STRAIGHT CORE GWP-106VE User manual

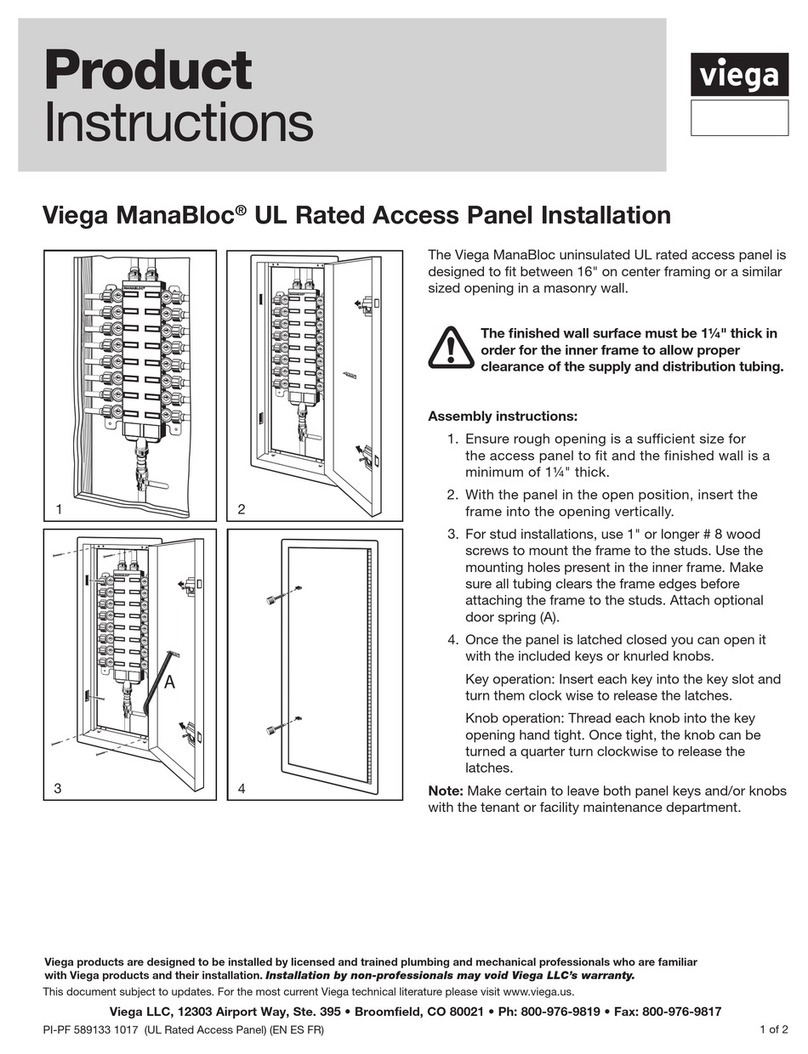
Introduction
English version 1
Multi-functional access point
GWP-106VE
IEEE 802.11b/g
54Mbps
User Manual
Straight
Core

Introduction
English version 2
Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction............................................................................................................................ 3
1.1 Content of the package................................................................................................................. 3
1.2 Functions of the unit...................................................................................................................... 3
1.3 Specification.................................................................................................................................. 3
1.4 Description and installation of the unit.......................................................................................... 4
1.4.1 External part - ODU ........................................................................................................ 4
1.4.2 Internal part – IDU........................................................................................................... 4
Chapter 2 Configuration of the unit.......................................................................................................7
2.1 Preparation for configuration ........................................................................................................ 7
2.1.1 Setting your PC............................................................................................................... 7
2.2 Statistics ........................................................................................................................... 8
2.2.1 Status of the unit............................................................................................................. 8
2.2.2 Available networks ................................................................................................ 8
2.2.3 Data .......................................................................................................................... 8
2.2.4 Wireless connection ................................................................................................. 8
2.2.5 DHCP Clients .......................................................................................................... 8
2.2.6 WDS Connection ....................................................................................................8
2.2.7 Routing table ............................................................................................................ 8
2.2.8 ARP Table .............................................................................................................. 8
2.3 Setting the operating mode ....................................................................................................... 9
2.4 Setting of the wireless part ........................................................................................................... 9
2.4.1 Setting the basic parameters of the wireless connection: ........................................... 10
2.4.2 Advanced setting of radio transmission ...................................................................... 11
2.4.3 Security ................................................................................................................. 12
2.4.4 Filtering of MAC addresses .................................................................................... 14
2.5 IP setting ..................................................................................................................................... 14
2.5.1 LAN port TCP/IP setting ............................................................................................ 14
2.5.2 WAN port TCP/IP setting .............................................................................................. 15
2.5.3 Gateway and Routing ............................................................................................ 15
2.6 Network and Firewall .................................................................................................................. 16
2.6.1 IP/MAC Address Blocking, Port Blocking ................................................................... 16
2.6.2 Port forwarding ...................................................................................................... 16
2.6.3 Setting DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) ................................................................................ 16
2.7 Services ...................................................................................................................................... 16
2.7.1 Rate limit ............................................................................................................... 16
2.7.2 DDNS setting ........................................................................................................ 16
2.7.3 Tile server ............................................................................................................. 17
2.7.4 Watchdog/Restart ................................................................................................. 17
2.7.5 Network test ......................................................................................................... 17
Chapter 3 Administration ..................................................................................................................... 18
3.1.1 Changing password ............................................................................................... 18
3.1.2 Save/Restore configuration .................................................................................... 18
3.1.3 Update ................................................................................................................. 18
3.1.4 Web interface ........................................................................................................ 18
3.2 Restart ........................................................................................................................................ 18
Chapter 4 Troubleshooting .................................................................................................................... 1

Introduction
English version 3
Chapter 1 Introduction
Thank you very much for purchasing the GWP-207VE wireless client unit. This is a unit for building
the network according to the 802.11b or 802.11g standard. Wireless units consist of access points (the unit
in the “Access Point” regime) and client devices (the unit in the infrastructure regime). For interconnection of
further computers without an access point it is possible to use an AD-HOC setting, for building a Point-Point
connection, it is possible to use WDS/Bridge regime.
This unit supports WEP, WPA, ESSID security systems and a MAC address filter to ensure security
of the wireless network. Due to these security standards it is possible to avoid any unauthorized access to
your wireless network.
This unit is equipped with a 14 dB gain aerial integrated panel. Using a www interface, this equipment
enables the control of the overall emitted output, i.e. the output which includes the gain of the aerial.
This unit can be easily controlled by any web browser which is localised into several languages.
Contact your supplier to receive the current list of language modifications for the user interface or you can
find it on the web pages of the producer at www.straightcore.net.
The firmware (the control program of the unit) is developed with the emphasis placed on the use in
large wireless networks. The cover of the unit is designed for use outside of buildings with sufficient
protection against drip and other atmospheric influences. For easy setting it is possible to connect the GWP-
HDF direction finder to the unit whose description and the use is contained in this Manual.
Note: This manual is written for firmware version 1.0.6. Recent firmware may contain functions not contained
in this version of the manual.
You can find pictures in the colour appendix in the end of the manual. The number of the picture
related to the respective chapter is always located beside the symbol
1.1 Content of the package
The package contains the following items:
yOne Quick Installation Manual
yOne Access Point
yOne Power Adapter
yOne PSW-105 Switch with POE system (optional)
1.2 Functions of the unit
yCompatible with specification IEEE 802.11b/g (DSSS) 2.4GHz.
yWaterproof construction with integrated 14 dB aerial
yPower-over-Ethernet (PoE) system
yHigh transmission rate up to 54 Mbps.
ySimple integration to current LAN networks.
yAutomatic access rate reduction in an interfering environment.
y64/128-bit WEP and WPA Encryption Function for wireless transmission security.
yIntegrated DHCP server for automatic IP address assigning.
yWeb based control.
1.3 Specification
yStandards: IEEE 802.11b/g (Wireless section), IEEE 802.3 (LAN section)
yTransmission Rates: 54/48/36/24/18/12/11/9/6/5.5/2/1Mbit/sec with automatic reduction in an
interfering environment
ySecurity: 64/128-bit WEP and WPA transmission encryption
yFrequency range: 2.400~2.4835GHz (ISM band)

Introduction
English version 4
yModulation:
802.11b - CCK@11/5.5Mbps, DQPSK@2Mbps a DBPSK@1Mbps
802.11g – BPSK,SPSK,16QAM,64QAM
yWireless Technology: DSSS pro 802.11b, OFDM pro 802.11g
yAerial: External disconnecting 2dB (connector RP-SMA)
yNetwork connector:
ODU-10/100Mbps RJ-45 x 2, GWP-HDF port (USB connector) x1
IDU – 5xRJ45 (PoE standard on port 1, optional 2,3,4)
yVoltage: 12V DC
yHigh-frequency output: max 19.8 dBmW
yLED diodes:
ODU - Supply, Link (on connectors RJ-45)
IDU - Supply, 4x LAN Line/Activity/PoE system, 1x LAN Line/Activity
yTemperature range:
Operation: -35°C~65°C
Storage: -35°C~70°C
yHumidity: 10-90% (non-condensing)
yCertification: FCC, CE
1.4 Description and installation of the unit
1.4.1 External part - ODU
Part of the unit is designated for locating on an installation mast. In the front part it contains an integrated 12
dB aerial.
1.4.1.1 Ethernet/POE port
In the bottom part of the external unit you can find the waterproof part covered by a plastic cover. In this
part there is port for an RJ-45 connector and the Reset button. For the connection of the unit to an internal
part it is always necessary to use fully equipped STP shielded cable of the category 5,5e or 6. In the case of
use of unshielded cable, the unit or the connected computer can be damaged due to the influence of static
discharge. After connection of the connector into the port ensure the correct installation of the waterproof
cover and its fixation with the attached bolt.
Mount the unit on the mast by means of the holder and fork which is a part of the accessories. If you
attach the unit to the mast so that the LED diodes on the front side are on the top, the unit will be in vertical
polarization. For attaching in horizontal polarization turn the holder by 90 degrees so that the Ethernet cable
is protected by the offset in the cover against drip. Then, connect the plastic form with the centre bolt and
after attaching the whole unit to the mast, tighten the bolt so that the declination of the unit best corresponds
to the direction of the location of the transmission point to which GWP-106VE will be connected.
1.4.1.2 Reset button
The unit is equipped with a button for its resetting or for switching to the factory setting. This button is
located on the right side of the RJ-45 connector. Use a ballpoint pen or other suitable tool to press it. Use
as follows:
•Press the button for a short period less than 4 seconds to restart the access point. In this case
the configuration parameters will remain kept.
•In the case of the loss of password or IP address it is possible to switch the contact for a period
longer than 4 seconds. In this case the factory setting will be reset and there will be a restart of
the access point to the initial address 192.168.1.1 and it will not be protected by a user name
and password.
1.4.2 Internal part – IDU
The internal part of the unit is delivered in two variants which correspond to the following descriptions:

Introduction
English version 5
1.4.2.1 Standard Power Injector
In the standard variant the unit is delivered with a standard injector without the integrated switch. The
connection is easy. Connect the Ethernet cable from your PC or the switch into the port marked LAN. The
POE port is used for the connection of the cable leading to the ODU unit. Connect the delivered network
adapter into the port of the described DC – now the installation is complete. Attention, in the case of
incorrect connection of cables into individual ports there can be serious damage to your switch or
computer. Therefore, we recommend to use for this connection a Cat.3 4 or 5 cable with only 1,2,3 and 6
contacts connected. In this case there is no risk of damage because the POE system uses transfer on
contacts 4/5 and 7/8 as schematically displayed on the upper side of the POE injector.
It is possible to use side clamps and small screws for mounting of the injector on the wall which is
not part of the delivery. The span of the assembly holes is 68 mm.
1.4.2.2 PSW-105/205
The optional accessory to the GWP-106VE unit is the PSW-105/205 projector with an integrated 4-
pole switch. This variant is equipped with an LED diode for checking the function. The description of the
status and the function of individual LED diodes are in the following table:
LED Colour Status Description
ON Supply to the unit is connected
Power Orange OFF No supply
OFF Line disconnected, POE inactive
Red Line disconnected, POE active for respective port
Orange ON Line connected, POE active for respective port
Orange, flashes Line connected, POE active, data transfer
Green ON Line connected, POE inactive
1-4/POE
Green
Orange
Red
Green flashes Line connected, POE inactive, data transfer
ON Line connected.
Flashes The line is transmitting or receiving data.
5 Green
OFF Line disconnected
1.4.2.2.1. POE System
The IDU PSW-105 is equipped with a POE system (Power-over-ethernet). In the standard configuration the
PoE is active only on port No.1 which is used for the supply of the unit. In special cases, by interconnection
of the J1 switch on the board of the switch it is possible to also switch the ON supply for ports 2-4 and to
supply up to 4 external units with one PSW-105 switch (in this case , it is necessary to replace the delivered
source with the 12V/2A source). Further options for the use of this regime is, for example, the installation of
one switch for PC with an active POE port 1 and the supply of a distant switch in the regime of 4 POE ports
by means of the POE system. It is possible to use the remaining 3 ports for connection of 3 external GWP-
207VE units.
For fast specification of the configuration of PSW-105, connect only the supply voltage. The ports on which
the POE system is active are indicated by a permanently lit red LED diode.
1.4.2.2.2. Supply of IDU/Connection of further units
The DC-12V connector serves for the connection of the supply voltage. The standard delivery includes the
12V/500mA source which is sufficient for the operation of the switch and one unit on the cable with a length
of 15 m. In the case of operation with a longer cable, it is possible to use for the supply a stabilized
maximum 18V source. With the increase of the input voltage it is possible to ensure stable operation up to
70 m of the Ethernet line. In the case of connection of further units to one PSW-105, it is necessary, on the
contrary, to increase the input current. For each connected unit it is necessary to consider the current as
400mA and for each remotely supplied switch the current as 100mA.

Introduction
English version 6
1.4.2.2.3. Ethernet ports 1/5
The connector is for the connection of the equipment into a standard LAN computer network with a Cat.5,5E
or Cat.6 cable. Attention, connect only StraightCore external units to ports with an active POE system. The
connection of any other equipment may damage the switch and the connected equipment.
.

Configuration of the wireless access point LAN
English version 7
Chapter 2 Configuration of the unit
2.1 Preparation for configuration
This unit provides easy control through a www browser. Access the configuration using the following steps.
2.1.1 Setting your PC
Make sure your computer is configured to the same IP address range as the wireless unit. The factory
setting of TCP/IP is as follows:
Default IP Address: 192.168.1.1
Network mask: 255.255.255.0
Configuration of TCP/IP parameters of your PC.
1a) Windows 95/98/Me
1. Click the Start button and select the Setting tab, then the Control Panel window will appear.
2. Double click on the Network connections icon.
3. Check the displayed items. If the TCP/IP protocol is not installed, press the Add button If the
TCP/IP has already been installed, follow step 6.
4. In the Network component type dialog select Protocol and click on Add.
5. In the Network protocol type window select TCP/IP and click on Add. To complete the
installation you may need the operation system installation disk.
6. After installation of the TCP/IP protocol, return to the network component list, select TCP/IP
protocol and press the Properties button.
7. Check all tabs and complete with the following parameters:
•Bindings: Check Client for Microsoft network and File and Printer sharing.
•Gateway: Leave all fields empty.
•DNS Configuration: Select Disable DNS.
•WINS: Select Disable WINS.
•IP Address: Select Enter IP Address. Enter the IP Address and the mask as in the
following example:
9IP Address: 192.168.1.3 (any IP address from 192.168.1.2~192.168.1.254 range
is possible, do not enter 192.168.1.1)
9Network mask: 255.255.255.0
8. Restart the computer. After rebooting, your computer will use the IP address you entered.
1b) Windows XP
1: Press the Start button and select Control panels then press the Network connection. The Network
connections windows will appear.
2: Double click on the Local network connection icon.
3: The window will appear. Select TCP/IP from the list and press the Properties button.
4: Fill the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) – properties dialog box according to the following example.
IP address: 192.168.1.2
Sub-network mask: 255.255.255.0
5: Press OK. Now your PC is configured to access the unit.
Enter the IP address of the unit 192.168.1.1 into your www browser to access the configuration. In
the default configuration the unit is protected by a password and user name. Now you can configure the
GWP-106VE unit for connection to the access point.

Configuration of the wireless access point LAN
English version 8
2.2 Statistics 1
Pic.1 in the Appendix shows the starting page for access of the unit control. Access the configuration
parameters using the pair of menus. In the left upper part under the logo of the producer there is a primary
menu with the main menu items. Above the screen there is a dynamic menu. Its content is changed
depending on the actual selected item of the main menu.
2.2.1 Status of the unit
This opening screen contains information about the current setting of the unit, the time of running
from the last restart, the version of the HW and SW unit, the selected network key, the operating mode of the
unit, etc. The important information which you will need for setting your wireless network is “WiFi MAC
address – BSSID” value. This is the network address of the wireless part of the unit which the unit uses to
login into your wireless network. If you use the unit in the “Station – Infrastructure” mode, and your access
point to connect to perform MAC address filtering, you must ensure your unit MAC address passes through
the filter.
2.2.2 Available networks 2
If the unit is in some of operating modes of the “Station” type, after pressing the “Restore“ button on
the “Available networks” page then all available wireless networks will be searched. The table provides
information about the SSID network, the MAC address of the unit found, the operating channel, type of
network and the strength of the signal. After selection of the respective network in the right column it is
possible to set the parameters of the respective network with the “Connect” button. If the network uses any
encrypting standards, it is necessary to set these parameters manually.
2.2.3Data 3
On the “Data” page it is possible to find the statistics of the received and sent packets for the individual
interfaces of the unit since its last restart.
2.2.4 Wireless connection 4
The “Wireless connection” page provides you in Access Point mode, information on the currently
connected Client stations, the amount of transmitted data and the signal strength. Click on the "advanced"
button to enhance the table with other detailed communication parameters with individual stations.
2.2.5 DHCP Clients 5
When the DHCP server is enabled on the unit, the table on the “DHCP Clients” page will report the
currently assigned IP addresses for each client.
2.2.6 WDS Connection 6
If the unit is configured as a part of a WDS system, the table on this page shows the parameters of
the individual stations of the WDS system.
2.2.7 Routing table 7
On the “Routing table” page you can find the actual rules for routing of the unit. It is possible to edit
these rules in the static routes menu.
2.2.8 ARP Table 8
The “ARP Table” page provides information about the MAC addresses of the connected devices
both on the wireless and the metallic side of the unit.

Configuration of the wireless access point LAN
English version 9
2.3 Setting the operating mode 9
The first step during the setting of the unit is the selection of the operating regime in terms of network
routing. You can access this configuration menu through the Network & Firewall menu, on the Network mode
tab. The unit offers 3 operating modes.
The unit is in 1-BRIDGE mode by default, with
both interfaces at the same level. The unit is
accessible at the same IP address at both
interfaces. This setting is usual when using the
device as an access point and in some cases in
client device mode. All settings related to NAT
operation are not available.
Mode 2 is typically used for the operation of the client
unit. The unit is then connected to the Internet using
the wireless interface. The ports on the PSW-105 can
be used for the connection of client computers. Then
the unit will serves as a default gateway for client
computers. The unit is accessible at the corresponding
IP addresses at the LAN and WAN side for
configuration. This setting is usually combined with the
DHCP server function, which automatically assigns addresses to individual computers.
The typical use of Mode 3 is as a unit used as
common wireless router, for example for the
connection of ADSL, or Ethernet. In this case the
Internet is connected with a cable to the PSW-105
switch port labelled as Ethernet.
Then the client computers are wireless connected.
In this case, the radio has to be set to AP mode.
2.4 Setting of the
wireless part
This multifunctional unit operates in the multiple operation modes of Access Point, Station, WDS
System and AP Bridge-WDS and Repeater. The GWP-207VE unit is the most frequently used in the
operating mode, for which it is designated.
The “Access Point” operating mode is used in the case where the unit serves as the central point of
your wireless network and other wireless adapters are then connected to it in the Station-Infrastructure
Mode.
The “Station” operating mode is divided into two types. The “Station” is used in networks with a
central access point as described above. In the case of using the "Ad Hoc" operating mode, you can create
the network directly between single adapters without participation of the access point. (Peer-to-Peer
communication)
The “WDS System” operating mode (also called BRIDGE) is intended mainly for the connection of
two (“Bridge Point-to-Point”) or more (“Bridge Point-to-Multipoint”) LAN networks.
If the “Repeater" operation mode is set, the unit behaves both as an access point and client adapter
of the master unit in the “AP mode”.

Configuration of the wireless access point LAN
English version 10
Why is the WDS System/Bridge mode more suitable for the connection of LAN networks?
When using Station operating modes (both types), the units conforming to WiFi standards change packet
header at second level – that is when the MAC address of the terminal is replaced with a MAC address unit.
In some applications where behind the unit there is more than one terminal, this replacement of the network
address may cause problems. On the contrary, in Bridge modes the unit behaves in a fully transparent
manner also at the second level and the MAC addresses in the header of the packet remain unchanged.
A special case of the WDS System modes is the "WDS Access Point" type. In this operating mode
the unit can be used simultaneously as an Access Point and Bridge connecting LAN networks.
2.4.1 Setting the basic parameters of the wireless connection:
10
The “Basic Setting” in the "Wireless section” menu defines the most important parameters of radio
data transmission. A description of these parameters is shown in the following table:
Parameter Description
Network Name – SSID
(Basic setting for radio module)
SSID parameter (up to 31 ASCII characters) represents the key, on the
basis of which there is the connection of individual adapters within the
wireless network. Setting the various network keys can ensure the
functioning of several wireless networks in the same area and within the
same frequency range. It is necessary to use SSID identically in the
access point and all client adapters connected to it. The default value of
this key is “GWP-207VEt” but we recommend changing this setting
during installation. SSID is configured in "Access Point", "Station AD-
HOC", "Station-Infrastructure", "WDS System" and "AP-Bridge WDS"
operating modes.
Type of operation:
(Basic setting of the radio module) This item provides the user with the option to define the operating mode
of the unit only for standard 802.11b, only for 802.11g or for both
standards at the same time.
Operating channel:
(Basic setting of the radio module)
Using this setting the user defines the operating channel of the unit. For
use in EU countries (with the exception of Spain) 13 channels are
available in total. Selection of the operating channel is not to be
performed in "Station-Infrastructure" mode as the channel is configured
automatically by the Access Point with same ESSID setting.
Overlapping of Operating Channels
With respect to the division of the frequency range and with regard
to the width of the frequency band used, there is overlapping of individual
channels. Therefore, you get the best results when using WiFi Access
Points so that the units in the respective area are located at least 3 - 5
channels from each other. For example, using channels 1,7,13 when
there is no any interference.
WiFi standard
(Basic setting of the radio module)
You select the standard for the radio section in this field. For use in then
Czech Republic select ETSI.
MAC Address:
(WDS/Bridge setting)
In Bridge and WDS System modes it is necessary to define the MAC
addresses of all connected wireless units which the system uses for the
identification of members of the respective Bridge or WDS structure.
Set Security
(WDS/Bridge Setting)
In WDS type operating modes you can use this button for setting the
encryption of the transmission for security reasons.
Show statistics:
(WDS/Bridge Setting)
In WDS mode using this button it is possible to view a table displaying
statistical information about individual WDS clients.

Configuration of the wireless access point LAN
English version 11
Connected Stations:
(Basic setting of the radio module)
Clicking on the "View Active Stations" button opens a window with the list
of currently connected clients and the transmission parameters of each
station.
Networks Available:
(Basic setting of the radio module)
Using this button for scanning of available networks in the Station
operating mode displays the table showing the available wireless
networks. By selecting the wireless network and pressing the Connect
button the unit will be automatically configured for connection to this
network. If the network uses any of the security protocols, you must
manually configure the security.
Click on the “Apply” button in the left corner of the page to save the changes. Now you can switch to set
other parameters or start using the unit.
2.4.2 Advanced setting of radio transmission 11
On this page it is possible to enter the detailed parameters influencing the wireless operation.
Parameters are set by default, so it is not necessary to change them during standard operation, nevertheless
in an interfered environment their optimising may bring an increase in the transmission speed or a lower
error rate.
Parameter Description
Authentication type This field offers three options. When you choose "Open System", any
station is able to connect to the network regardless of the encryption.
When you choose "Shared key", only the unit can be connected, which
has the same shared key as configured in the security settings. The
"Auto" value combines both these modes.
Threshold of fragmentation The threshold of fragmentation states the maximum size of the packet
during the fragmentation of data to be sent. If too low a value is set, the
performance will decrease.
RTS level When the site of the packet is smaller than the RTS threshold, the access
point will not use the RTS/CTS mechanism to send this packet.
Beacon Interval The time interval in which the access point broadcasts a beacon.
A
beacon is used for synchronization of the wireless network.
Line rate The line rate states the speed of data transmission used by this access
point. The access point uses for transfer the maximum possible selected
transmission rate.
DTIM Period DTIM is part of the beacon packet which informs units in the energy
saving mode that data transmission will follow. In the case of an increase
in this value, the timeout between the energy saving status and the
transfer into operating mode is increased.
Preamble type The preamble type defines the length of the CRC block within the
wireless communication. The "Short Preamble" option is suitable for a
high traffic wireless network. The "Long Preamble" option can provide
more reliable communication.
Hide SSID If you disable “Hide SSID”, each wireless station located within the
coverage of this access point can ascertain its presence. If you build a
public wireless network, it is recommended to enable this function.
Enabling “Hide SSID” can provide better security.

Configuration of the wireless access point LAN
English version 12
IAPP Function If you enable “IAPP”, the access point will automatically broadcast
information regarding any associated wireless stations to its neighbours.
This makes for easy and fluent switching of the wireless station between
access points. If your wireless LAN network contains more than one
access point, it is necessary that these stations will move, so it is
recommended to enable this function. Disabling “IAPP” can provide
better security.
802.11g Protection This is also called CTS Protection. It is recommended to enable the
protection mechanism. It enables to decrease the rate of collision
between 802.11b and 802.11g wireless stations. If the protection mode is
enabled, the throughput of the access point will be a bit lower due to the
demand to transmit a high number of frames.
Insulation of wireless clients This function is to be used in AP operating mode only. When enabling
this function, the communication between individual clients within a single
AP will be blocked.
802.11b Output Power This can define the transmission output for operation according to
standard 802.11b, therefore with CCK modulation. When configuring
the output, always check the restrictions for the area where you are
using the unit. Refer to the "Device Usage" chapter when using in
the Czech Republic.
802.11g Transmission output This can define the transmission output for operation according to
802.11g standard, therefore with OFDM modulation. When configuring
the power, always check the restrictions for the area where you are
using the unit. Refer to "Device Usage" chapter when using in
Czech Republic.
Input Amplification Sets the level of amplification for the input pre-amplifier during receipt of
the signal. Setting the higher values enables to receive previously
unavailable wireless networks, nevertheless the interference from the
receiving signal and consequently the transmission error rate increases.
Click on the Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above mentioned configurations.
You can now configure the other sections or start using the Access Point.
2.4.3Security
12
This Access Point provides all security functions of a wireless LAN network, including WEP, IEEE
802.11x, IEEE 802.11x with WEP, WPA with a pre-shared key and WPA with RADIUS. These security
functions prevent unauthorized access to your wireless LAN network. Make sure that all wireless stations
use the same security function.
In addition to standard types of encryption, it is always possible to turn on the pre-authentication with the
Radius server and the 802.1x standard. IEEE 802.1x is an authentication protocol. Each user must use a
valid account to login to this Access Point before accessing the wireless LAN. The authentication is
performed by a RADIUS server. This mode only authenticates a user by IEEE 802.1x, but it does not encrypt
the data during communication. You can use 802.1 x without encryption in "AP mode" and “AP Bridge-WDS
mode”.
Note: This access point can behave both as a station and AP in "AP Bridge-WDS mode". The security
settings only apply to the AP function in the "AP Bridge-WDS mode".

Configuration of the wireless access point LAN
English version 13
2.4.3.1 WEP encryption 13
Use the “WEP encryption” page to set the WEP encryption keys. A description of the individual
parameters is in the table below:
Parameter Description
Key length 64 bit and 128 bit key for encryption of transmitted data can be selected.
A longer WEP key provides a higher level of security, but lowers
throughput.
Key format For the WEP key, ASCII characters (alphanumeric format) or
hexadecimal digits (in “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9” range) can be selected. For
Example:
ASCII characters: guest
Hexadecimal digits 12345abcde
Default key Select one of four keys to encrypt your data. Use only the key selected in
“Default key”.
Encryption key 1 – 4 The WEP keys are used for encryption of the data transmitted in the
wireless network. Fill in the text box by following the rules below.
64-bit WEP: input 10-digit Hex values (in the “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9” range)
or 5-digit ASCII characters as the encryption keys.
128-bit WEP: input 26-digit Hex values (in the “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9”
range) or 10-digit ASCII characters as the encryption keys.
Click on the Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now
configure other advance sections or start using the Access Point.
2.4.3.2 WPA/WPA2 14
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is an advanced security standard. You can use a pre-shared key to
authenticate wireless stations and encrypt data during communication. After changes of encryption keys are
performed using TKIP or CCMP (AES) methods. Therefore the encryption key is not easy to be broken by
hackers. This can substantially improve wireless network security. You can use WPA encryption with a pre-
shared key in the “AP mode”, “Station-AD HOC mode”, “Station-Infrastructure mode” and “AP Bridge-WDS
mode”.
Parameter Description
Authentication Mode You can select pre-shared key authentication or authentication with
Radius server. In this case, the Radius server will be used as set in the
upper part of the screen.
Key format For a pre-shared WEP key it is possible to select for the input phrase
ASCII characters (alphanumeric format) or hexadecimal digits (in “A-F”,
“a-f” and “0-9” range). For Example:
Input phrase: iamguest
Hexadecimal digits 1234567890abcdef
Parameter Description
Security Type: You can select the type of security which will be used. WEP, WPA and
WPA with RADIUS support is available.
Format of WEP Key : This field is used when using WEP Encryption. It indicates the format for
entering keys. You can choose ASCII or Hexadecimal format.
WEP Key: Default key value for WEP Encryption.
Shared Key Format: In this field you can choose the WPA key format. Again you can select
ASCII or Hexadecimal format.
Shared key: Key for data encryption in the WPA system.

Configuration of the wireless access point LAN
English version 14
Shared key A pre-shared key is used for authentication end encryption of the data
transmitted in the wireless network. Fill in the text box according to the
following rules. Hex: input 64-digit Hex values (in the “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9”
range) or as pre-shared encryption keys or minimum 8-digit input phrase.
Click on the Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now
configure other advance sections or start using the Access Point.
2.4.4 Filtering of MAC addresses 15
This Access Point provides MAC Address Filtering, which prevents unknown (unauthorized) MAC
Addresses from accessing your wireless network.
Parameter Description
MAC Address Filter Setting Enables or disables the MAC Address Filtering function.
MAC Address Filtering Table This table contains records of the MAC addresses of the wireless stations
you want to allow to access your network. The “Comment” field is the
description of the wireless station associated with the “MAC Address”
and is helpful for you to recognize the wireless station.
Add MAC address into the table In the bottom “New” area, fill in the “MAC Address” and the “Comment” of
the wireless station to be added and then click on “Add”. Then this
wireless station will be added into the “MAC Address Filtering Table”
above.
Remove selected MAC
addresses
If you want to remove some MAC address from the “MAC Address
Filtering Table”, select the MAC addresses you want to remove in the
table and then click on “Delete Selected”. If you want remove all MAC
addresses from the table, just click on the “Delete All” button.
Remove all Click on the "Remove All" button to clear the whole table.
Click on the Apply button at the bottom of the screen to save the above configurations. You can now
configure other advance sections or start using the Access Point.
2.5 IP setting
You can define all parameters associated with TCP/IP in the Ethernet section in the Main Menu.
2.5.1 LAN port TCP/IP setting 16
On this page you can set the TCP/IP parameters related to the LAN interface, i.e. the interface
directed to the local network in ROUTER mode. This setting will also be used in BRIDGE operation. In
addition to standard TCP/IP parameters such as IP address, network mask, default gateway, you can also
define DHCP related parameters here.
DHCP can be used in several operating modes:
DHCP Client: The device is waiting for the parent DHCP Server to assign its TCP/IP parameters by DHCP
Server in this mode.
DHCP Server: Using this operation mode the unit itself provides TCP/IP settings information for other clients
and the IP Address, Mask and Gateway parameters are delivered. The "DHCP Address Range" field is used
for definition of the addresses that will be assigned to clients. Click on the "Show Client” button to display the
currently assigned address list.
DHCP Disabled: DHCP service is disabled in this case.
Another setting possibility is to enable the Spanning Tree routing protocol defined by the 802.1d standard.
The MAC address cloning feature is used for changing of the configuration of the HW address of the LAN
interface.

Configuration of the wireless access point LAN
English version 15
2.5.2 WAN port TCP/IP setting
On this page you can define the settings for the wireless interface, directed to the Internet. These settings
will not be used when the unit is in BRIDGE mode. This page is dynamic and changes according to the
Internet connection type currently selected. The suitable connection type is determined according to the
application mode or your connection provider. There are 5 types in total:
2.5.2.1 StaticIPaddress
The IP Address is set manually to the device in this mode. In addition to the IP Address, Gateway and
Mask you can set three DNS servers to back each other up. The last item entered is the possible MAC
Address definition for the WAN interface.
2.5.2.2 DHCP Client
When using the DHCP Client setting, you can define the manner of assigning DNS server information, or
WAN Port MAC Address only. The other TCP/IP parameters are assigned automatically by the parent DHCP
server.
2.5.2.3 PPPoE
PPPoE (Point-To-Point Protocol over Ethernet) settings are often used by Internet connection providers.
It is simple method of authenticated connection, secured with the name and password specified in the
configuration. In addition, the type of connection is defined (Permanent, At Request, Manual), automatic
disconnect timeout and maximum transmit packet length. You can also manually define the MAC interface
Addresses.
2.5.2.4 PPTP
PPTP setting is used for the automatic connection to a Virtual Private Network. Connection is defined by
the Server IP Address, Username and Password. Again you can define the MTU, DNS servers and interface
MAC Addresses, next MPPE or MSCHAP encryption type. Contact the VPN network administrator to acquire
the parameters for connection.
2.5.2.5 PPTP+DHCP
This option is used for connection to the VPN network as before, although the local IP address is
acquired from the DHCP server located in the given VPN.
2.5.3 Gateway and Routing 17
The page “Gateway and routing” is used for defining static items of the routing table to ensure the correct
functioning of the Unit in “Router mode”. To set these parameters you need to know the network structure
and where the unit is installed. “Default Gateway” defines the border router, to which all packets with non-
defined routing will be sent (an automatic or manually set up routing rule).

Configuration of the wireless access point LAN
English version 16
2.6 Network and Firewall
Next to the network mode is the basic setting described in chapter 3.3, the following options are shown in
the “Network and Firewall” tab:
2.6.1 IP/MAC Address Blocking, Port Blocking 18
With regard to the identical direction of the configuration possibilities of “IP address Blocking" and "MAC
address Blocking" tabs, there is only the view for the first one.
“IP address Blocking” table items are used for limitation of the throughput of some packets directed from the
internal network, which reduces the abuse of your internet connection as well as the leakage of information
from some stations in your network.
“Blocking MAC address” table items enable to prevent data sending from your network by definition of the
rights bound with the HW addresses of individual devices.
“Blocking Port” table items allow restricting the range of TCP/IP or UDP ports through the Unit. It enables to
limit the accessibility of certain services provided from an external network.
For easy orientation in the created tables it is possible to create for each entered item a note with a
description of the respective rule.
2.6.2 Port forwarding 19
Entries in this table control the forwarding of incoming ports to the external gateway interface to any
IP in the internal network. It allows using the chosen computers in the internal network as servers or allows
their remote administration access. The symbol “S” represents a forward change of the origin address which
is necessary for some programmes. The symbol “C” indicates a change of the target port (the second value
is the number of the target port).
2.6.3 Setting DMZ (Demilitarized Zone)
The demilitarized Zone function allows you to configure that one computer in your network is directly
accessible from Internet. All services will be routed to this computer, except the services provided by the
router itself.
2.7 Services
In the Main Menu "Control" tab there are functions linked to the correct unit operation, software equipment
update functions, password changes, etc.
2.7.1Ratelimit 20
On this page it is possible to define the rate limits valid for whole unit. The upload and download direction is
always considered from the viewpoint of the client.
For advanced users: If the unit is in BRIDGE operation mode, upload means Ethernet interface broadcast
limit and download is the wireless interface broadcast limit. In ROUTER operating mode the tasks of the
individual interfaces are reversed.
2.7.2 DDNS setting 21
Dynamic DNS is a service, which allows registering a valid domain for changing (dynamic) IP Address. This
unit supports 2 providers of this service, DynDNS and TZO. TZO provides a 30-day free trial version of this
service. Refer to www.tzo.com for more information.

Configuration of the wireless access point LAN
English version 17
2.7.3Tileserver 22
The "Time Server" tab allows you to configure synchronization with a NTP Time server. You can select a
server from the prepared list or define your own.
2.7.4 Watchdog/Restart 23
Due to operating reasons it is sometimes suitable to restart the unit at automatically set intervals. In this case
use the "Watchdog/Restart" tab settings. This enables this function and also defines the interval for
automatic restart.
Another possibility is to restart the unit when there is a lost connection with the respective IP address. It is
necessary to define the test interval and one or two IP Addresses. IP address 1 is always checked during the
test and when the packet loss is more than 20%, it proceeds to test IP address 2. If the IP address testing
passes, IP address 2 is not tested. When neither IP address 2 is available, the unit will automatically restart.
2.7.5Networktest 24
The "Network Test" tab includes standard TCP/IP network testing tools. It provides Ping, Arping and
Traceroute tools, including the corresponding parameters. The test result is displayed in the lower window.
After entering the parameters use the "Send" button.

Configuration of the wireless access point LAN
English version 18
Chapter 3 Administration
3.1.1 Changing password 25
The "Change of Password" tab, as results from the name, allows you to change access passwords for unit
control.
The “Super-user Off” parameter can block the possibility to connect to the unit with a non-public password
set by producer.
3.1.2 Save/Restore configuration 26
The "Backup/Restore Configuration" screen enables to save the current configuration settings of the access
point. The saving of the configuration provides further security and a suitable manner of solving potential
problems with the access point when it is necessary to restore the default factory settings. If you save the
configuration setting, you can reload the saved configuration to the access point using the "Restore" button.
In the case of serious problems it is possible to use the "Restore the default factory settings" option. This
option resets all the configuration values of the Access Point to the default factory values.
3.1.3Update 27
The "Update" page allows you to update the software used by the unit, in the case that the unit is not
working as expected or new operation software is released. When you select the file to update, use the
"Restore" button. The update can take up to 180 seconds – do not interrupt the power of the unit during
this time. It is recommended to perform the update through metallic cable connection only.
When you connect to the unit using low data throughput connection, mark the "Slow Upload" tab. This will
make the transmission timeout longer.
3.1.4 Web interface 28
This page is used for configuration of the interface parameters for the unit service and its accessibility
from each port. In addition, you can define the TCP/IP port for access, which is appropriate, for example in
such cases, when it is necessary to release port 80 for reason of the www server in DMZ operation or by
port forwarding.
3.2 Restart
If the unit does not work correctly you can remotely restart the operating system. Your settings will not
be changed. You can perform the reset by clicking on the Restart button in the Main Menu. Restarting is
instant, without confirmation dialog.

Introduction
Česká verze 1
Chapter 4 Troubleshooting
This chapter provides solutions to problems usually occurring during the installation and operation of the
access point.
1. How to manually find your PC’s IP and MAC Address?
1) In Windows, open the Command Prompt program
2) Enter Ipconfig /all and press Enter.
yYour PC’s IP address is the one entitled IP address.
yYour PC’s MAC address is entitled Physical address.
2. What is Ad-hoc?
An Ad-hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers, each with a WLAN adapter, connected as an
independent wireless LAN.
3. What is Infrastructure?
Configuration of the infrastructure means an integrated wireless and wired LAN (interconnected by
cable).
4. What is BSS ID?
A group of wireless stations and an access point comprise a Basic Service Set (BSS). Computers in a
BSS must be configured with the same BSSID.
5. What is ESSID?
An Infrastructure configuration can also support roaming capability for mobile workers. More than one
BSS can be configured as an Extended Service Set (ESS). Users within an ESS can roam freely
between BSSs while maintaining a continuous connection to the wireless network stations and the
Wireless LAN Access Points.
6. Can data be intercepted while transmitting over the air?
WLAN features two-fold protection in security. On the hardware side, as with Direct Sequence Spread
Spectrum technology, it has the inherent scrambling security feature. On the software side, the WLAN
network offers an encryption function (WEP, WPA, WPA2) to enhance security and access control.
7. What is WEP?
WEP stands for Wired Equivalent Privacy, a data privacy mechanism based on a 64(40)-bit shared key
algorithm.
8. What is WPA?
WPA is an acronym for Wi-Fi Protected Access. It is a security protocol for 802.11 wireless networks.
WPA can provide data protection with the use of encryption and the use of access controls and user
authentication.
9. What is WPA2?
In addition to WPA, WPA2 provides a stronger encryption mechanism through Advanced Encryption
Standard (AES).
10. What is a MAC Address?
The Media Access Control (MAC) address is a unique number assigned by the manufacturer to any
Ethernet networking device, such as a network adapter, that allows the network to identify it at the
hardware level. For all practical purposes, this number is usually permanent. Unlike IP addresses,
which can change every time a computer logs on to the network, the MAC address of a device stays
the same, making it a valuable identifier for the network.

Introduction
Česká verze 2
Multifunkční přístupový bod
GWP-106VE
IEEE 802.11b/g
54Mbps
Uživatelský manuál
Straight
Core
Other manuals for GWP-106VE
1
Table of contents
Other STRAIGHT CORE Wireless Access Point manuals
Popular Wireless Access Point manuals by other brands

Grandstream Networks
Grandstream Networks GWN7662 Quick installation guide

Ruckus Wireless
Ruckus Wireless ZoneFlex 7762-S user guide

Dell
Dell PowerConnect W-AP175 installation guide

Edimax
Edimax EW-7206APg user manual

ZyXEL Communications
ZyXEL Communications NAP303 quick start guide

H3C
H3C WA2110-AG Quick start-up