Rheonics | Switzerland | U.S.A.
SRV, SRD, SRV-FPC, SRD-FPC Installation and Intrinsic Safety Manual P. 3
Version 2.0, Updated: October 29, 2020
Rheonics GmbH, Klosterstrasse 19, 8406 Winterthur, Switzerland
©Rheonics. Rheonics confidential and proprietary information.
Contents
1. Purpose of this manual ........................................................................................................................................5
2. Description of the sensors and general installation considerations ..................................................................5
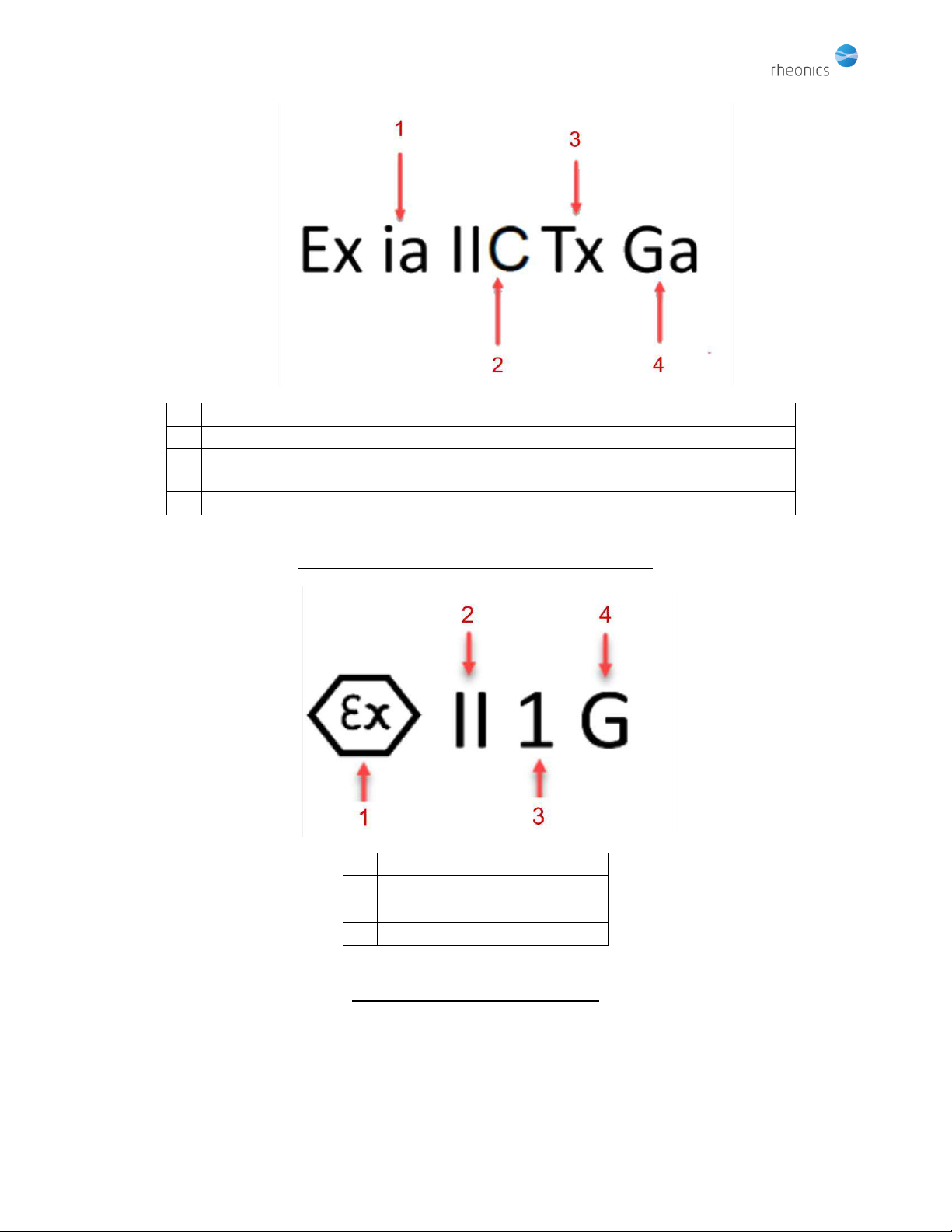
3. EX label description:.............................................................................................................................................7
3.1. General note on Category of protection and operating zone......................................................................9
3.2. Description of “X” conditions: operating conditions not described on the label, but that are necessary in
order to maintain intrinsic safety..............................................................................................................................9
3.2.1. Area classification & Gas Grouping .....................................................................................................9
3.2.2. Electrical parameters relevant to intrinsic safety..............................................................................10
3.2.3. Temperature rating of the sensors according to T class ...................................................................10
3.2.4. Pressure rating of the sensors ...........................................................................................................11
3.2.5. Damage protection............................................................................................................................11
4. Safe use of ATEX approved equipment .............................................................................................................13
4.1. Notes on Safe Use of the ATEX Approved Equipment ...............................................................................13
4.2. Mounting, Commissioning, and Operation ................................................................................................13
5. Electrical Installation..........................................................................................................................................13
5.1. Cabling........................................................................................................................................................14
5.2. Zener diode barriers...................................................................................................................................18
5.3. Installation diagrams..................................................................................................................................20
5.4. Equipotential bonding................................................................................................................................25
5.4.1. Bonding/grounding conductor ..........................................................................................................25
5.4.2. Bonding to the sensor .......................................................................................................................26
5.4.3. Bonding configurations .....................................................................................................................27
6. Maintenance ...........................................................................................................................................................31
6.1. External Maintenance ......................................................................................................................................31
6.2. Sensor Maintenance.........................................................................................................................................31
6.3. Internal Maintenance.......................................................................................................................................31
7. Returning Equipment to the factory ......................................................................................................................31
8. Intrinsic safety certificates......................................................................................................................................32
9. Revisions and approvals .........................................................................................................................................32
English version of this manual is the only approved version from Rheonics and
installers should refer to it to confirm the correctness of information. In case of
any questions contact your local partner or Rheonics support.