II 1
The lens of the Rhino “Large View” Welding Helmet typically has double the view-
ing area of a standard helmet. As a result of the increased size, more care needs to
be taken with the helmet because the lens is a LCD made of glass, similar to many
television and cell phone screens manufactured today. If the helmet is acciden-
tally dropped onto a hard surface or smashed, the lens can crack or shatter .
Place the helmet in a bag or box after use. Ambient lighting in a shop, garage, or
workplace can activate the lens, but not provide enough solar energy for power,
which will employ the batteries to keep the lens activated. Over a long period of
time this can drain the batteries. Storage in a bag or box will eliminate this pos-
sibility. Replacement CR2025 batteries are available at a very low cost from most
stores and online. Instructions for battery installation are pictured and described
later in this manual.
If you would like to test your helmet before use, then please do the following:
1. Turn the lens sensitivity to “MAX”
2. Position the helmet with the lens facing a light bulb with a minimum of
60-Watts. To insure an accurate test, the helmet must be within 12 inches of the
light bulb. Equivalent and brighter light sources can be substituted.
3. If the lens does not darken, check/replace the (2) CR2025 batteries and retest.
1.2 Customer Care & Warranty Inquiries - Welding Helmets Direct
Please check your helmet and lens for any damage that may have occurred during
shipping and notify us immediately. If you experience any problems, we are here
to help. Helmets carry a 2-year warranty. Warranty inquiries are handled by our
customer care department.
Customer Care Department:
customercare@weldinghelmetsdirect.com
Welding Helmets Direct
PO Box 8628
Bend, OR 97708
Phone: (541) 749-0903 Toll Free: (855) 207-9865
1.1 Important Information
Section 1 - Required Reading - Important Points and Safety
Table of Contents & Common Troubleshooting.......................................
Section 1 - Required Reading - Important Points and Safety..............
Section 2 - Headgear Assembly Components and Installation...........
Section 3 - Adjusting Headgear......................................................................
Section 4 - Lens Cover Replacement.............................................................
Section 5 - Variable Shade, Sensitivity, and Delay Adjustment............
Section 6 - Battery Replacement....................................................................
Below
1-2
3-5
6
7
8-9
10
Problem Solution
Auto-darkening lens stays
in light state when welding,
does not darken.
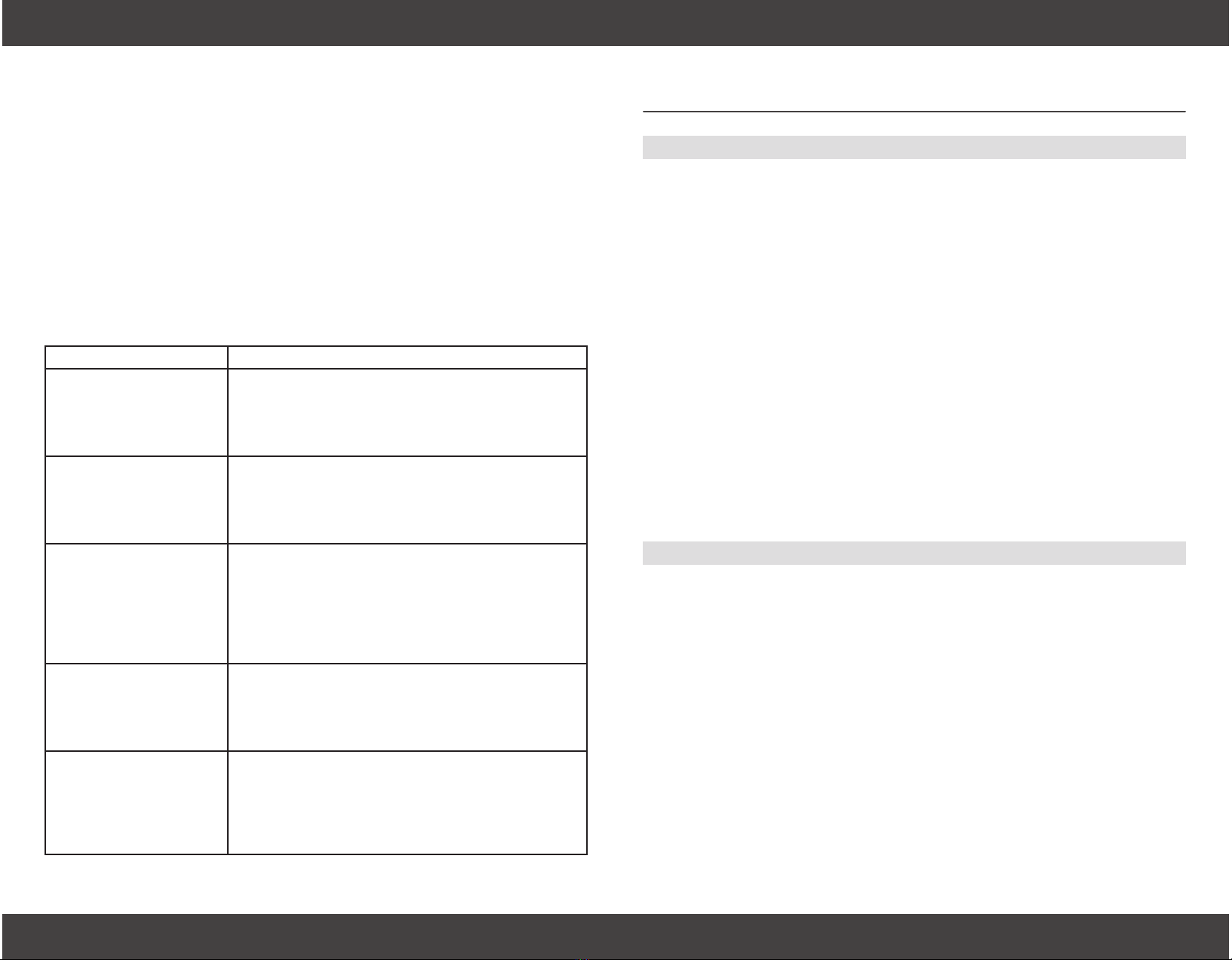
STOP WELDING! Adjust lens sensitivity to higher setting.
Change exterior lens cover if it is dirty or damaged. Make
sure there are no obstructions between arc and sensors,
extreme angles will obstruct the arc from sensors. Possible
dead batteries, replace with two CR2025 lithium batteries.
Auto-darkening lens stays in
dark state after the welding
arc is gone or the lens stays
dark when no welding arc is
present.
Adjust the sensitivity setting lower with small changes,
gradually moving it towards low. In some light conditions
where lots of ambient light exists, reduction of ambient light
may be necessary with barriers or other blocking devices.
Areas of the auto-darkening
lens are not darkening; lines
separate light and dark areas
of the lens.
STOP WELDING! The auto-darkening lens may contain a
crack, which can be caused from the impact of the helmet
being dropped or smashed. Weld spatter on the lens can
also cause a crack. The lens needs to be replaced; this is not
covered under warranty in most cases, email customer care
at customercare@weldinghelmetsdirect.com to nd out how
we can help you.
Auto-darkening lens is
ickering when welding arc is
present.
Adjust the sensitivity setting to a higher level. Change exte-
rior lens cover if it is dirty or damaged. Make sure there are
no obstructions between arc and sensors, extreme angles
will obstruct the arc from sensors. Reduce the delay setting
to minimum.
Variable lighter auto-dark-
ening lens shading in the
dark state, noticeable on the
outside edges and corners
of lens.
Called “angle of view eect,” auto-darkening lenses have an
optimum viewing angle of operation. That angle is per-
pendicular to the surface of the lens or 90 degrees. This is a
normal behavior of the lens and does not reveal a health or
safety hazard. Cheater lenses or magnifying lenses enable
this eect to become more noticeable.