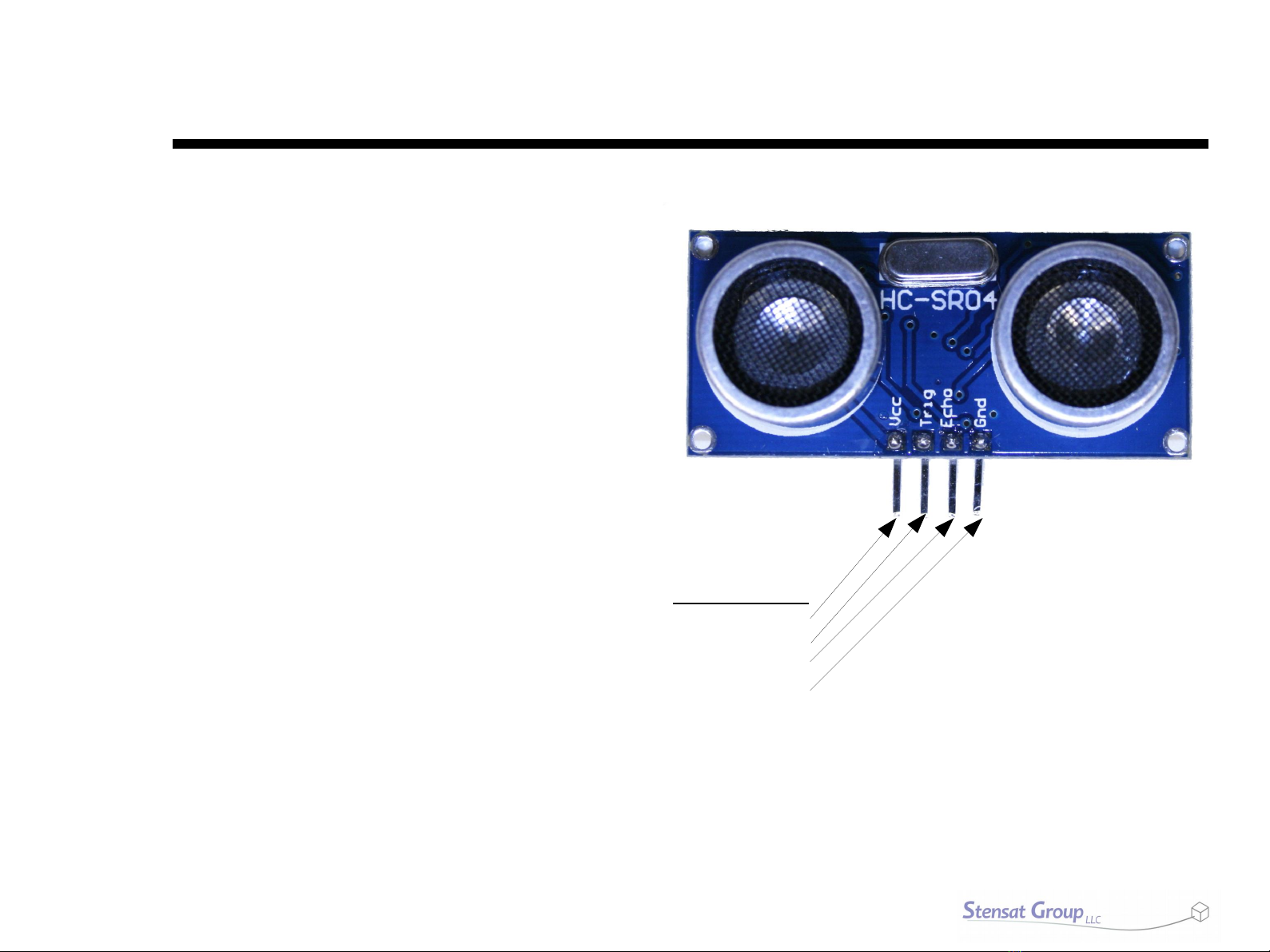
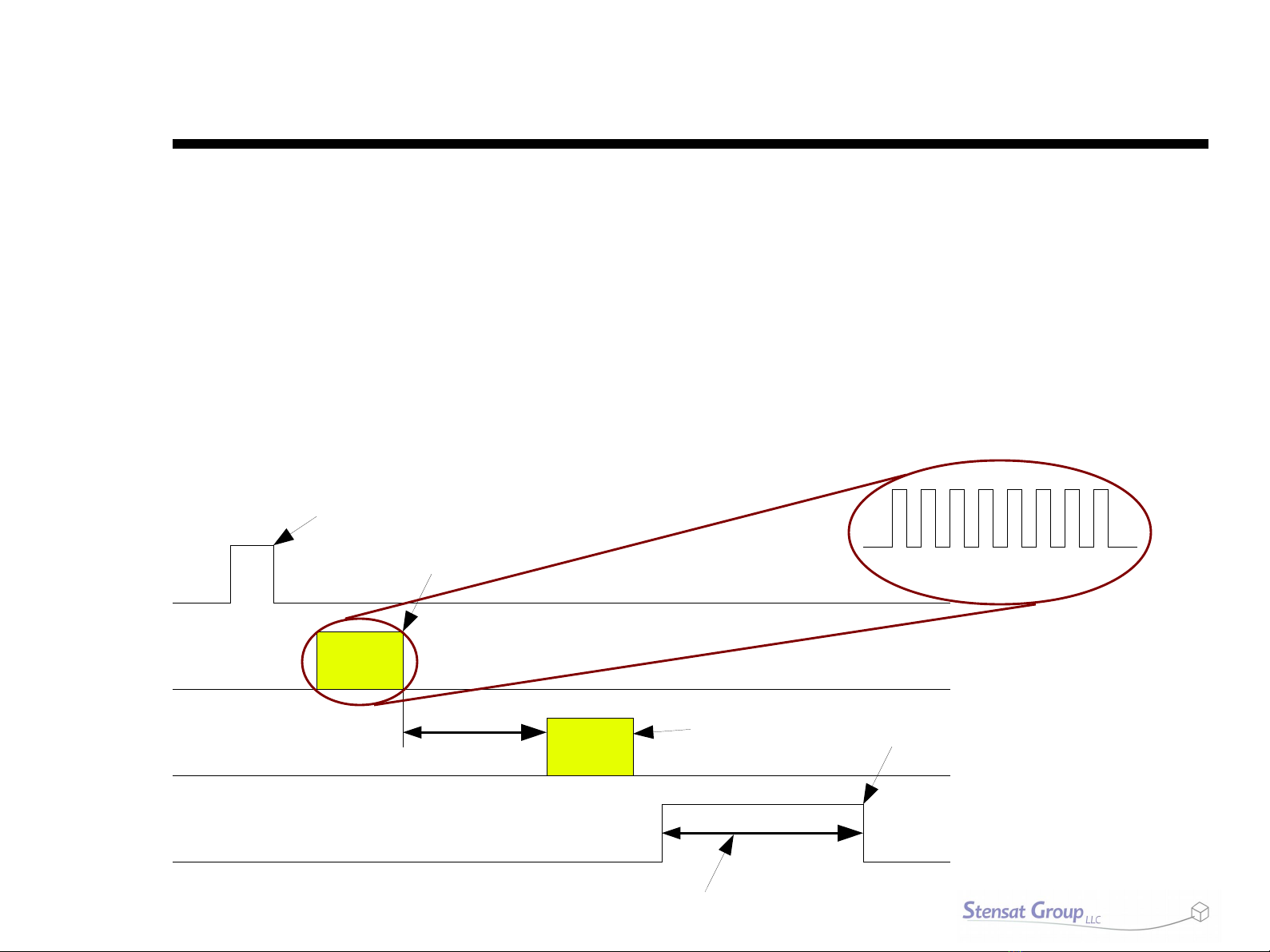
Stensat StenBOT Rover Kit User manual














Popular Toy manuals by other brands

lalaloom
lalaloom Babycue instruction manual

Viessmann
Viessmann H0 series Operation manual
Fisher-Price
Fisher-Price RESCUE HEROES ACTION TRACKERS BILLY BLAZES WITH FIRE... instructions

Fisher-Price
Fisher-Price GEOTRAX T7159 user manual

GAUI
GAUI X3 instruction manual

Eduard
Eduard MiG-23MF interior S.A. manual

Mountain Models
Mountain Models Tantrum instructions

Fisher-Price
Fisher-Price DRL52 manual

The Learning Journey
The Learning Journey Techno Gears Marble Mania Zoomerang instruction manual

BeeWi
BeeWi BWZ200 user guide

LEGO
LEGO 70747 Assembling manual

Playskool
Playskool Star Wars Chewbacca with Wookiee Scout Flyer... instruction manual

Horizon Hobby
Horizon Hobby E-FLITE Night Radian 2.0m instruction manual

Chicco
Chicco 4-in-1 Ride On Car owner's manual

Playskool
Playskool Air-tivity Ball Popper 6104 instructions

GREAT PLANES
GREAT PLANES Reactor instruction manual

Fisher-Price
Fisher-Price W5636 instruction sheet

Carl Goldberg Products
Carl Goldberg Products FREEDOM 20 instructions