C
on
ten
t
s
Chapter I: Product Introduction
1. Product Characteristics ...............................................................................................01
2. Main Applications ........................................................................................................02
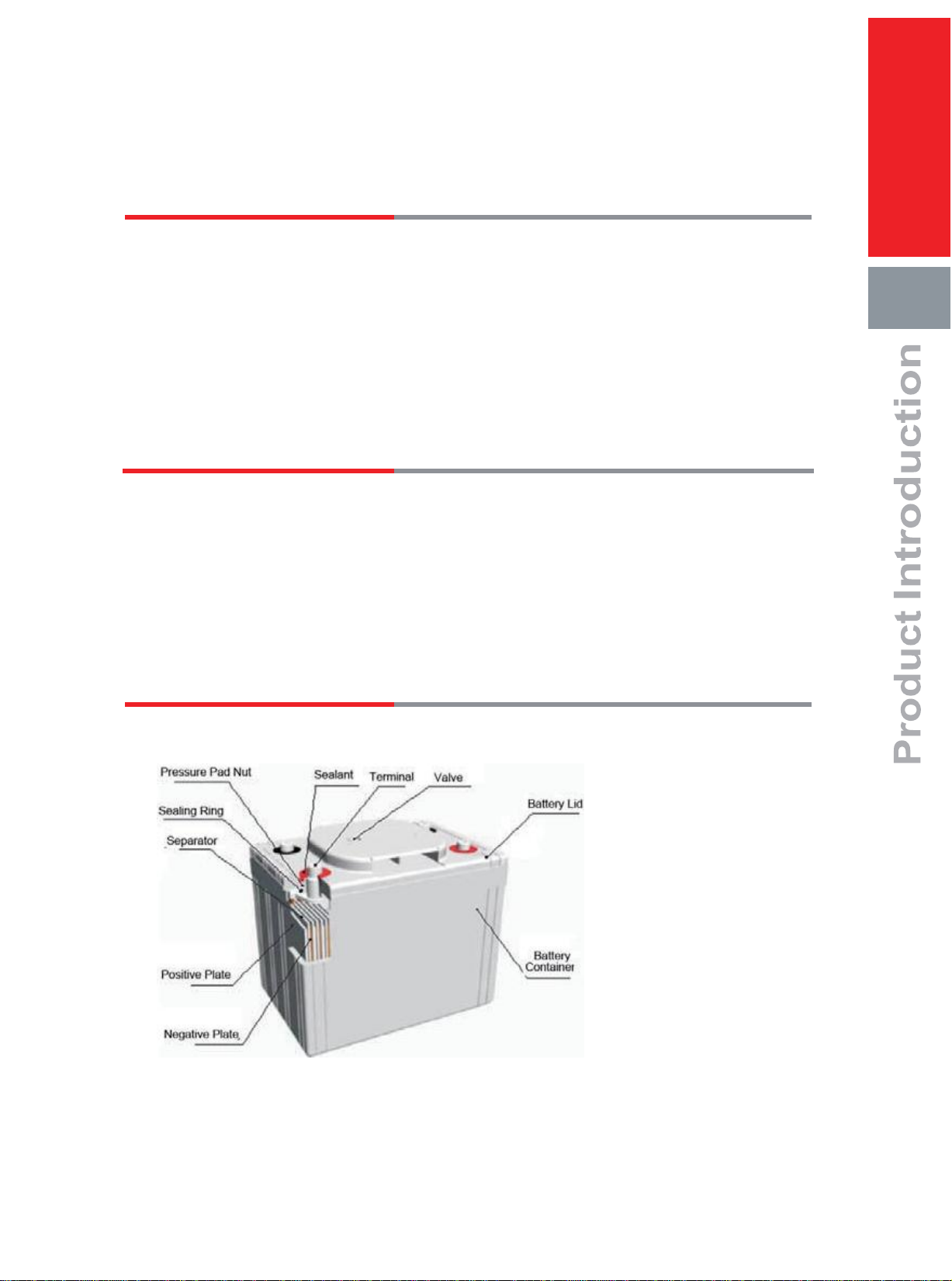
3. Battery Construction ....................................................................................................02
4. General Specification ..................................................................................................03
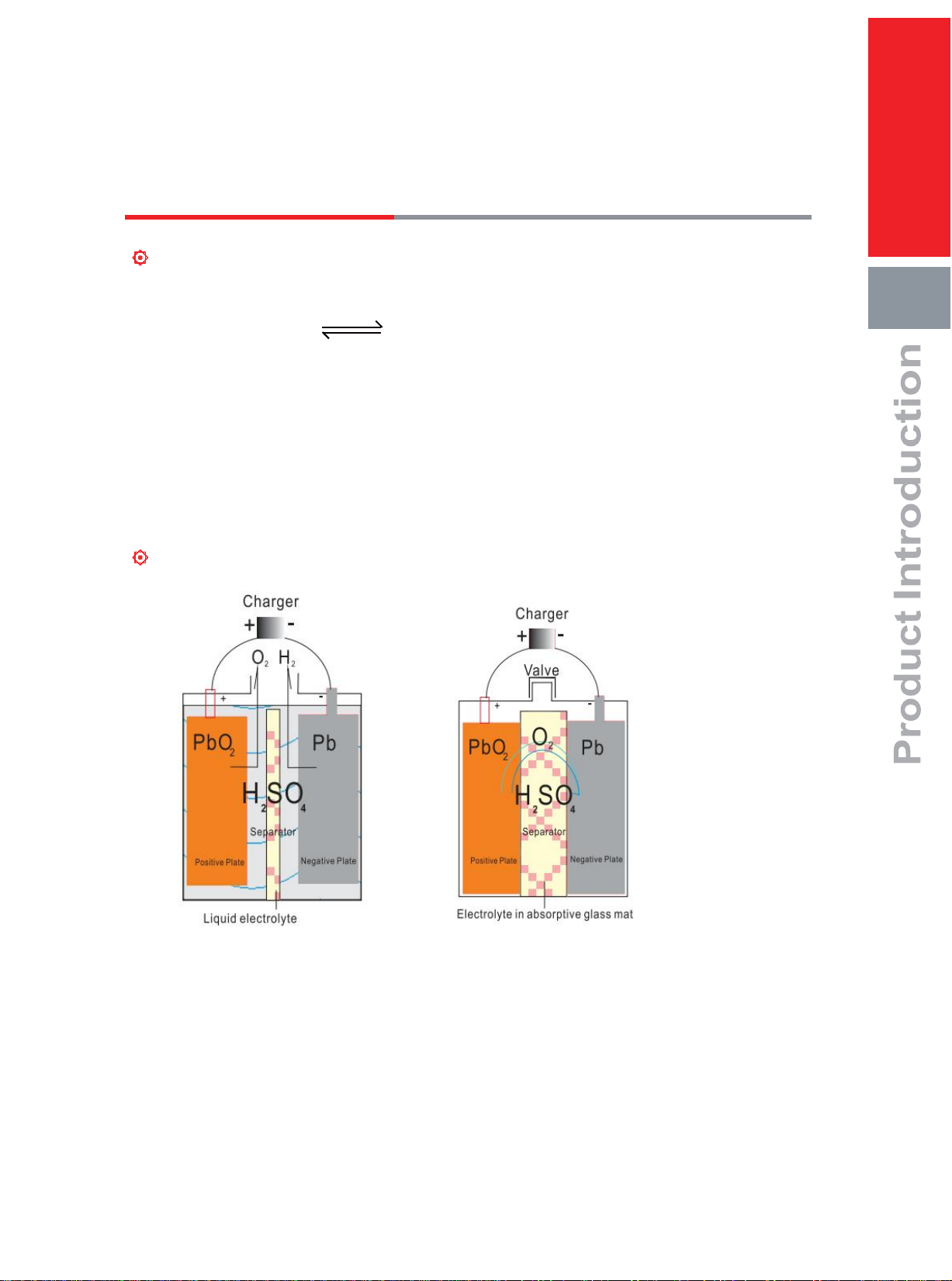
5. VRLA Technology ........................................................................................................05
Chapter II: Electrical Characteristics
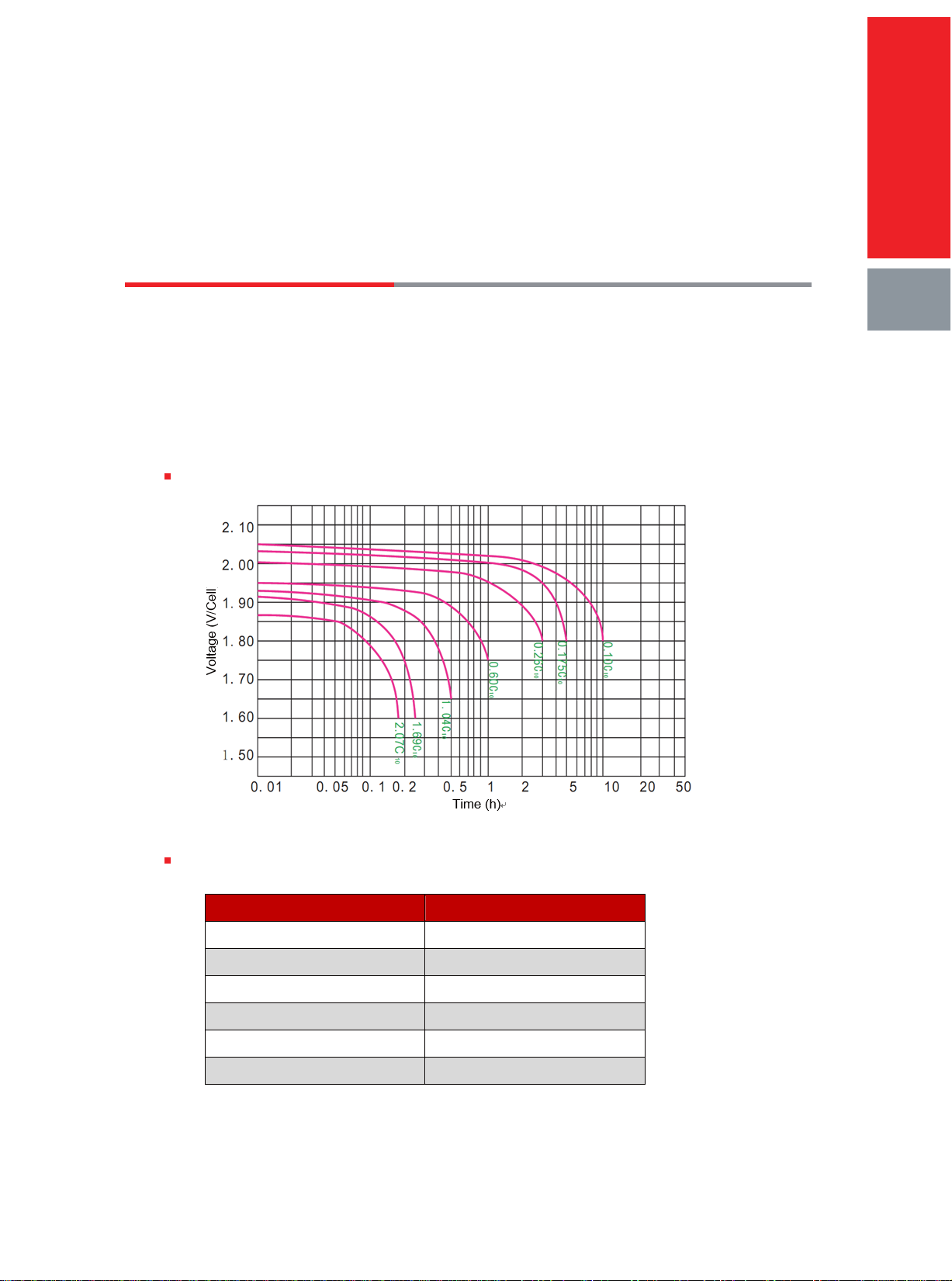
1. Discharge Characteristic Curve ...................................................................................06
2. Charge Characteristic Curve .......................................................................................07
3. Performance Data........................................................................................................08
Chapter III: Operation and Maintenance
1. Security Instruction ......................................................................................................12
2. Operation Parameters .................................................................................................13
3. Factors Influencing Capacity .........................................................................15
4. Temperature Effect On Battery Capacity .........................................................15
5. Temperature and Floating/Equalizing Charge Voltage ........................................16
6. Temperature Effect on Battery Service Life ......................................................17
7. Charge Requirement ..................................................................................17
8. Storage ....................................................................................................19
9. Maintenance .............................................................................................19