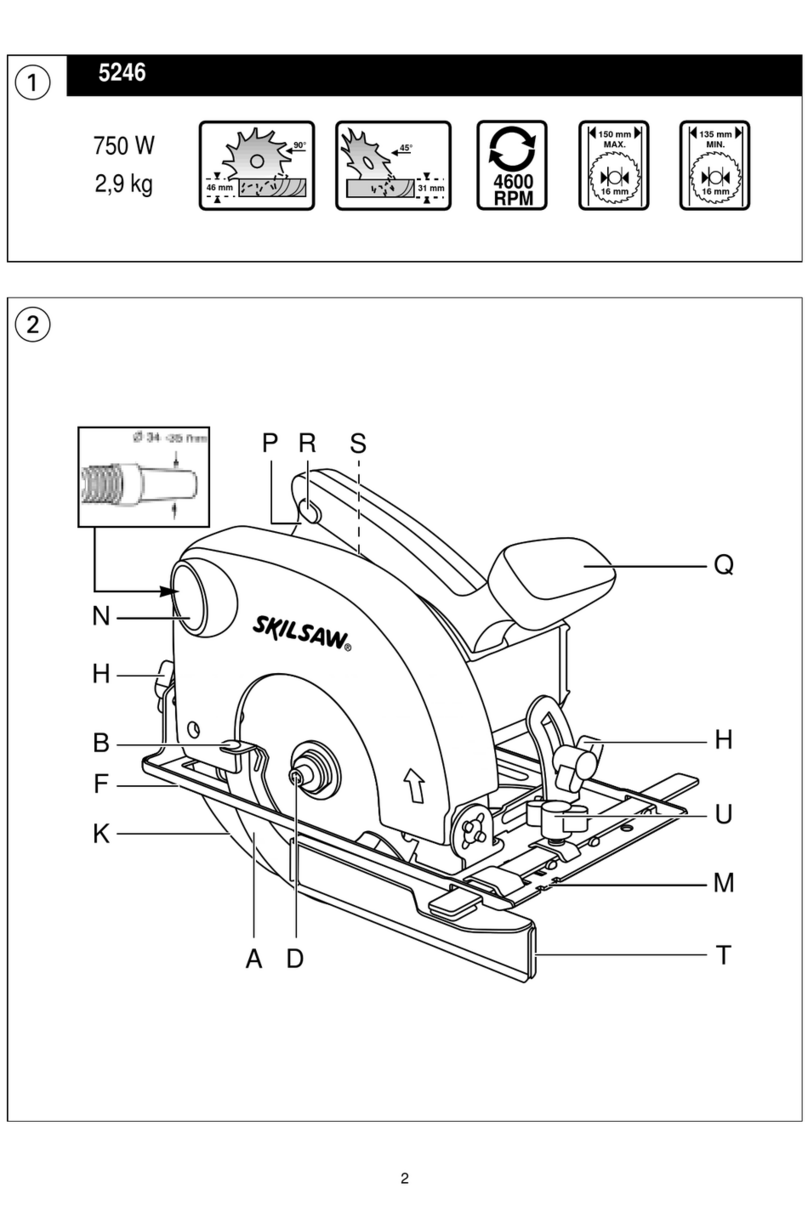
5
The workpiece must be stationary and clamped or held against both the fence and
the table. Do not feed the workpiece into the blade or cut “freehand” in any way.
Unrestrained or moving workpieces could be thrown at high speeds, causing injury.
Push the saw through the workpiece. Do not pull the saw through the workpiece. To
make a cut, raise the saw head and pull it out over the workpiece without cutting, start
the motor, press the saw head down and push the saw through the workpiece. Cutting
on the pull stroke is likely to cause the saw blade to climb on top of the workpiece and violently
throw the blade assembly towards the operator.
Never cross your hand over the intended line of cutting either in front or behind the
saw blade. Supporting the workpiece “cross handed” i.e. holding the workpiece to the right of
the saw blade with your left hand or vice versa is very dangerous.
Do not reach behind the fence with either hand closer than 100 mm from either side
of the saw blade, to remove wood scraps, or for any other reason while the blade is
spinning. The proximity of the spinning saw blade to your hand may not be obvious and you
may be seriously injured.
Inspect your workpiece before cutting. If the workpiece is bowed or warped, clamp it
with the outside bowed face toward the fence. Always make certain that there is no
gap between the workpiece, fence and table along the line of the cut. Bent or warped
workpieces can twist or shift and may cause binding on the spinning saw blade while cutting.
There should be no nails or foreign objects in the workpiece.
Do not use the saw until the table is clear of all tools, wood scraps, etc., except for the
workpiece. Small debris or loose pieces of wood or other objects that contact the revolving
blade can be thrown with high speed.
Cut only one workpiece at a time. Stacked multiple workpieces cannot be adequately
clamped or braced and may bind on the blade or shift during cutting.
Ensure the mitre saw is mounted or placed on a level, rm work surface before use. A
level and rm work surface reduces the risk of the mitre saw becoming unstable.
Plan your work. Every time you change the bevel or mitre angle setting, make sure the
adjustable fence is set correctly to support the workpiece and will not interfere with
the blade or the guarding system. Without turning the tool “ON” and with no workpiece on
the table, move the saw blade through a complete simulated cut to assure there will be no
interference or danger of cutting the fence.
Provide adequate support such as table extensions, saw horses, etc. for a workpiece
that is wider or longer than the table top. Workpieces longer or wider than the mitre saw
table can tip if not securely supported. If the cut-off piece or workpiece tips, it can lift the lower
guard or be thrown by the spinning blade.
Do not use another person as a substitute for a table extension or as additional
support. Unstable support for the workpiece can cause the blade to bind or the workpiece to
shift during the cutting operation pulling you and the helper into the spinning blade.
The cut-off piece must not be jammed or pressed by any means against the spinning
saw blade. If conned, i.e. using length stops, the cut-off piece could get wedged against the
blade and thrown violently.
Always use a clamp or a xture designed to properly support round material such as
rods or tubing. Rods have a tendency to roll while being cut, causing the blade to “bite” and
pull the work with your hand into the blade.
Let the blade reach full speed before contacting the workpiece. This will reduce the risk
of the workpiece being thrown.
If the workpiece or blade becomes jammed, turn the mitre saw off. Wait for all moving
parts to stop and disconnect the plug from the power source and/or remove the battery
pack. Then work to free the jammed material. Continued sawing with a jammed workpiece
could cause loss of control or damage to the mitre saw.