SIMCom Wireless Solutions SIM8262E-M2 User manual

SIM8262E-M2 5G HAT
Features
•Based on Qualcomm platform, support 5G NSA and SA networking, support multi-mode and
multi-band
•Integrated multi-constellation system dual-frequency positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou,
Galileo and QZSS
•Support Windows / Linux / Android and other operating systems
•USB 3.1 port (USB 2.0 compatible) for connecting to PC, Raspberry Pi, or Jetson Nano host
board to enable high speed 5G communication
•Onboard M.2 B KEY slot, compatible with 5G modules such as SIM8202X-M2 / SIM8200EA-M2 /
SIM8262X-M2 series
•Onboard UART, PWR, and RST control pin, built-in voltage level translator, enabled via DIP
switch, for use with hosts like Raspberry Pi or Arduino
•Onboard USB-C connector, enabled via switch, for connecting standalone power supply for
the module, allows more loads, stable and flexible power supply
•Onboard power switch, reset button, and LED indicator, easy to switch the control module
on and off and check the running status
•Onboard 4-way SMA to IPEX antenna adapting interface, factory default welded SMA
terminals, antenna installation is more convenient
•Onboard two SIM card slots, dual-card single-standby, can be switched and enabled by AT
command
•Onboard audio interface and audio decoding chip, which can be used for voice manipulation
such as making calls
•High-efficiency power supply circuit, up to 3A output current
5G Module Parameters
SIM8200EA-M2
SIM8202G-M2
SIM8262E-M2
SIM8262A-M2
5G Standard
3GPP R15
3GPP R16

Chip solution
Qualcomm Snapdragon X55
Qualcomm Snapdragon X62
Working Band
Sub-6G
n1, n2, n3, n5, n7,
n8, n12, n20, n28,
n38, n40, n41,
n48, n66, n71, n78
n1, n2, n3, n5, n7,
n8, n12, n20, n28,
n38, n40, n41,
n66, n71, n77,
n78, n79
n1, n3, n5, n7,
n8, n20, n28,
n38, n40, n41,
n77, n78,n79
n2, n5, n7, n12,
n13, n14, n25,
n30, n41, n48,
n66, n71, n77,
n78, n79
LTE-FDD
B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B7, B8, B12, B13,
B14, B17, B18, B19, B20, B25, B26,
B28, B29, B30, B32, B66, B71
B1, B3, B5, B7,
B8, B18, B19,
B20, B26, B28,
B32
B2, B4, B5, B7,
B12, B13, B14,
B25, B26, B29,
B30, B66, B71
LTE-TDD
B34, B38, B39, B40, B41, B42, B43,
B48
B38, B39, B40,
B41, B42, B43
B41, B46, B48
WCDMA
B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B8
B1, B5, B8
B2, B4, B5
GNSS
GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, Galileo and QZSS
Data Transfer
Sub-6G
2.4 Gbps (DL) / 500 Mbps (UL)
LTE
1 Gbps (DL) / 200 Mbps (UL)
HSPA+
42 Mbps (DL) / 5.76 Mbps (UL)

Software Function
Operating
System
Windows/Linux/Android
Communication
Protocol
TCP/IP, IPV4, IPV6, Multi-PDP, FTP, FTPS, HTTP, HTTPS, MQTTS, DNS,
SSL3.0
Dial-up
RNDIS, NDIS, PPP, MBIM
Text Message
(SMS)
Support MT, MO, CB, Text, PDU
Firmware
Upgrade
Supports firmware upgrade via USB interface
Hardware Description
SIM Card
1.8V/2.95V
Antenna
Interface
for 3G/4G/5G/GNSS
6 ×IPEX-4 ports
4 ×IPEX-4 ports
Power Supply
3.135~4.4V
Outline Package
M.2

Dimensions
52.0 ×30.0 ×
2.3mm
42.0 ×30.0 ×2.3mm
Operating
Temperature
-30℃~ +70℃
Application Scenarios
Applicable Area
China, US, Japan, Korea, Europe,
Middle East, Americas
All regions
except
Americas
Americas
The applicable area is for reference only, and the appropriate module
should be selected according to the frequency band covered and
supported by the local operator's network.
Typical
Applications
CPE, smart gateway, drone, live video, telemedicine, smart security
What's On Board

Number
Name
Description
①
Raspberry Pi
GPIO header
For connecting to Raspberry Pi
②
Switch
Enable the corresponding pin
③
M.2 connector
Compatible with RM500U-CN / RM500Q-CN / RM500Q-GL
/RM50XQ-AE and other series of 5G modules
④
SIM card
holder
Onboard two SIM card slots, dual card single standby. The
default SIM1 card slot works, SIM2 is on the back, requires
module support, and must be switched through AT commands
⑤
USB3.1
interface
Backward compatible with USB 2.0, can be used to connect to
PC/Raspberry Pi/Jetson Nano, etc.
⑥
USB Type-C
connector
5V 3A input; stable and flexible power supply

⑦
Audio port
SIM82XX series support audio function, RM50XX series do not
support this audio function
⑧
Antenna
interface
Onboard four-way antenna, strong signal
⑨
Reset switch
One-key reset
⑩
Power Switch
To facilitate the power supply mode of the control module:
——If set to USB, the module will provide power through
the "⑤.USB3.1 interface";
——If set to EXT PWR, the module will provide power
through the "⑥.USB Type-C interface" external power supply
⑪
Cooling fan
Cool down the Raspberry Pi and 5G module at the same time
⑫
Indicator light
Check the module running status anytime, anywhere
1. Pinout Definition

After connecting to Raspberry Pi with a 2*20 female header, these pins (TX, RX, D4, and
D6) can be connected or not through the DIP switch:
4G/5G modules function testing
Catego
ry
4G/5G
Module
Network
Communicati
on
GNSS
Positioni
ng
Voice
calls
through
Earpho
ne Port
Dual
SIMs
UART
Interfa
ce
External
Power
Supply?
5G
SIM8202G
-M2
5G/4G/3G
Support
Support
Suppo
rt
Support
Optional,
but

recommend
ed
5G
SIM8262E
-M2
5G/4G/3G
Support
Support
Suppo
rt
Support
Optional,
but
recommend
ed
5G
SIM8200E
A-M2
5G/4G/3G
Support
Support
Suppo
rt
Support
Optional,
but
recommend
ed
5G
RM500U-
CN
5G/4G/3G
NOT
Support
NOT
Support
Suppo
rt
Support
Recommend
ed
5G
RM500Q-
GL
5G/4G/3G
Support
NOT
Support
Suppo
rt
NOT
Support
Recommend
ed
5G
RM500Q-
AE
5G/4G/3G
Support
NOT
Support
NOT
Suppo
rt
NOT
Support
Recommend
ed
5G
RM502Q-
AE
5G/4G/3G
Support
NOT
Support
NOT
Suppo
rt
NOT
Support
Recommend
ed
LTE-A
EM06-E
LTE-A/4G/3G
NOT
Support
NOT
Support
NOT
Suppo
rt
NOT
Support
Optional

LTE-A
A7906E
LTE-A/4G/3G
NOT
Support
NOT
Support
NOT
Suppo
rt
NOT
Support
Optional
4G
SIM7600G
-H-M2
4G/3G/2G
Support
Support
NOT
Suppo
rt
Support
Optional
4G/5G Module Compatibility
If you need to use the M.2 TO 4G/5G HAT for other 4G/5G modules, you can refer to the
M.2 connection diagram below, check whether there is any pin conflict, and then connect

Download a driver (Resource->Software->SIM8200 Driver) on your computer and then
unzip it.
Enter SIM8200_OS_Driver\Windows directory.
For most hosts, you can enter "1_install" directory and then click "setup.exe" to install.
After connecting, a mobile network icon will appear. You can disconnect from other
networks and test the mobile network.
3. Install Driver Manually
For some hosts, the port may not appear even if "1_install" is installed. In this case, you
need to use the files in "2_AddManully" to add them manually. The way to use it is to find
the unrecognized device in the device manager and right-click to add the driver, as
follows:
Power on the G module and turn the switch to ON, the module starts, and the computer
will recognize 4 unknown devices (maybe some boards will recognize 5 or 6), only 5 in
the picture:

Right-click the device, update the driver manually, choose SIM8200_OS_Driver\Windows,
and then choose the driver according to the version of your OS. You need to update for
all the four/five/six devices.:
Four COM ports: AT is used for AT command controlling, and Audio is used for dail up.
Diagnostics is used for debugging, and NMEA is used for GPS.

A mobile network will be set up automatically after updating, you can disconnect other
networks and test it.
4. Manual NDIS Dial-up Internet
If the above 2 steps have been done, Windows cannot access the Internet, you need to
manually start the NDIS dial-up.
Open the sim8200 AT port and send the command:
AT$QCRMCALL=1,1+Enter
After dialing is successful, as shown in the figure below, the computer can go online
normally.
At this
time, the NDIS dialing takes effect, and the computer can connect to the network; if it
returns No Carrier, it may have dialed up, and you can go online to see it directly.

5. GPS Positioning
SIM8200EA-M2 is ANT5; SIM8202G-M2 is ANT2; SIM8262E-M2 is ANT3; see the module
hardware manual for details
Connect the passive GPS antenna to the ANT5 of the module, and place the antenna
outdoors facing the sky. Then send the AT command to turn on the GPS:
AT+CGPS=1#Enter
Now open the NEMA port, you can get GPS data:

Working With Raspberry Pi
It is recommended that you use the latest system image (the latest system address) of
the Raspberry Pi, and the system's Linux kernel version 5.4. If your kernel is different, it is
recommended that you update to the same version as this one. This tutorial is based on
the 5.4 kernel, which can minimize errors.
If you are using other Linux systems, please download the driver under
SIM8200_OS_Driver\linux, and transplant it according to the document under it; you can
also use the built-in driver of the system for SIM820X RNDIS dial-up internet.
6. Configuration At The First Time
Please don't type the wrong letter, it's better to copy and paste.

sudo apt-get install p7zip-full
wget https://www.waveshare.com/w/upload/8/89/SIM8200_for_RPI.7z
7z x SIM8200_for_RPI.7z -r -o./SIM8200_for_RPI
sudo chmod 777 -R SIM8200_for_RPI
cd SIM8200_for_RPI
sudo ./install.sh
Please do not delete or modify the "option" directory, "qmi_wwan_simcom" directory,
"default.script", "install.sh" files, otherwise it will affect the loading of the driver.
If there is an error, please confirm whether the system is "2020-08-20-raspios-buster-
armhf", and take a screenshot of the error message so that engineers can help you
analyze and solve the problem.
Run "ifconfig -a" to see that "WWAN0" has been generated.

wwan0 and wwan1 can be recognized. The two network cards can be dialed at the same
time through the following commands: (The network speed cannot be superimposed)
sudo ./simcom-cm -i wwan0
sudo ./simcom-cm -i wwan1
•Note: If the IP cannot be obtained or the networking is not successful, use the
following commands to obtain the IP and set the DNS networking:
sudo dhclient -v wwan0
sudo route add -net 0.0.0.0 wwan0
•Auto-run
If you want to set the codes auto-run after booting, you can modify rc.local file:
sudo nano /etc/rc.local
Add the line to file as below:
sudo /home/pi/SIM8200-M2_5G_HAT_code/Goonline/simcom-cm &
Note that you have to add "&" to the end of the command, make sure that the command
can be run in the background, or the Pi may not boot normally.
•Live streaming with ffmpeg

If you are using the 2020-08-20-raspios-buster-armhf image, then you don't need to
install anything as the system already comes with ffmpeg.
Going straight to the topic, assuming you already have a camera and it's properly
connected to the Raspberry Pi, then proceed with the tutorial.
•The camera must be enabled by running the raspi-config command before using
it:
sudo raspi-config
Select Enable Camera, select YES
•If it is a camera using the CSI interface, the system cannot find the device node of
/dev/video0. A line for bcm2835-v4l2 needs to be added to the /etc/modules file:
sudo nano /etc/modules
add:
bcm2835-v4l2
Then after the system starts, the system will load the module name in this file and restart
the system:

sudo reboot
ls /dev/video*
The video0 device node is found below.
Note: If after performing the first steps, please confirm that the operation and
instructions are correct.
Suppose you are using Douyu Live now, register your account and enable the host
function, open Douyu Live Host Center, and find the live broadcast settings.
Open video plug flow setting:
Table of contents
Popular Computer Hardware manuals by other brands

Crestron
Crestron DSP-860 Do guide

Fujimoto
Fujimoto CP51 instruction manual

VIA Technologies
VIA Technologies ARTiGO-A1200 quick guide

Tews Technologies
Tews Technologies TMPE627 user manual
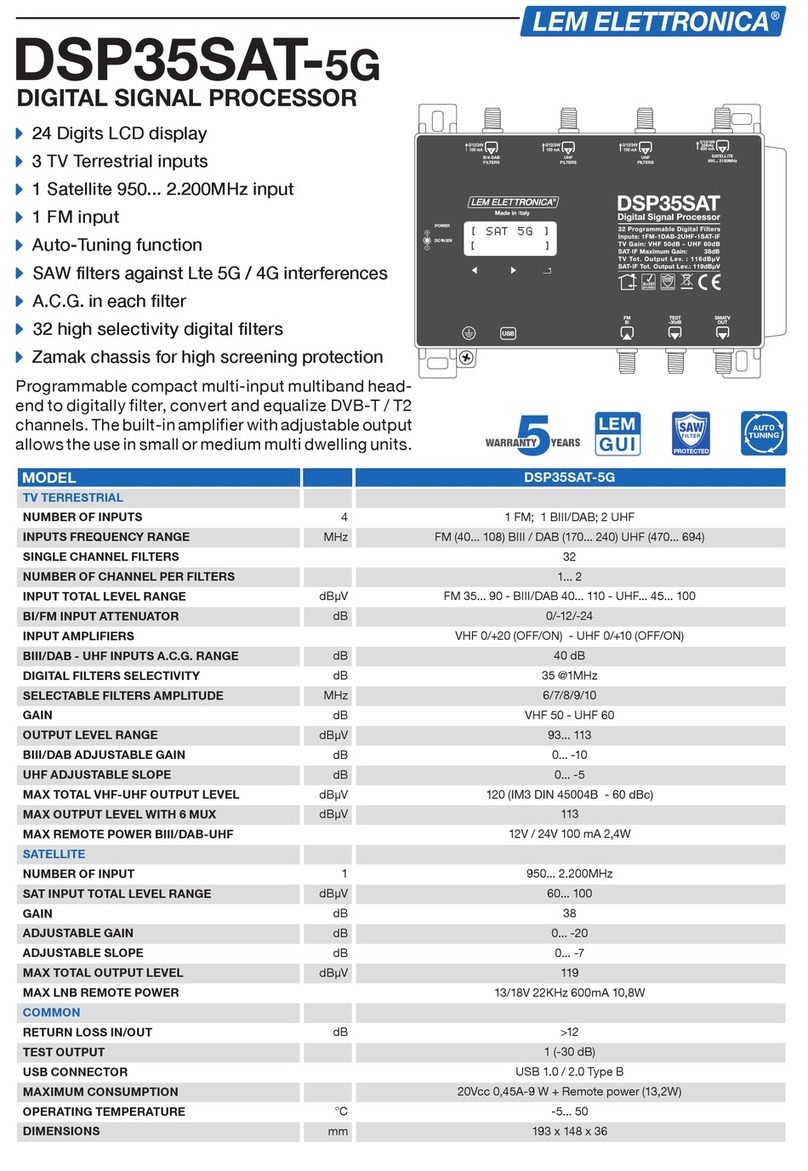
Lem Elettronica
Lem Elettronica DSP35SAT-5G manual

ekwb
ekwb EK-FB EVGA X58 CLASSIFIED Installation and mounting instructions