Samsung Electronics1-2
1-1 Safety Precautions (Continued)
7. Components, parts and wiring that appear
to have overheated or that are otherwise
damaged should be replaced with parts
that meet the original specifications.
Always determine the cause of damage or
overheating, and correct any potential
hazards
8. Observe the original lead dress, especially
near the following areas: Antenna
wiring, sharp edges, and especially the
AC and high voltage power supplies.
Always inspect for pinched, out-of-place,
or frayed wiring. Do not change the
spacing between components and the
printed circuit board. Check the AC
power cord for damage. Make sure that
no wires or components touch thermally
hot parts.
9. Product Safety Notice:
Some electrical and mechanical parts
have special safety-related characteristics
which might not be obvious from visual
inspection. These safety features and the
protection they give might be lost if the
replacement component differs from the
original--even if the replacement is rated
for higher voltage, wattage, etc.
10 Components that are critical for safety are
indicated in the circuit diagram by
shading, or . Use replacement
components that have the same ratings,
especially for flame resistance and
dielectric strength specifications. A
replacement part that does not have the
same safety characteristics as the original
might create shock, fire or other hazards.
1-2 Servicing Precautions
1. Servicing precautions are printed on the
cabinet. Follow them.
2. Always unplug the unit's AC power cord
from the AC power source before
attempting to: (a) Remove or reinstall any
component or assembly, (b) Disconnect an
electrical plug or connector, (c) Connect a
test component in parallel with an
electrolytic capacitor.
3. Some components are raised above the
printed circuit board for safety. An
insulation tube or tape is sometimes used.
The internal wiring may be clamped to
prevent contact with thermally hot
components. Reinstall all such elements to
their original position.
4. After servicing, always check that the
screws, components and wiring have been
correctly reinstalled. Make sure that the
portion around the serviced part has not
been damaged.
5. Check the insulation between the blades of
the AC plug and accessible conductive parts
(examples: metal panels, input terminals
and earphone jacks).
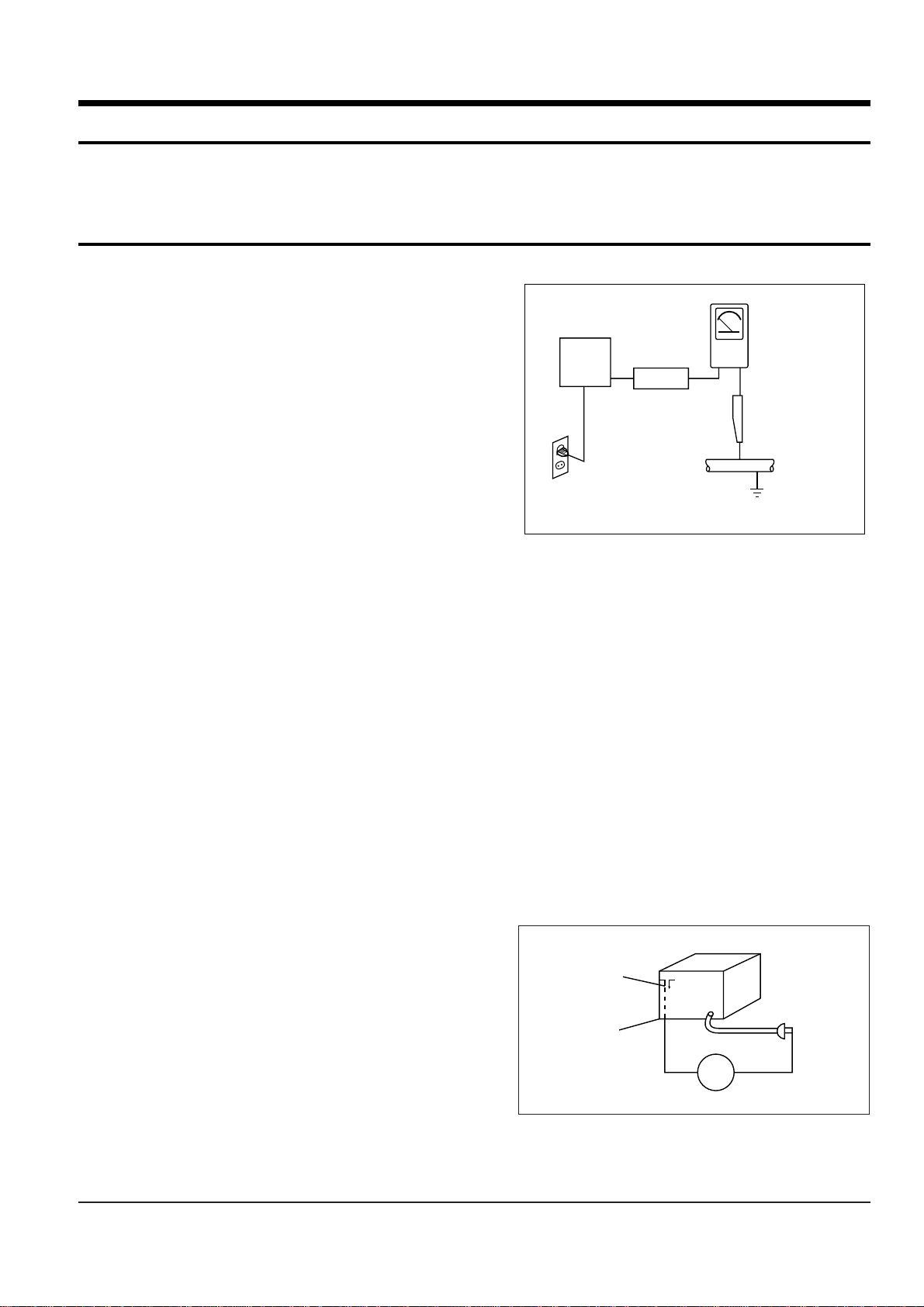
6. Insulation Checking Procedure: Disconnect
the power cord from the AC source and
turn the power switch ON. Connect an
insulation resistance meter (500V) to the
blades of the AC plug.
The insulation resistance between each
blade of the AC plug and accessible
conductive parts (see above) should be
greater than 1 megohm.
7. Never defeat any of the B+ voltage
interlocks. Do not apply AC power to the
unit (or any of its assemblies) unless all
solid-state heat sinks are correctly installed.
8. Always connect a test instrument's ground
lead to the instrument chassis ground
before connecting the positive lead; always
remove the instrument's ground lead last.
Precautions
Warning1: First read the "Safety Precautions" section of this manual. If some unforeseen circumstance creates a conflict
between the servicing and safety precautions, always follow the safety precautions.