SICO SGH10 User manual

153/20
SGH10 / SGH10L
Absolute wire-actuated encoder with CANopen
interface
User manual

General Information
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 2 of 57
Table of contents
1General Information .................................................................................................. 5
1.1 Documentation ........................................................................................... 5
1.2 Definitions ................................................................................................. 5
2Intended use............................................................................................................. 5
2.1 Switching on the supply voltage .................................................................... 5
3Functional description ............................................................................................... 6
3.1 Counting direction....................................................................................... 6
3.2 Calibration ................................................................................................. 6
3.3 Reset to factory settings............................................................................... 6
4Communication via CAN bus (CANopen) ...................................................................... 6
4.1 Frame structure........................................................................................... 6
4.2 Node control .............................................................................................. 8
4.2.1 Network management (NMT) services .......................................................................8
4.2.1.1 NMT communication states .................................................................................9
4.2.1.2 Toggling between the NMT communication statuses ...............................................9
4.2.2 Boot-Up.............................................................................................................10
4.2.3 SYNC object........................................................................................................10
4.3 Process data exchange ................................................................................10
4.3.1 Transmission of process data objects (PDO) ............................................................10
4.3.1.1 Transmit PDO (from the SGH10 / SGH10L to the master) .......................................10
4.4 Parameter data exchange.............................................................................11
4.4.1 Transmission of Service Data Objects (SDO).............................................................11
4.4.1.1 Expedited Request/Response .............................................................................12
4.4.1.2 Normal Request/Response.................................................................................13
4.4.1.3 Error Response in SDO exchange ........................................................................14
4.4.1.4 SDO examples .................................................................................................14
4.5 Node monitoring ........................................................................................16
4.5.1 Emergency Service (EMCY) ....................................................................................16
4.5.2 Node Guarding....................................................................................................17
4.5.3 Heartbeat ..........................................................................................................18
4.6 Layer Setting Service (LSS) ..........................................................................18
4.6.1 State change ......................................................................................................19
4.6.1.1 Switch states of all LSS devices (Switch state global) ...........................................19
4.6.1.2 Switch states of individual LSS devices (Switch state selective)..............................20
4.6.2 Configuration .....................................................................................................20
4.6.2.1 Setting the node ID (Configure Node-ID) ............................................................20
4.6.2.2 Configuration of the baud rate (Configure bit timing parameters)...........................21
4.6.2.3 Activate baud rate (Activate bit timing parameters) .............................................22
4.6.2.4 Store configuration..........................................................................................23
4.6.3 Requesting parameters.........................................................................................23

General Information
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 3 of 57
4.6.3.1 Request Vendor ID ...........................................................................................24
4.6.3.2 Request Product Code.......................................................................................24
4.6.3.3 Request revision number...................................................................................24
4.6.3.4 Request serial number ......................................................................................25
4.6.3.5 Request Node ID..............................................................................................25
4.7 Directory of objects ....................................................................................25
4.7.1 Overview of objects .............................................................................................25
4.7.2 Object description...............................................................................................27
4.7.2.1 1000h: Device Type..........................................................................................27
4.7.2.2 1001h: Error Register .......................................................................................28
4.7.2.3 1002h: Manufacturer Status Register ..................................................................28
4.7.2.4 1003h: Pre-defined Error Field...........................................................................28
4.7.2.5 1005h: COB-ID SYNC-message............................................................................29
4.7.2.6 1008h: Manufacturer Device Name .....................................................................30
4.7.2.7 1009h: Manufacturer Hardware Version ...............................................................30
4.7.2.8 100Ah: Manufacturer Software Version................................................................30
4.7.2.9 100Ch: Guard Time...........................................................................................31
4.7.2.10 100Dh: Life Time Factor....................................................................................31
4.7.2.11 1010h: Store Parameter....................................................................................31
4.7.2.12 1011h: Restore Parameter.................................................................................33
4.7.2.13 1014h: COB-ID Emergency message ....................................................................36
4.7.2.14 1017h: Producer Heartbeat Time........................................................................36
4.7.2.15 1018h: Identity Object.....................................................................................37
4.7.2.16 1200h: Server SDO Parameter ............................................................................38
4.7.2.17 1800h: 1st Transmit PDO Parameter.....................................................................39
4.7.2.18 1801h: 2nd Transmit PDO Parameter ....................................................................40
4.7.2.19 1A00h: 1st Transmit PDO Mapping Parameter........................................................42
4.7.2.20 1A01h: 2nd Transmit PDO Mapping Parameter .......................................................42
4.7.2.21 5000h: Diagnosis CAN Bus error.........................................................................43
4.7.2.22 5F0Ah: Node-ID and baud rate of Bus CAN ..........................................................44
4.7.2.23 6000h: Operating Parameters ............................................................................45
4.7.2.24 6002h: Overall number of measurement steps ......................................................45
4.7.2.25 6003h: Preset value (calibration value)...............................................................45
4.7.2.26 6004h: Position value ......................................................................................46
4.7.2.27 6005h: Resolution ...........................................................................................46
4.7.2.28 6010h: Calibration value...................................................................................47
4.7.2.29 6020h: Position value ......................................................................................47
4.7.2.30 6030h: Velocity...............................................................................................48
4.7.2.31 6200h: Cycle timer...........................................................................................48
4.7.2.32 6400h: Operating range (Area state register).......................................................49
4.7.2.33 6401h: Work Area Low Limit..............................................................................50
4.7.2.34 6402h: Work Area High Limit ............................................................................50
4.7.2.35 6500h: Operating Status...................................................................................51
4.7.2.36 6501h: Single-turn resolution............................................................................52

General Information
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 4 of 57
4.7.2.37 6502h: Number of distinguishable revolutions .....................................................52
4.7.2.38 6503h: Alarms.................................................................................................52
4.7.2.39 6504h: Supported Alarms..................................................................................53
4.7.2.40 6505h: Warnings .............................................................................................53
4.7.2.41 6506h: Supported Warnings ..............................................................................53
4.7.2.42 6507h: Profile and Software Version...................................................................54
4.7.2.43 6508h: Operating Time.....................................................................................54
4.7.2.44 6509h: Offset value .........................................................................................54
4.7.2.45 650Ah: Module Identification............................................................................55
4.7.2.46 650Bh: Serial number.......................................................................................56
4.7.2.47 650Ch: Offset value for the multi-sensor device ...................................................56

General Information
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 5 of 57
1General Information
1.1 Documentation
The following documents are associated with this product:
Data sheet; it describes the technical data, the dimensions, the pin assignment, the
accessories and the order key.
Mounting instructions, they describe the mechanical and electrical installation with all
safety-relevant conditions and the associated technical specifications.
User manual; for commissioning the sensor and integrating it into a fieldbus system.
EDS file (electronic data sheet); this file enables integration and configuration in a
CANopen network by means of standard CANopen configurators.
You can also download these documents at http://www.siko-global.com/p/sgh10 and
http://www.siko-global.com/p/sgh10l.
1.2 Definitions
Decimal values are given as numbers without addition (e. g. 1234), except when indicated in
direct connection with binary or hexadecimal values in which case the extension d will be
used (e. g. 1234d). Binary values are identified by adding b (e. g. 1011b) to the figures
whereas hexadecimal values are extended by h (e. g. 280h).
2Intended use
The SGH10 / SGH10L captures the travel of a hydraulic cylinder as an absolute distance
information. By means of the CANopen protocol, the wire-actuated encoder can be configured
and read out via the CAN interface.
2.1 Switching on the supply voltage
The SGH10 / SGH10L initializes after being switched on. The configuration parameters are
loaded from the non-volatile memory to the RAM of the controller.
The sensor will work with its default values as long as no changes have been made to it. With
parameters changed, the sensor will work with the changed data, which must be stored if they
are intended to be used after power off/on.
After completing the initialization procedure, a specific NMT command, the boot-up message
is sent, which informs the system about availability. The SGH10 / SGH10L is now in the pre-
operational mode. In this state, the encoder can be parameterized via SDO commands in
accordance with the requirements of the application. This applies to configuration parameters
of the sensor unit as well as to the way it makes available to the system its position values
(asynchronous or synchronous data transmission).

Functional description
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 6 of 57
3Functional description
3.1 Counting direction
The encoder provides ascending position values. This property can be changed via Object
6000h: Operating Parameters.
3.2 Calibration
Owing to the absolute system, calibration is required only once when the system is taken into
operation and can be performed at any position. This enables alignment of the encoder zero
point with the system’s mechanical zero point. With calibration, the calibration value is
adopted for calculation of the position value. The resulting offset value is output in Object
6509h: Offset value. The following equation is applied in case of calibration:
Position value = 0 + calibration value
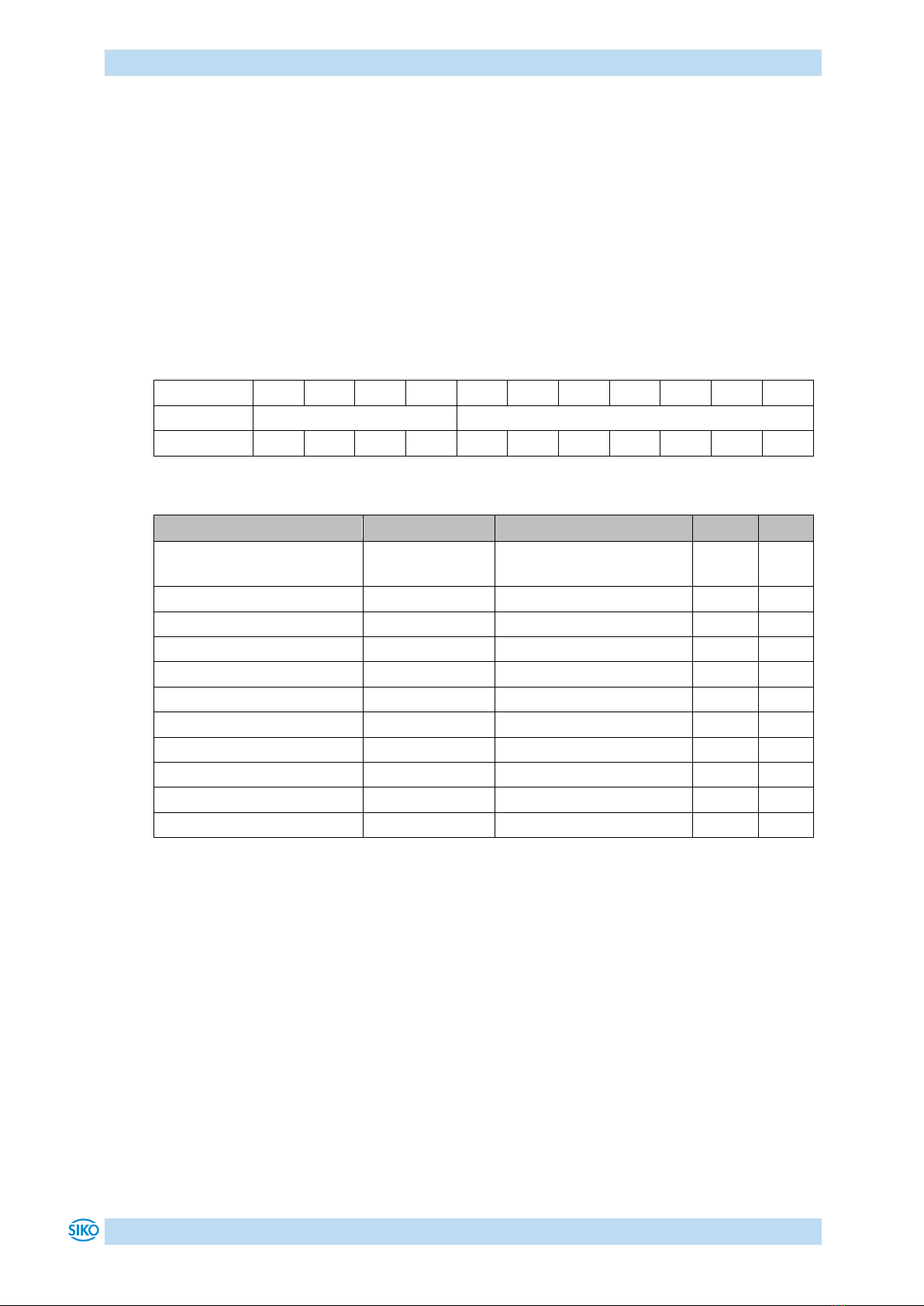
3.3 Reset to factory settings
To return to the original condition of the device as delivered, there exist the following
options:
Access
Coding
Settings are restored
CANopen (see
Object 1011h:
Restore Parameter)
1011h
"load"
Subindex 1
All parameters
Subindex 2
Only bus parameters
Subindex 3
Only CiA DS-406 parameters
Subindex 4
Only manufacturer-specific parameters
Table 1: Access to factory settings
4Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
The CiA DS-301 V4.2 CANopen communication profile, the Device profile for Encoders CiA DS-
406 V3.2, forms the basis of the SGH10 / SGH10L. The SGH10 / SGH10L supports device class
C2. The details required for a better understanding of operation are included in this
documentation. If more in-depth information is required, we recommend the applicable
technical literature on CAN or CANopen.
4.1 Frame structure
The data frame of a CAN message consists of the following fields:
SOF
Identifier (COB-ID)
Control field
Data field (max. 8 byte)
CRC
ACK/EOF
SOF:
(Start of Frame) start bit of the frame
Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 7 of 57
Identifier (COB-ID):
By means of the identifier, all bus subscribers check whether the message is relevant for
them.
The identifier determines the priority of the message. The lower the value of the identifier,
the higher is the priority of the message This enables preferential transmission of
important messages via the bus.
The Identifier field contains the identifier as well as bits for the recognition of the length of
the identifiers (11 or 29 bits). The device address, channel selection as well as data direction
are determined via the identifier as well.
Thus, the 11bit identifier (COB identifier) consists of a 4bit functional code and a 7bit node
number.
Bit no.
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Type
Functional code
Node number (Node ID)
Assignment
x
x
x
x
0
0
x
x
x
x
X
The following functional codes have been defined in the "Pre-defined Connection Set" (only
the functional codes used in the present device are shown):
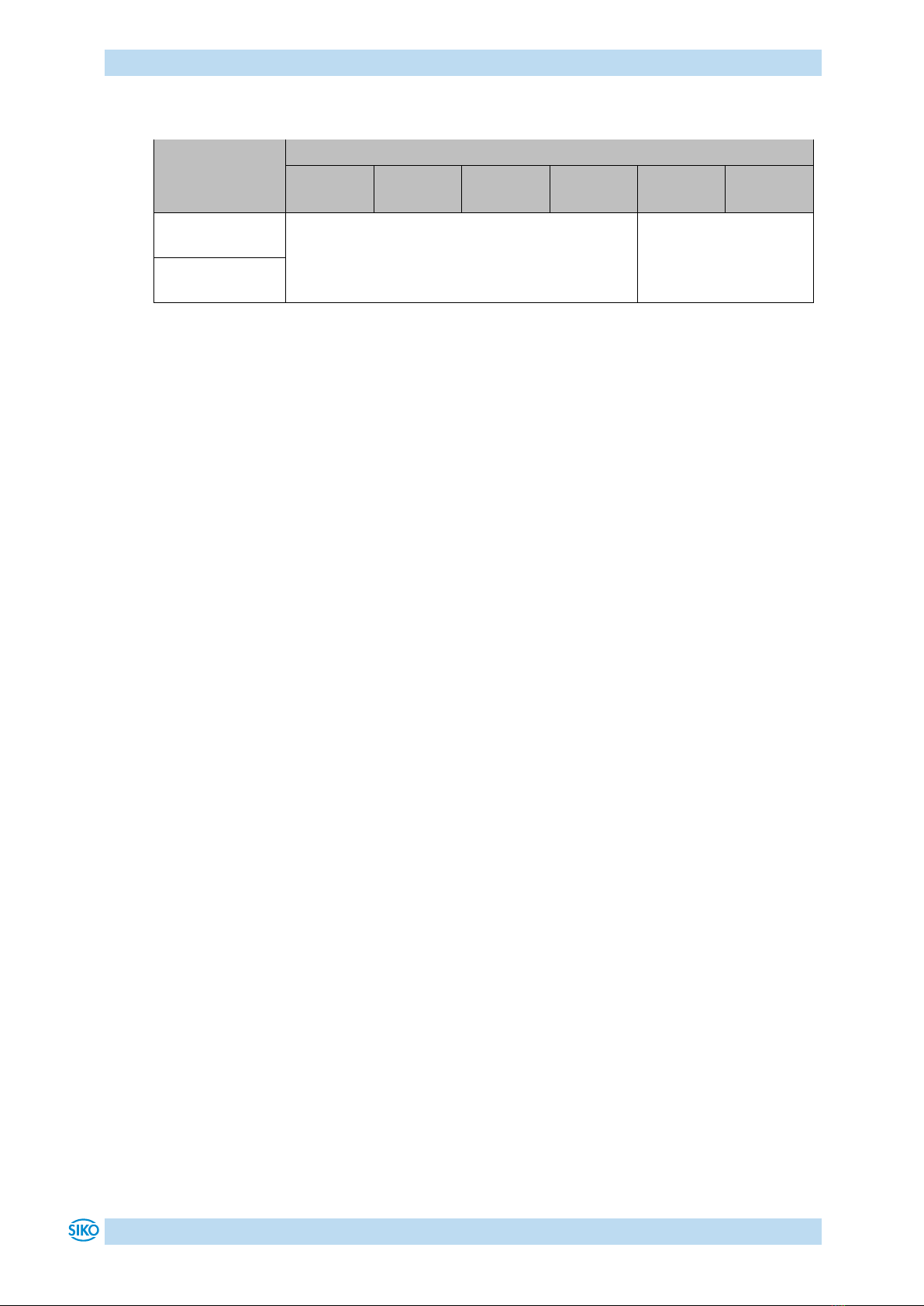
Object
Functional code
Resulting COB-ID
Object
Page
Network management
(NMT)
0000b
0
-
8
SYNC message
0001b
128d (80h)
1005h
29
Emergency message
0001b
128d (80h) + Node-ID
1014h
36
TPD01
0011b
384d (180h) + Node-ID
1800h
39
TPD02
0101b
640d (280h) + Node-ID
1801h
40
SDO (tx)
1011b
1408d (580h) + Node-ID
1200h
38
SDO (rx)
1100b
1536d (600h) + Node-ID
1200h
38
Heartbeat message
1110b
1792d (700h) + Node-ID
-
18
Node Guard message
1110b
1792d (700h) + Node-ID
-
17
LSS (tx)
-
2021d (7E4h)
-
18
LSS (rx)
-
2020d (7E5h)
-
18
Table 2: Overview of COB identifiers
Changes to COB IDs are only possible in the PRE-OPERATIONAL NMT status. First, the COB ID
must be switched invalid via bit 31 = 1b before it can be changed and reactivated.
The COB ID of the Sync object is an exception, where bit 30 must be = 0b to enable the COB
ID to be changed. Since bit 30 cannot be set to 1b, the COB ID could be changed at any time.
The node number (Node ID) (see also object 5F0Ah: Node-ID and baud rate of Bus CAN) is
assigned once in every bus system with configuration of the master on SGH10 / SGH10L. The
node numbers range from 1 to 127. Node ID = 0 is reserved and must not be used.
The adoption of a node ID or baud rate which was reset occurs only after re-initialization (see
chapter 4.2.1: Network management (NMT) services).
Ex works, the SGH10 / SGH10L wire-actuated encoder is delivered with node number 1 (1h).

Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 8 of 57
Control field:
contains bit-by-bit information concerning the number of user data and determines whether a
data frame or Remote Transmission Request (RTR) frame is concerned.
Data field:
contains up to 8 bytes of user data. The user data has a different meaning depending on the
channel selection.
CRC:
contains bits for error detection.
ACK/EOF:
The ACK/EOF field contains frame acknowledgment bits as well as bits for determining the end
of frame.
For a detailed description of the frame please refer to the applicable technical CAN literature.
For simplification, only identifier (COB ID) and data field will be dealt with in the subsequent
frame descriptions.
4.2 Node control
4.2.1 Network management (NMT) services
The master configures, manages and monitors network nodes via the NMT service. The device
is always in one of the four communication states "INITIALISATION", "PRE-OPERATIONAL",
"OPERATIONAL" or "STOPPED" (see Fig. 1).
Power on oder Software Reset
Initialisation
CAN-Kommunikation
BootUp Message
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
4
1
Re-Initialisierung
CAN-Karte
5
55
Init
Fig. 1: NMT Status diagram

Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 9 of 57
4.2.1.1 NMT communication states
NMT Status 'INITIALISATION'
The device is not involved in the bus actions in this state. All hardware and software
components are initialized. This state is attained after switching on the device or after receipt
of the command code 81h ("Reset node") of the own or global addresses. Following receipt of
the command code 82h ("Reset Communication"), the display will enter the initialization
stage as well. But only hardware and software associated with CAN communication will be
reinitialized. The device signals automatically the completion of initialization by sending a
boot-up message. As soon as the boot-up message was sent successfully, the device will enter
the "PRE-OPERATIONAL" status.
NMT Status PRE-OPERATIONAL
Parameterization data (SDO) can be exchanged in the pre-operational mode. However, no
process data (PDO's) is transmitted.
NMT Status OPERATIONAL
The exchange of process data is enabled as well. However, COB-ID and Transmit PDO Mapping
parameters can no longer be changed in this state.
NMT Status STOPPED
Communication is stopped except for heartbeat and node guarding. Only NMT communication
is enabled.
4.2.1.2 Toggling between the NMT communication statuses
For toggling between the communication statuses, frames with the following structures are
used:
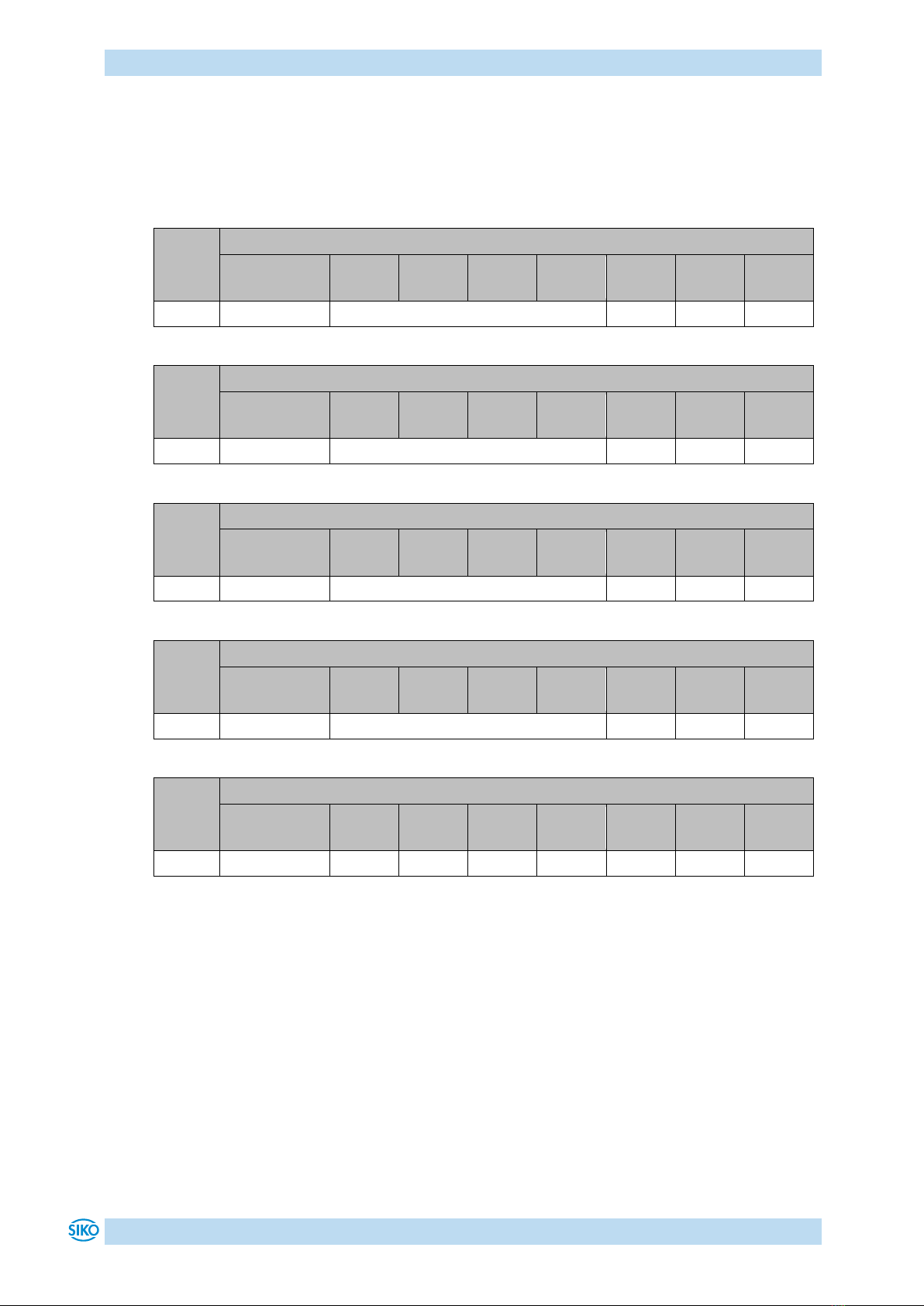
Change of state
Transition
in Fig. 1
COB-
ID
Com-
mand
Node
ID
from
to
PRE-OPERATIONAL /
STOPPED
OPERATIONAL
1d
0h
01h
x
OPERATIONAL/ PRE-
OPERATIONAL
STOPPED
2d
0h
02h
x
OPERATIONAL / STOPPED
PRE-OPERATIONAL
3d
0h
80h
x
OPERATIONAL / PRE-
OPERATIONAL / STOPPED
INITIALISATION
(Reset Node)
5d
0h
81h
x
OPERATIONAL / PRE-
OPERATIONAL / STOPPED
INITIALISATION
(Reset
Communication)
4d
0h
82h
x
Table 3: Toggling between communication states
If x = 0h is transmitted as node ID, then the message is intended for all bus subscribers.

Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 10 of 57
4.2.2 Boot-Up
The COB ID of the boot-up message is made up of 700h and the node ID. The "Initialization"
NMT status is output as data content.
COB-ID
Byte 0
700h + Node-ID
00h
Table 4: Boot-Up message
4.2.3 SYNC object
CANopen enables the simultaneous query of all inputs and the simultaneous setting of all
outputs. The synchronization message (SYNC), a CAN message with high priority serves this
purpose. The identifier of the Sync object can be set via object 1005h (see 1005h: COB-ID
SYNC-message).
4.3 Process data exchange
4.3.1 Transmission of process data objects (PDO)
Process data objects (PDO) serve for fast exchange of process data. A maximum of 8 bytes of
user data can be transmitted in a PDO. The SGH10 / SGH10L supports the Transmit PDO
services TPDO1 and TPDO2 according to CiA DS-301 and CiA DS-406.
4.3.1.1 Transmit PDO (from the SGH10 / SGH10L to the master)
PDO transmission from the display to the bus master (TPDO) can be initiated as a result of
various events:
asynchronous, controlled by an internal device timer
synchronous as a response to a SYNC message
as a response to an RTR message
TPDO1 and TPDO2 are generated from the position value and the speed value. The
transmission behavior of TPDO1 is determined via the objects 1800h, 1A00h and 6200h and is
assigned to asynchronous transmission. TPDO2 is defined via the objects 1801h and 1A01h
and serves synchronous transmission. Assignment is static and cannot be changed.
Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 11 of 57
The messages are structured as shown below.
COB-ID
Process data in binary code
Byte 0
(LSB)
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
(MSB)
Byte 4
(LSB)
Byte 5
(MSB)
TPDO1
180h + Node-ID
Position value
Velocity value
TPDO2
280h + Node-ID
Table 5: TPDO message
Asynchronous data transmission (TPDO1)
If a TPDO1 is to be sent cyclically, then the cycle time must be entered in milliseconds into
object 1800h, subindex 05h. The TPDO1 will not be sent if the value 0 ms is written. The
function is disabled. The minimum value to be set is 1 (= 1 ms). Alternately, the value can
also be written into the permanently internally linked object 6200h.
Synchronous data transmission (TPDO2)
As delivered, the device responds to every SYNC Message received with the output of the
TPDO2 message. 1h is entered for synchronous transmission in object 1801h, subindex 02h. If
a value n is entered between 1d and 240d (= F0h), the device will respond to every nth SYNC
message.
RTR
Queries can be sent via RTR (see chapter 4.1: Frame structure, control field) toTPDO1 and
TDPO2.
4.4 Parameter data exchange
4.4.1 Transmission of Service Data Objects (SDO)
Service data objects serve mainly device configuration via the directory of objects. SDOs in
the expedited Request/Response and in the normal Request/Response are supported.
The identifier is set to 11 bits and cannot be changed.
Two SDO services are available:
SDO (rx) (Master SGH10 / SGH10L): 600h + Node-ID
SDO (tx) (SGH10 / SGH10L Master): 580h + Node-ID
These SDO identifiers cannot be changed!

Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 12 of 57
4.4.1.1 Expedited Request/Response
Except for reading the object 1008h: Manufacturer Device Name, all SDOs are exchanged
between two subscribers in the expedited Request/Response method. The user data is
provided already with the initialization message.
These SDO messages are set up as follows:
COB-ID
User data in binary code
Byte
0(read /
write)
Byte 1
LSB
Byte 2
(MSB)
Byte 3
Byte 4
LSB
Byte 5
Byte 6
Byte 7
(MSB)
SDO rx/tx
+ Node-ID
Command
byte
Index
Subindex
User data (parameter)
Command byte, byte 0:
The command byte determines the type of access and the number of valid data bytes. The
following command bytes are valid for the SGH10 / SGH10L:
Command byte
Type
Function
Write Request
23h
SDO (rx), Initiate Download
Request, expedited
Send parameter to slave
(All 4 data bytes valid)
Write Request
2Bh
SDO (rx), Initiate Download
Request, expedited
Send parameter to slave
(2Bytes of 4 data bytes valid)
Write Request
2Fh
SDO (rx), Initiate Download
Request, expedited
Send parameter to slave
(1Byte of 4 data bytes valid)
Write Response
60h
SDO (tx), Initiate Download
Response
Acknowledgment of data
acquisition to master
Read Request
40h
SDO (rx), Initiate Upload
Request
Request parameter from slave
Read Response
43h
SDO (tx), Initiate Upload
Response, expedited
Report parameter to master
(All 4 data bytes valid)
Read Response
4Bh
SDO (tx), Initiate Upload
Response, expedited
Report parameter to master
(2Bytes of 4 data bytes valid)
Read Response
4Fh
SDO (tx), Initiate Upload
Response, expedited
Report parameter to master
(1Byte of 4 data bytes valid)
Error Response
80h
SDO (tx), Abort Domain
Transmission
Slave reports error code to master
Table 6: Command coding
Index, bytes 1 and 2:
The index (object number) is entered in the user data byte 2 (low byte) and user data byte 3
(high byte) in the Intel data format. Here, the index of the object to be parameterized is
entered.
Subindex, Byte 3:
The subindex indicates the number of the fields for objects realized as an array.

Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 13 of 57
User data (parameters), byte 4-7:
In the user data, the value of the parameter is entered in left-aligned Intel notation. Byte 4 =
Low-Byte ... Byte 7 = High-Byte.
4.4.1.2 Normal Request/Response
If more than 4 bytes of service data are to be transmitted, the data is exchanged between two
subscribers via the normal Request/Response. This procedure is also initiated by an
initialization message, and the actual user data will be transmitted in the subsequent
segment messages.
For the SGH10 / SGH10L this is only the case with reading of the object 1008h: Manufacturer
Device Name.
The initialization message has the following structure:
COB-ID
User data in binary code
Byte
0(read /
write)
Byte 1
LSB
Byte 2
(MSB)
Byte 3
Byte 4
LSB
Byte 5
Byte 6
Byte 7
(MSB)
SDO rx/tx
+ Node-ID
Command
byte
Index
Subindex
User data (number of user data)
The segment message has the following structure:
COB-ID
User data in binary code
Byte
0(read /
write)
Byte 1
LSB
Byte 2
Byte 3
Byte 4
Byte 5
Byte 6
Byte 7
(MSB)
SDO rx/tx
+ Node-ID
Command
byte
User data
Initialization and segment message: Command byte, byte 0:
The command byte determines the type of access and the number of valid data bytes. The
following command bytes are valid for the encoder:
Command byte
Type
Function
Read Request
40h
SDO (rx), Normal Initiate
Upload Request
Request parameter from slave
(number of bytes to be
transmitted).
Read Request
60h
SDO (rx), Normal Segment
Upload Request
Request parameter from slave
(user data)
Read Response
41h
SDO (tx), Normal Initiate
Upload Response
Report parameter to master
(number of bytes to be
transmitted).
Read Response
03h
SDO (tx), Normal Segment
Upload Response
Report parameter to master (user
data)
Error Response
80h
SDO (tx), Abort Domain
Transmission
Slave reports error code to master
Table 7: Command coding

Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 14 of 57
Initialization message: Index, bytes 1 and 2:
The index (object number) is entered in the user data byte 2 (low byte) and in the user data
byte 3 (high byte) in the Intel data format. Here, the index of the object to be parameterized
is entered.
Initialization message: Subindex, byte 3:
The subindex indicates the number of the fields for objects which are realized as an array.
Initialization message: User data (parameters), byte 4-7:
In the service data range, the value of the parameter is entered in left-aligned Intel notation.
Byte 4 = Low-Byte ... Byte 7 = High-Byte.
Segment message: User data (parameters), byte 1-7:
In the user data range, the value of the parameter is entered in left-aligned Intel notation.
Byte 1 = Low-Byte ... Byte 7 = High-Byte.
4.4.1.3 Error Response in SDO exchange
With invalid access, an error message (Abort) is returned to the master.
The error codes are described in the CANopen profile (CiA DS-301) or in the encoder profile
(CiA DS- 406), respectively. The table below shows the error codes used:
Error code
Description
05030000h
Toggle bit in Normal Transmission of Request/Response unequal.
06010000h
Wrong access to an object.
06010001h
Read access to Write-Only
06010002h
Write access to Read-Only.
06020000h
Object doesn't exist in the object directory.
06090011h
Subindex does not exist
06090030h
Wrong value range of selected parameter.
08000020h
Parameters cannot be transmitted to application or stored.
08000022h
Parameters cannot be transmitted to application or stored due to the
current device status.
08000024h
No data available
Table 8: Error codes
4.4.1.4 SDO examples
Example of reading SDO parameters with the expedited Request/Response:
The calibration value stored in object 6010h subindex 01h of the directory of objects is to be
read from the slave with device address 1h.
Calculation of the identifier: 600h + Node-ID = 600h +1h = 601h

Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 15 of 57
Command: 40h
Index: 6010h
Subindex: 01h
The current value is 510d = 01FEh
Request of master from slave with node ID 1h:
COB-
ID
User data
Command
Index L
Index H
Subindex
Data
0
Data
1
Data
2
Data
3
601h
40h
10h
60h
01h
x
x
x
x
Response to the request by the slave
Calculation of the identifier: 580h + Node-ID = 581h
COB-
ID
User data
Command
Index
LB
Index
HB
Subindex
Data
0
Data
1
Data
2
Data
3
581h
43h
(4 bytes
valid)
10h
60h
01h
FEh
01h
00h
00h
Example of writing SDO parameters with the expedited Request/Response:
The calibration value stored with 2 bytes in object 6002 of the directory of objects is to be
changed in the slave with device address 1h.
Calculation of the identifier: 600h + Node-ID = 600h + 1h = 601h
Command: 2 bytes are to be written 2Bh
Index: 6200h
Subindex: 00h
The new value shall be 4500d = 1194h
Writing of a value from master to slave with node ID 1h:
COB-
ID
User data
Command
Index L
Index H
Subindex
Data
0
Data
1
Data
2
Data
3
601h
2Bh
(2 bytes
valid)
00h
62h
00h
94h
11h
00h
00h
Response to the command by the slave:
Calculation of the identifier: 580h + Node-ID = 580h + 1h = 581h
COB-
ID
User data
Command
Index L
Index H
Subindex
Data
0
Data
1
Data
2
Data
3
581h
60h
00h
62h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
Example of reading SDO parameters with normal Request/Response:
The manufacturer device name stored in object 1008h of the directory of objects is to be read
from the SGH10 / SGH10L with device address 1h.

Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 16 of 57
Calculation of the identifier: 600h + Node-ID = 600h +1h = 601h
Command: 40h
Index: 1008h
Subindex: 00h
First request (= initialization) of master from slave with node ID 1h:
COB-
ID
User data
Command
Index L
Index H
Subindex
Data
0
Data
1
Data
2
Data
3
601h
40h
08h
10h
00h
x
x
x
x
Response to the request by the slave
Calculation of the identifier: 580h + Node-ID = 581h
COB-
ID
User data
Command
Index
LB
Index
HB
Subindex
Data
0
Data
1
Data
2
Data
3
581h
41h
08h
10h
00h
05h
00h
00h
00h
Number of expected user data bytes: 5
Second request of master from slave with node ID 1h:
COB-
ID
User data
Command
Index L
Index H
Subindex
Data
0
Data
1
Data
2
Data
3
601h
60h
08h
10h
00h
x
x
x
x
Response to the request by the slave
COB-
ID
User data
Command
Data 0
Data 1
Data 2
Data 3
Data 4
Data 5
Data 6
581h
03h
53h
("S")
47h
("G")
48h
("H")
31h
("1")
30h
("0")
00h
-
00h
-
4.5 Node monitoring
4.5.1 Emergency Service (EMCY)
In the case of an error, the status of the bus subscriber is transmitted via high-priority
emergency messages (emergency frames). These messages have a data length of 8 bytes and
contain error information.
The emergency message is transmitted as soon as a sensor or communication error has
occurred or when such errors have been corrected. The cause of the error is deposited in the
error buffer (see object 1003h: Pre-defined Error Field). An emergency object is sent only once
per error event. Removal of the cause of the error is signaled by sending an emergency
message with the error code 0000h (no error). If multiple errors have occurred and one cause
of error is removed, the error code 0000h is output as well; the persisting error status is
indicated in the error register, however.

Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 17 of 57
Identifier
Byte 0
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte
3
Byte
4
Byte
5
Byte
6
Byte
7
11/ 29 Bit
Emergency Error
Code
Error Register
(Object
1001h)
Manufacturer-specific error field
(not used)
Emergency Error Code:
Error description
Error Code
Cause of the error removed
0000h
Bus status changed over to the error passive mode
8120h
Recovered from Bus Off
8140h
Manufacturer-specific: Position value error
FF05h
Manufacturer-specific: Position error work area 1
FF15h
Manufacturer-specific: Position error work area 2
FF16h
Table 9: Emergency Error Code
The identifier of the emergency object is set to 80h + node ID by default but can be changed
via object 1014h (see 1014h: COB-ID Emergency message). Transmission of an emergency
message is enabled in the NMT statuses "OPERATIONAL" or "PRE-OPERATIONAL" only.
Transmission of the emergency messages can be disabled by setting the COB-ID Valid bit to 1.
4.5.2 Node Guarding
Node guarding is available for failure monitoring of the CANopen network. During node
guarding, the master transmits remote frames (RTR, remote transmit request, message request
frames) on the guarding identifiers of the bus nodes to be monitored. The latter respond with
the guarding message. This message contains the current NMT status of the node as well as a
toggle bit whose value must change after each message. The master assumes that a node error
has occurred if status or toggle bits do not correspond with the values expected by the master
or if there is no response.
Via objects 100Ch (Guard Time) and 100Dh (Life Time Factor) the time interval (Life-Time) is
set within which the NMT master expects to receive a response. The time interval "Life Time"
is calculated from the cycle time "Guard Time", multiplied with the factor "Life Time Factor".
If the NMT master does not receive a response to its RTR frame within the "Life Time", it may
react with suitable measures. Upon switching on, node guarding will be enabled by sending
the first RTR frame of the master to the slave. Node Guarding is deactivated if the value of
either object (100Ch or 100Dh) is set to 0h.
The response of the node to the RTR frame of the master is formed as follows:
Identifier
Byte 0
700h + Node-ID
Bit 7: Toggle Bit
Bit 6 …0 NMT state
Toggle Bit:
The toggle bit must alternate between two subsequent responses of the device. After the
guarding protocol has been enabled, the toggle bit must have the value 0 with the first
response.

Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 18 of 57
NMT state:
4: STOPPED
5: OPERATIONAL
127: PRE-OPERATIONAL
The identifier of the node guarding protocol is permanently set to 700h + Node ID and cannot
be changed. A node guard message can be sent in the NMT statuses "OPERATIONAL", "PRE-
OPERATIONAL" or "STOPPED".
Note:
Literature recommends heartbeat to be used for node monitoring. Only the master can detect
missing communication via the node guarding protocol as opposed to the heartbeat that can
be received by all subscribers.
4.5.3 Heartbeat
The master monitors the state of the slave device via Heartbeat protocol. While doing this,
the device sends independently its NMT status cyclically. The SGH10 / SGH10L is a heartbeat
producer, it does not receive nor process heartbeat protocols itself. The cycle time of the
heartbeat message is set via object 1017h. The heartbeat protocol is deactivated if the cycle
time is 0h.
The heartbeat message consists of the COB ID and an additional byte. In this byte, the
current NMT state is deposited.
COB-ID
Byte 0
700h + Node-ID
NMT state
NMT state:
4: STOPPED
5: OPERATIONAL
127: PRE-OPERATIONAL
The identifier of the heartbeat protocol is permanently set to 700h + Node ID and cannot be
changed. Heartbeat messages are sent in the NMT statuses "OPERATIONAL", "PRE-
OPERATIONAL" or "STOPPED".
4.6 Layer Setting Service (LSS)
Layer Setting Service (LSS) is a special method described in CiA DS-305it serves for retrieving
and configuring various parameters (node ID, baud rate, and Identity Object 1018h).
Every device must have a unique LSS number composed of the entries in Object 1018h.
Vendor ID: 0000 0195h
Product Code: FFFF FFFFh
Revision number: FFFF FFFFh
Serial number: xxxx xxxxh (relevant serial number of the encoder)

Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 19 of 57
In order to enable the use of full LSS functionality, all devices on the bus must support the
LSS method. An LSS master must exist and all nodes must start with the same baud rate. After
starting, the device will be in the LSS waiting state. To enable configuration, one or all
devices must be switched to the LSS configuration state. If the LSS master expects to receive
an answer to its command, only one LSS slave must be switched to the LSS configuration
mode.
Two LSS services are available:
LSS (rx) (LSS master SGH10 / SGH10L): 7E5h
LSS (tx) (SGH10 / SGH10L LSS master): 7E4h
These LSS identifiers cannot be changed!
A message consists always of 8 bytes. Byte 0 contains the command (Command –Specifier
cs), followed by max. 7 data bytes. Unused data bytes are reserved and must be filled with
00h.
Services
LSS waiting
LSS configuration
Switch state global
yes
yes
Switch state selective
yes
no
Activate bit timing parameters
no
Yes, if all devices on the bus support
LSS
Configure bit timing parameters
no
yes
Configure node-ID
no
yes
Store configuration
no
yes
Request LSS address
no
yes
Request Node ID
no
yes
Table 10: State behavior of the supported LSS services
4.6.1 State change
4.6.1.1 Switch states of all LSS devices (Switch state global)
With this command, all devices on the bus can be set to the LSS Waiting or LSS Configuration
states. The LSS slave devices do not respond.
Master all LSS slaves
COB-
ID
User data
Byte 0
Command
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
Byte 4
Byte 5
Byte 6
Byte 7
7E5h
04h
Mode
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
Mode:
00h: Switch to LSS waiting state
01h: Switch to LSS configuration state
Communication via CAN bus (CANopen)
SGH10 / SGH10L Date: 09.07.2020 Art. No. 89013 Mod. status 153/20 Page 20 of 57
4.6.1.2 Switch states of individual LSS devices (Switch state selective)
With this command, individual LSS slave devices can be set to the LSS Configuration state via
the unique LSS number.
Master SGH10 / SGH10L
COB-
ID
User data
Byte 0
Command
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
Byte 4
Byte 5
Byte 6
Byte 7
7E5h
40h
Vendor ID
00h
00h
00h
COB-
ID
User data
Byte 0
Command
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
Byte 4
Byte 5
Byte 6
Byte 7
7E5h
41h
Product code
00h
00h
00h
COB-
ID
User data
Byte 0
Command
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
Byte 4
Byte 5
Byte 6
Byte 7
7E5h
42h
Revision number
00h
00h
00h
COB-
ID
User data
Byte 0
Command
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
Byte 4
Byte 5
Byte 6
Byte 7
7E5h
43h
Serial number
00h
00h
00h
SGH10 / SGH10L master
COB-
ID
User data
Byte 0
Command
Byte 1
Byte 2
Byte 3
Byte 4
Byte 5
Byte 6
Byte 7
7E4h
44h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
4.6.2 Configuration
4.6.2.1 Setting the node ID (Configure Node-ID)
The LSS master can configure the node ID of single LSS slaves switched to the configuration
mode. If the new node ID is intended to still be available after Power off/on, the "Store
configuration" command must be executed after the change. For immediate activation of the
new node ID, the LSS slave must be set to the LSS Waiting mode, followed by an NMT "Reset
Communication" 82h. Another possibility would be to execute power off/on after "Store
configuration".
Other manuals for SGH10
1
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents