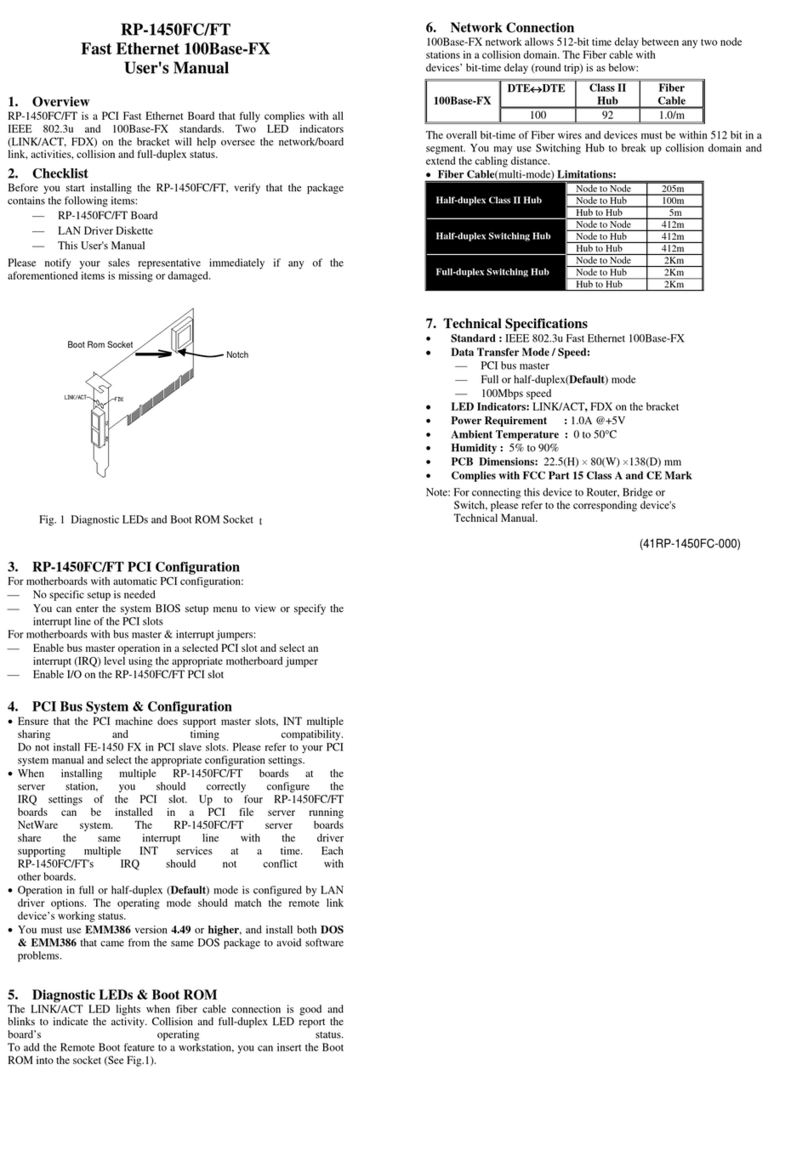
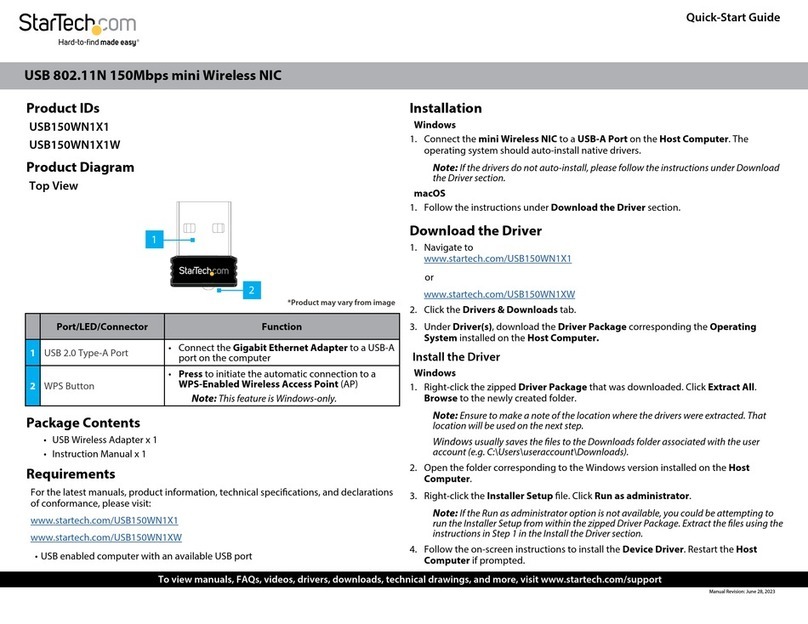
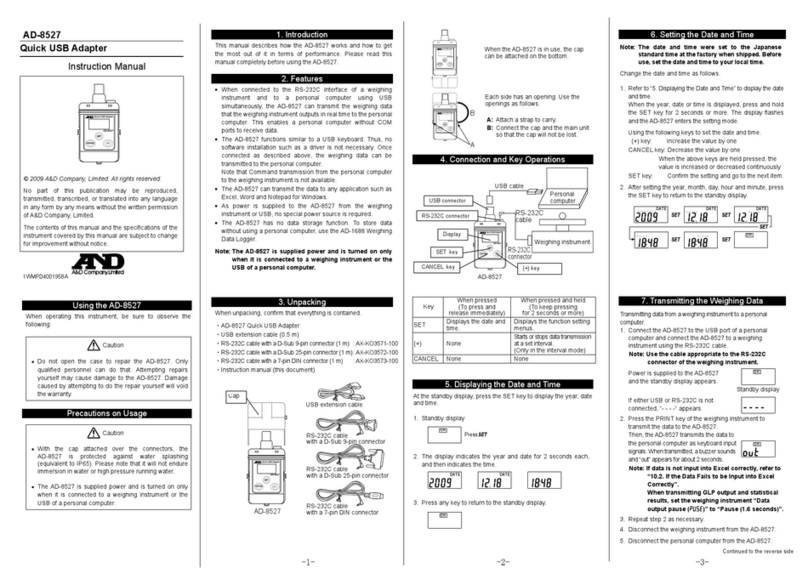
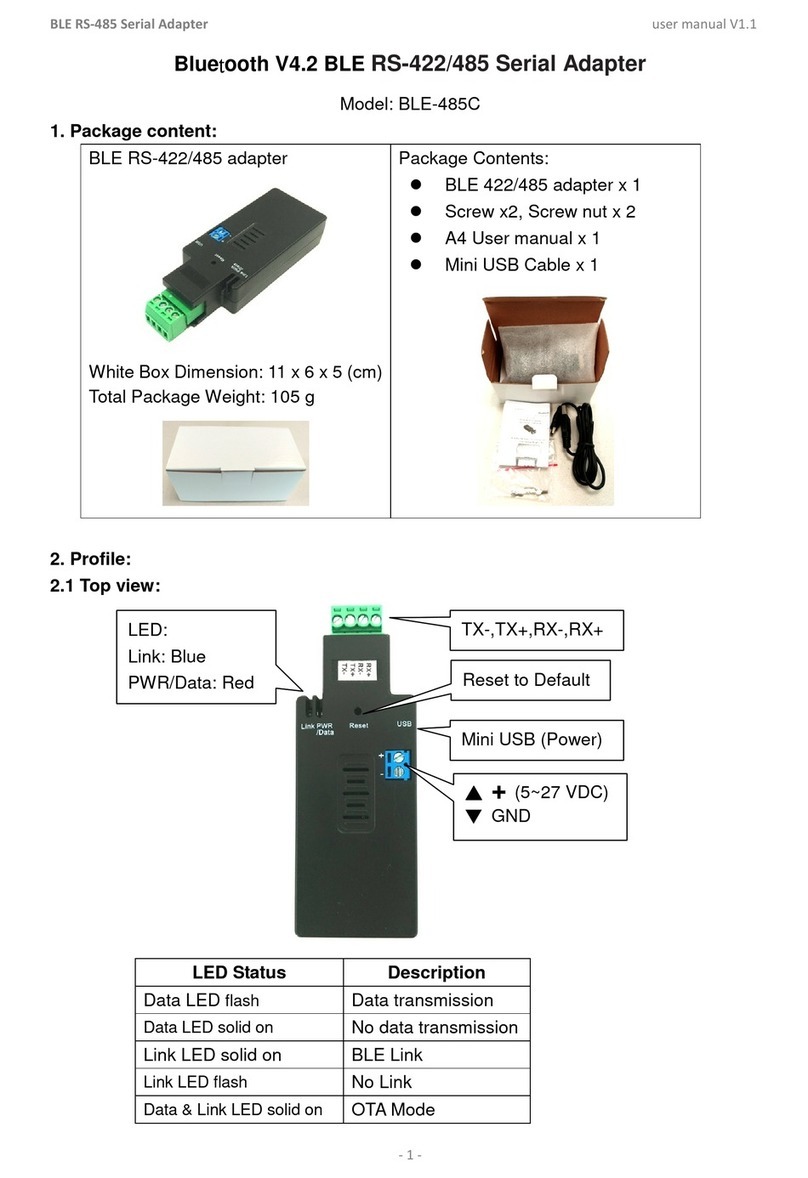
3. Specifications
3.1 Cable Specifications
Table 3.1 lists the cables you can use and their specifications.
Caution: Please do not use telephone cables. Telephone cables do not support
Ethernet or Fast Ethernet
Table 3.1 Straight-Through and Crossed-Over Cable Specifications
Ethernet Type Cable Requirements Maximum Length
10BASE-T Category 3 or better, UTP or STP 328 ft (100M)
100BASE-TX Category 5 or better, UTP or STP 328 ft (100M)
Twisted-pair cabling comes in various grades, or categories. Category 5 is required for
Fast Ethernet, and is also the most reliable and most commonly used category. You
can buy UTP Category 5 (Unshielded Twisted Pair) Ethernet cabling in precrimped
lengths, or you can crimp your own. Crimping your own can result in faulty
connections if the
RJ-45 tips are not attached properly. Precrimped Category 5 cabling is available at
most computer retail stores.
The most reliable and commonly used type of Category 5 cabling used is UTP, or
"unshielded twisted pair." STP, or "shielded twisted pair" wiring is only necessary for
network environments exposed to excessive amounts of electromagnetic interference,
or EMI. These environments include areas with high sources of electrical power, air
conditioning, generators, and radio signals. STP is also used for wiring outdoors.
There are two types of the wiring: Straight-Through Cables and Crossover Cables.
Category 5 UTP/STP cable has eight wires inside the sheath. The wires form four
pairs. Straight-Through Cables has same pinouts at both ends while Crossover
Cables has a different pin arrangement at each end.
In a straight-through cable, wires 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 and 8 at one end of the cable are still
wires 1~8 at the other end. In a crossover cable, the wires of 1,2,3,6 are reversed so
that wire 1 become 3 at the other end of the cable, 2 becomes 6, and so forth.
To determine which wire is wire 1, hold the RJ-45 cable tip with the spring clip facing
towards the ground and the end pointing away from you. The copper wires exposed
upwards to your view. The first wire on the far left is wire 1. You can also refer to the
illustrations and charts of the internal wiring on the following page.