RFTSeries|6AxisForceTorqueSensor
©ROBO
T
OUS
Co.,Ltd.www.robotous.com|[email protected]2
Contents
1. Caution ·························································································································································· 4
1.1. Notices ···································································································································································································4
1.2. Warning ·································································································································································································4
2. Installation ···················································································································································· 5
2.1. Overview ·······························································································································································································5
2.2. Power Supply Specifications ·························································································································································6
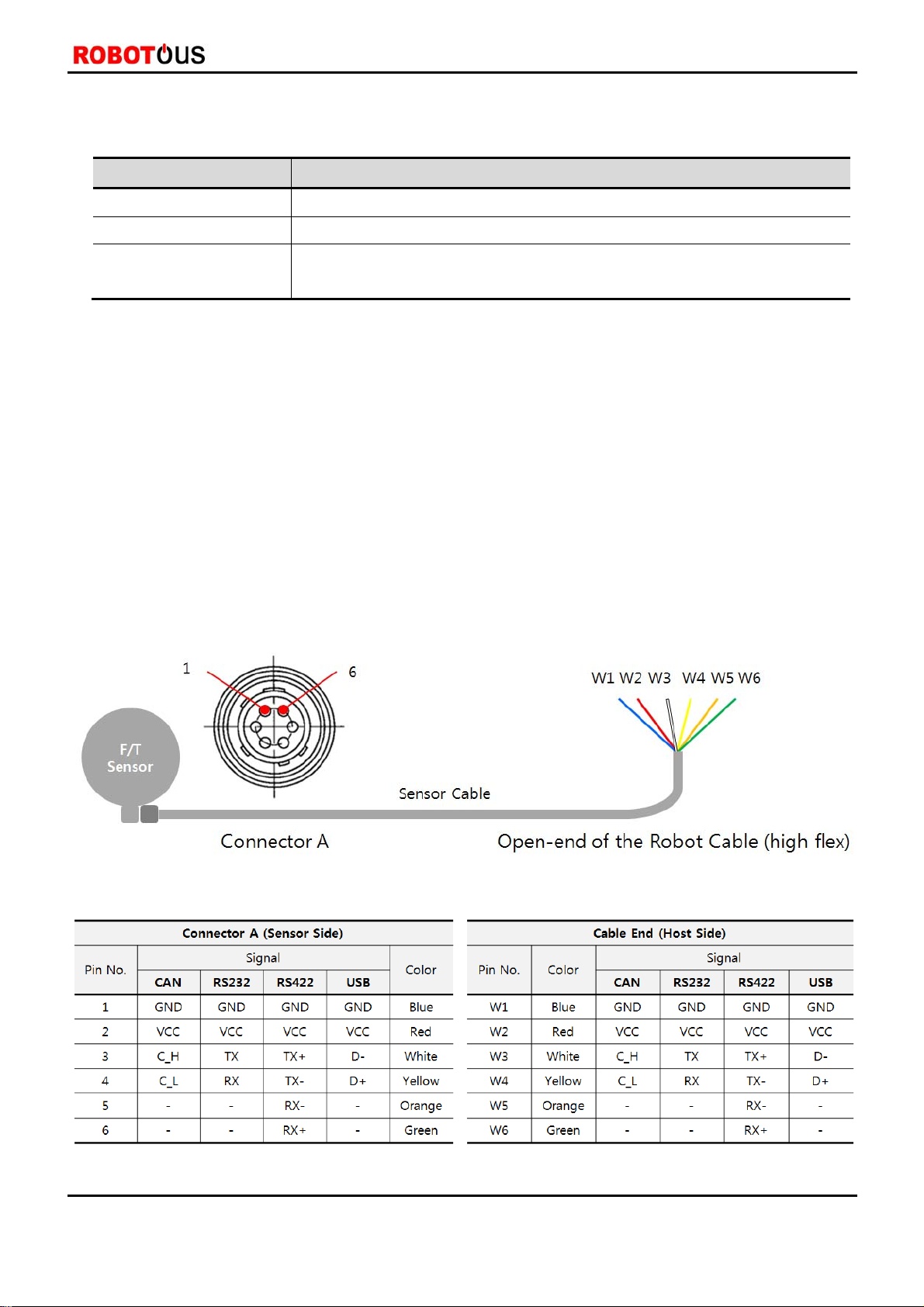
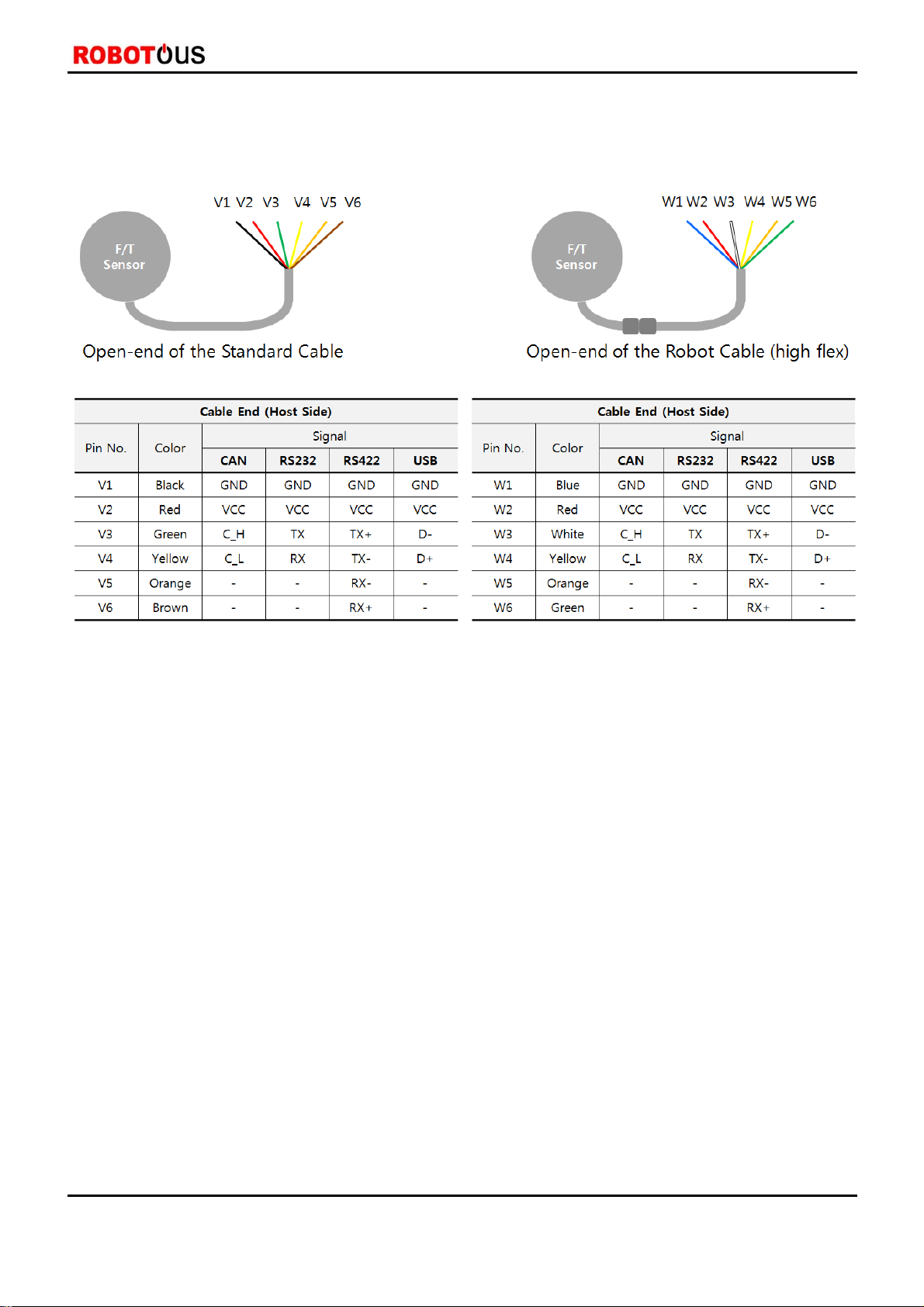
2.3. Wiring ····································································································································································································6
3. Operation ······················································································································································ 8
3.1. F/T Sensor Output Interfaces ·······················································································································································8
3.2. Communication Packets ·································································································································································8
3.3. Basic Operation ··················································································································································································8
3.4. Default Setting of Communication ············································································································································9
3.5. Packet Structure ·············································································································································································· 10
3.5.1. Packet Structure of CAN Interface ······················································································································································· 10
3.5.2. Packet Structure of UART interface······················································································································································ 10
3.6. Packet Definition ············································································································································································ 11
3.6.1. Summary of command packets ···························································································································································· 11
3.6.2. Read Model Name ······················································································································································································ 11
3.6.3. Read Serial Number ··················································································································································································· 12
3.6.4. Read Firmware Version ············································································································································································· 12
3.6.5. Set Communication ID (for CAN only) ·············································································································································· 12
3.6.6. Read Communication ID (for CAN only) ··········································································································································· 13
3.6.7. Set Baud-rate (for UART only) ······························································································································································· 13
3.6.8. Read Baud-rate ····························································································································································································· 1 4
3.6.9. Set Filter ·········································································································································································································· 14
3.6.10. Read Filter Setting ···················································································································································································· 15
3.6.11. Read F/T Data (once) ·············································································································································································· 15
3.6.12. Start F/T Data Output ············································································································································································· 17
3.6.13. Stop F/T Data Output ············································································································································································· 17
3.6.14. Set Data Output Rate ············································································································································································· 17
3.6.15. Read Data Output Rate ·········································································································································································· 18
3.6.16. Allowable Data Output Rate ································································································································································ 18
3.6.17. Set Bias ·········································································································································································································· 19