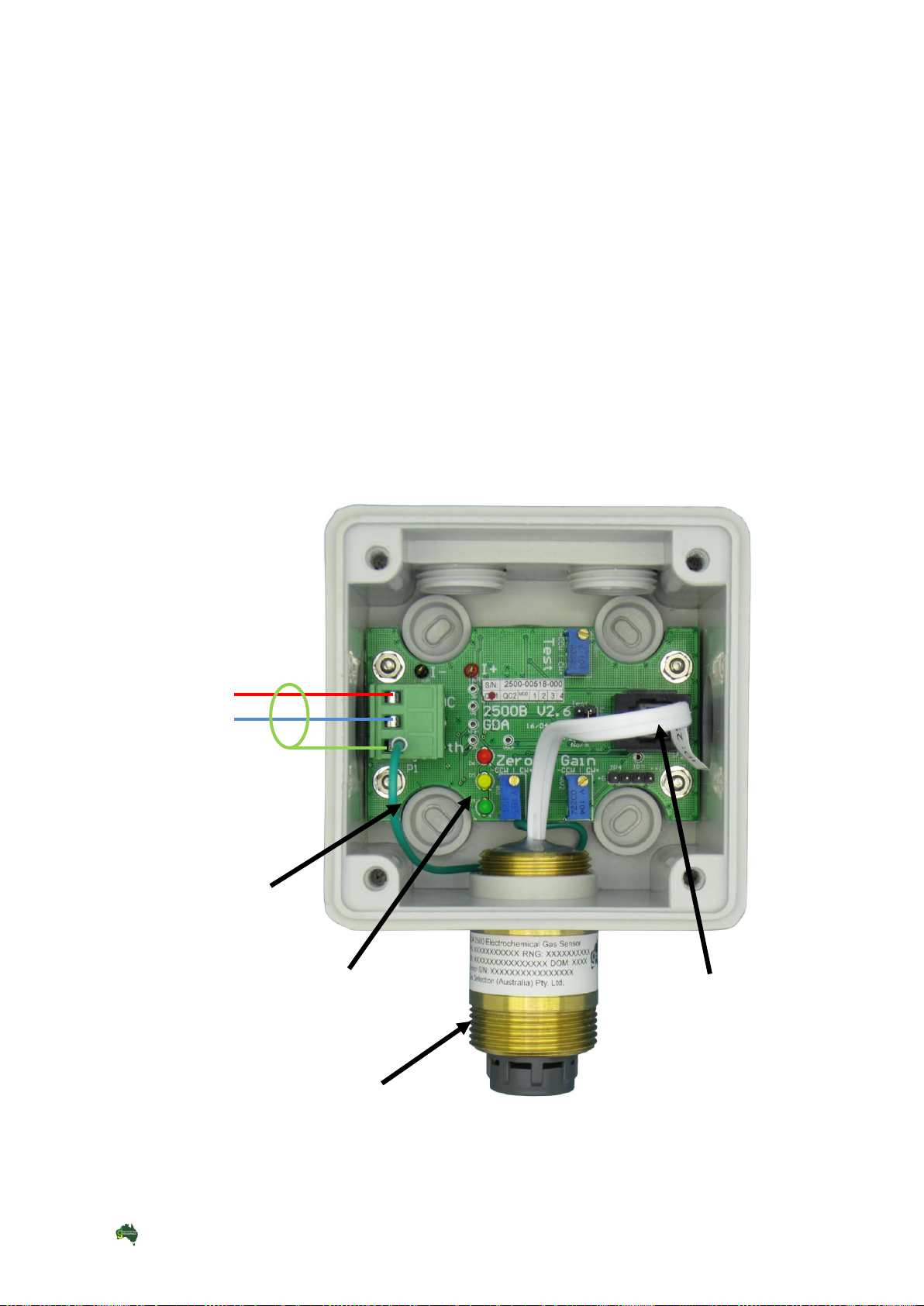
Gas Detection (Australia) Pty Ltd Page 3 of 20 M-GDA-2500 V2.6 Rev 1.0
WARNINGS
The GDA 2500 Series Sensors are only to be used in areas classified as SAFE AREAs. The
sensor is not designed for use in classified HAZARDOUS AREAs.
If GDA 2500 Series Sensors are used for safety critical applications the Calibration/Bump test
period should be evaluated according to risk management procedure associated the area the
sensor is installed.
The GDA 2500 Series Sensors use an electrochemical sensor, the chemical is used up when
the target gas is present. Therefore the chemical in the sensor will be used up at a faster rate,
shorting its life. From the time of calibration at the GDA factory the sensors output accuracy
will have degraded and may require re-calibration if some time has elapsed.
The sensor element contains substances that can be harmful to health. In the unlikely event of
a sensor element leaking, the sensor contents should not be touched. If the sensor contents
come in contact with eyes or skin, please seek immediate medical attention.
The sensor is designed to work only with the GDA transmitter. Connection to any other
transmitter will damage the sensor.
It is important not to exceed the specified DC voltage as indicated in this manual.
PROPRIETARY RIGHTS
No part of the hardware or documentation may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored
in a retrieval system, or translated into any language or computer language, in any form or by
any means, without prior written permission of GDA.
While great efforts have been made to ensure the accuracy and clarity of this document, GDA
assumes no liability resulting from any omissions in this document, or from misuse of the
information contained herein. The information in this document has been carefully checked
and is believed to be entirely reliable with all of the necessary information included. GDA
reserves the right to make changes to any products described herein to improve reliability,
function, or design, and reserves the right to revise this document and make changes from
time to time in content hereof with no obligation to notify any persons of revisions or changes.
GDA does not assume any liability arising out of the application or any use of any product or
circuit described herein; neither does it convey license under its patent rights or the rights of
others.