.
“Typical” parameters which may be provided in SCILLC data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All
operating parameters, including “Typicals” must be validated for each customer application by customer’s technical experts. SCILLC does not convey any license under its patent rights
nor the rights of others. SCILLC products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or other applications
intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the SCILLC product could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should
Buyer purchase or use SCILLC products for any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold SCILLC and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates,
and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death
associated with such unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that SCILLC was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part. SCILLC is an Equal
Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer. This literature is subject to all applicable copyright laws and is not for resale in any manner.
PUBLICATION ORDERING INFORMATION
N. American Technical Support: 800−282−9855 Toll Free
USA/Canada
Europe, Middle East and Africa Technical Support:
Phone: 421 33 790 2910
Japan Customer Focus Center
Phone: 81−3−5773−3850
MC14028B/D
LITERATURE FULFILLMENT:
Literature Distribution Center for ON Semiconductor
P.O. Box 5163, Denver, Colorado 80217 USA
Phone: 303−675−2175 or 800−344−3860 Toll Free USA/Canada
Fax: 303−675−2176 or 800−344−3867 Toll Free USA/Canada
ON Semiconductor Website: www.onsemi.com
Order Literature: http://www.onsemi.com/orderlit
For additional information, please contact your local
Sales Representative