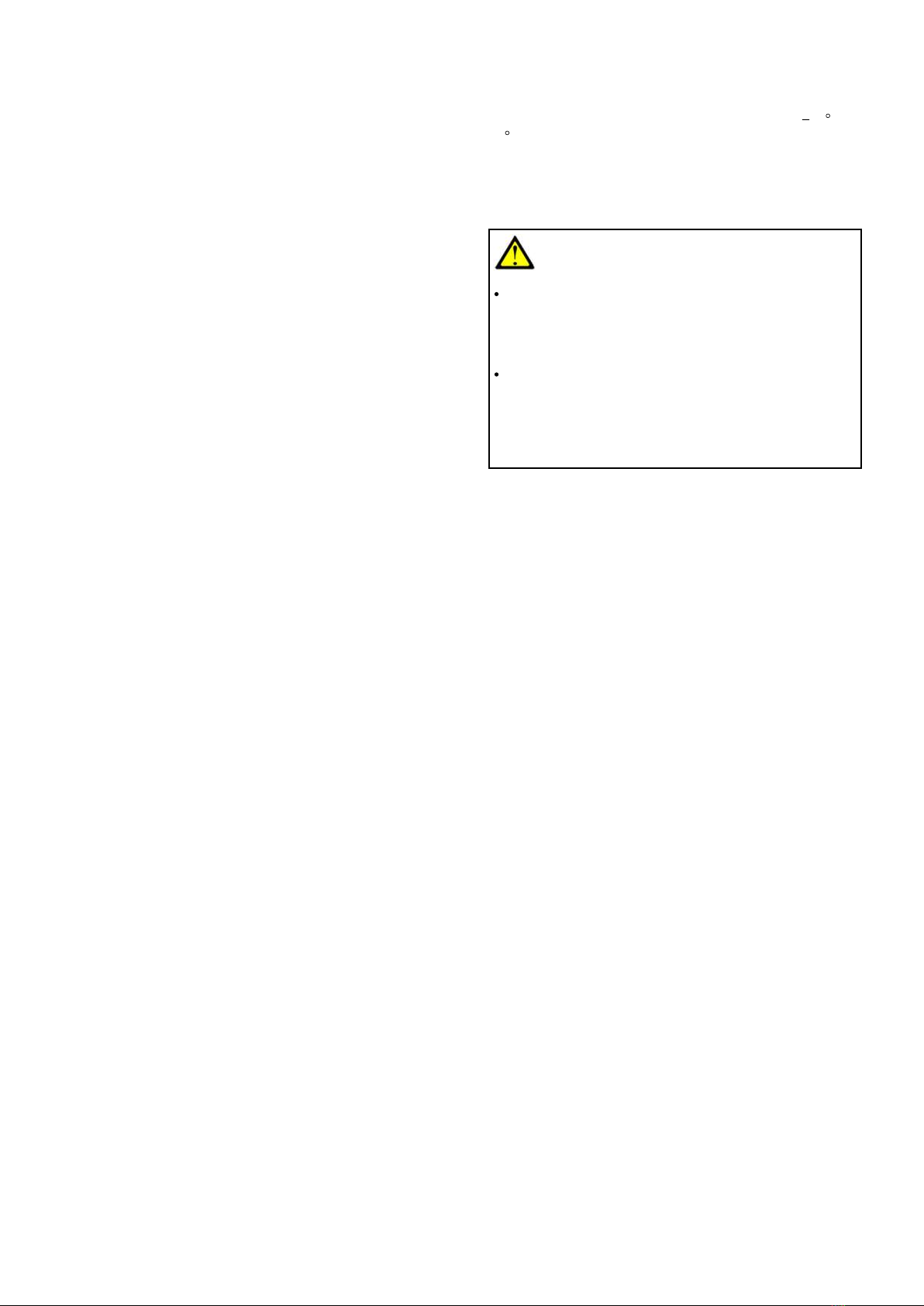
- 2 -
1. Things to be confirmed
upon arrival
Upon arrival of the pump, please check and
confirm followings:
(1) The specifications on the nameplate of the pump
match the order specifications.
(2) All accessories are in place.
(3) All bolts and screws are securely fastened.
Looseness may occur during transportation, so be
sure to check the casing and drain bolts for looseness
before trial operation.
(4) The pump has no visible damage during the
transportation.
(5) Remove the motor fan cover and check that the motor
fan can be turned easily by hand. If the rotation seems
heavy or the fan does not turn, there may be some
internal damage. Contact the vendor or supplier
immediately.
2. Safety precautions
Like other high-speed or high-pressure machinery, a
magnetic drive pump can be very dangerous if it is not used
properly. Special attention is required if a corrosive or
hazardous chemical is used.
Instructions listed as "Warning" must be followed to avoid
property damages or fatal accidents.
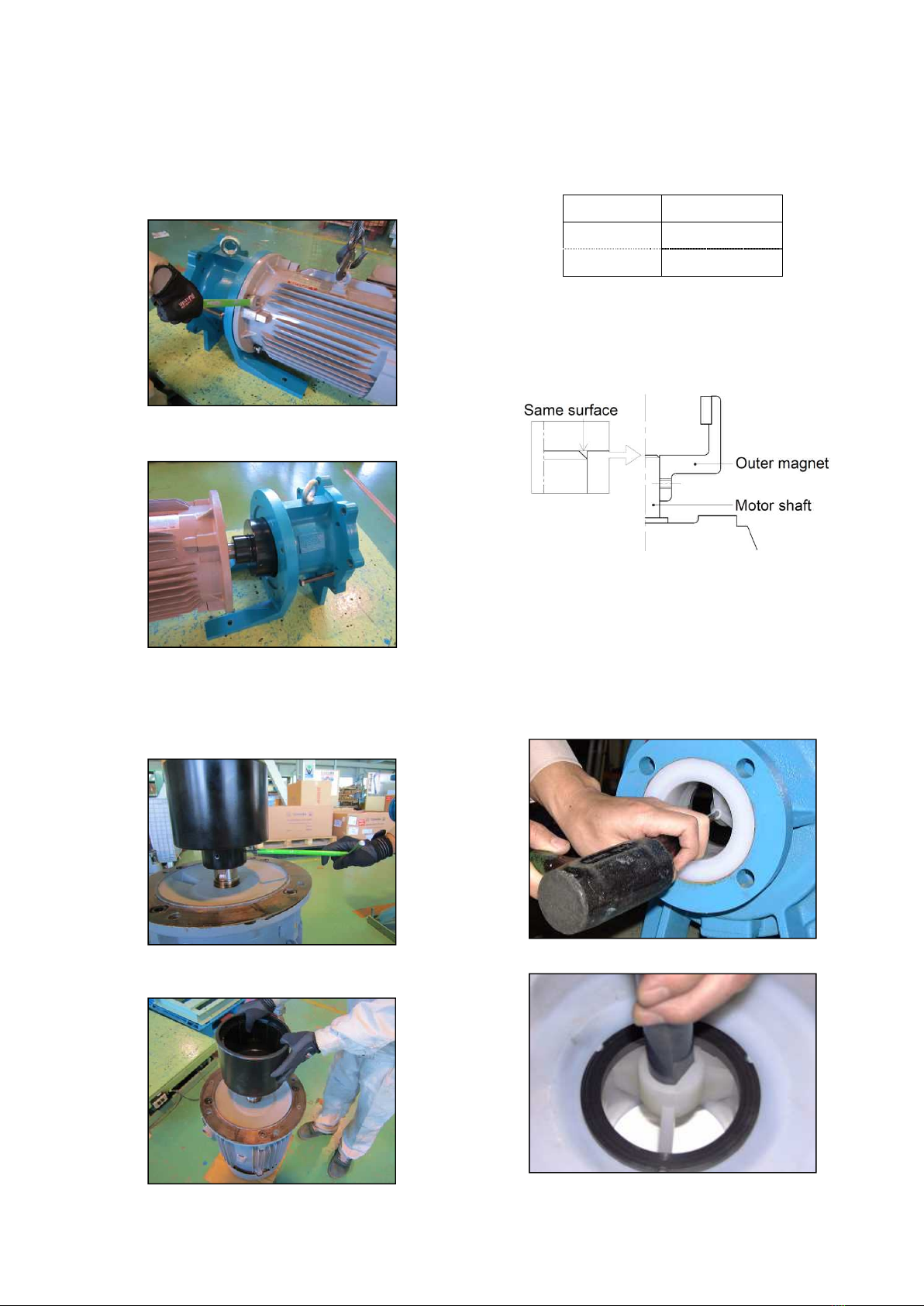
2.1. Transportation
The entire pump can be lifted using the eye-bolt provided on
the pump. However, ensure to secure the motor part with a
suspension rope (nylon sling) prior to the operation for
safety.
Warning
(1) An eye-bolt or a hooking hole provided on the motor
is rated only for the motor weight. Avoid suspending
the entire pump using the hooking hole on the motor.
(2) If a special base (not specified in the contract or listed
as standard) is set on the pump, do not suspend the
pump using the eye-bolt.
2.2. Confirmation
Before a test run after pump installation or a maintenance
work, make sure that all bolts including drain bolts and
casing bolts are securely fastened.
2.3. Application
The pump is designed and manufactured for the specific
application and specifications designated in the contract. If
the pump needs to be used for any other application, please
consult with the vendor or supplier prior to such use.
2.4. Alteration
Alterations to the pump carry a high degree of risk. It is not
the manufacturer’s responsibility for any failure or injury
resulting from alterations to the pump.
2.5. Ventilation
When handling chemical liquids that may generate harmful
gases, install safety equipment such as a ventilation system
in case of liquid leakage from the pump.
2.6. Qualified personnel only
The pump should be handled or operated by qualified
personnel with a full understanding of the pump. Any person
who is not familiar with the product should not take part in
the operation or management of the pump.
3. Storage
While in storage, perform maintenance and inspections by
following the instructions shown below until pump startup.
3.1.
Short-term storage (less than 3 months)
(1) Do not remove the bore seal.
(2) Store the pump in a well ventilated location without
humidity. Also ensure to avoid.
wind-blown rainwater, leak from the roof, pool of water, etc.
(3) Protect the cable holes on the motor terminal box with
a duct tape to close the gap and prevent dusts from
entering the box.
(4) Avoid a location where there is a potential risk of pump
damage due to surrounding equipments falling on the
pump or due to a contact with other devices being
transported. If it is not possible to avoid such locations,
provide sufficient protections for the pump.
(5) Do not place heavy objects on the pump.
(6) In winter, there is a possibility of dew condensation
and the dew being frozen inside the pump. Drain the
liquid to avoid this.
(7) In case a pump that had been used needs to be stored,
do the followings:
Clean the interior of the pump with fresh water.
Provide protections to the pump inlet and outlet to
prevent infiltration of foreign materials.
If the sum of initial operation period and the
storage period becomes longer than one year,
replace the gasket inspect the interior of the pump
before running it again.
3.2.
Long-term storage (more than 3 months)
(1) Follow instructions (1) through (7) for the short-term
storage stated above.
(2) Measure and record the insulation resistance at the
time of delivery and check it regularly as the insulator
of the motor may absorb moisture and the insulation
resistance may drop. If the insulation resistance is
dropped, dry the insulator following instructions from
the manufacturer and provide protection against
moisture. (Refer to the motor instruction manual.)
Warning
If the pump is run with poor insulation of the motor, a
leak of electricity or other accident may occur. Ensure
to check the insulation resistance regularly.
(3) Remove the motor fan cover once a month and turn
the motor fan manually.
(4) If the pump is run after a period of one year or longer,
ensure to replace the gasket with a new one.