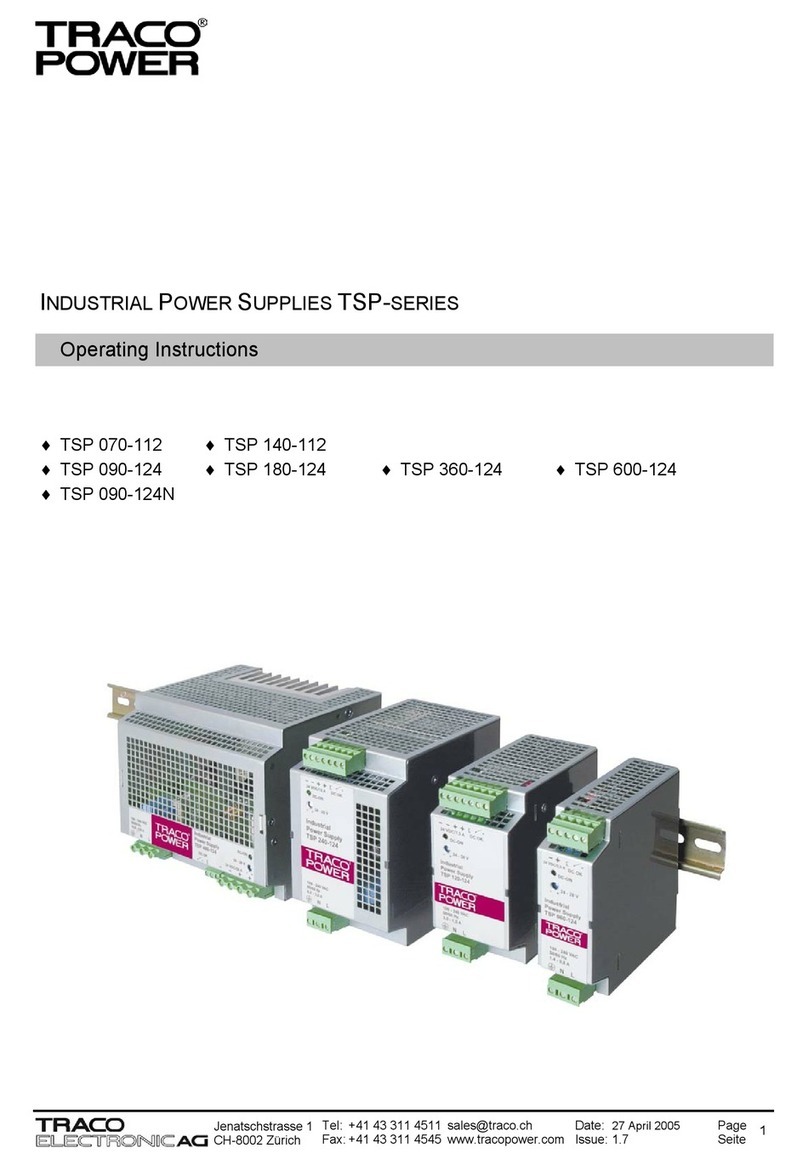
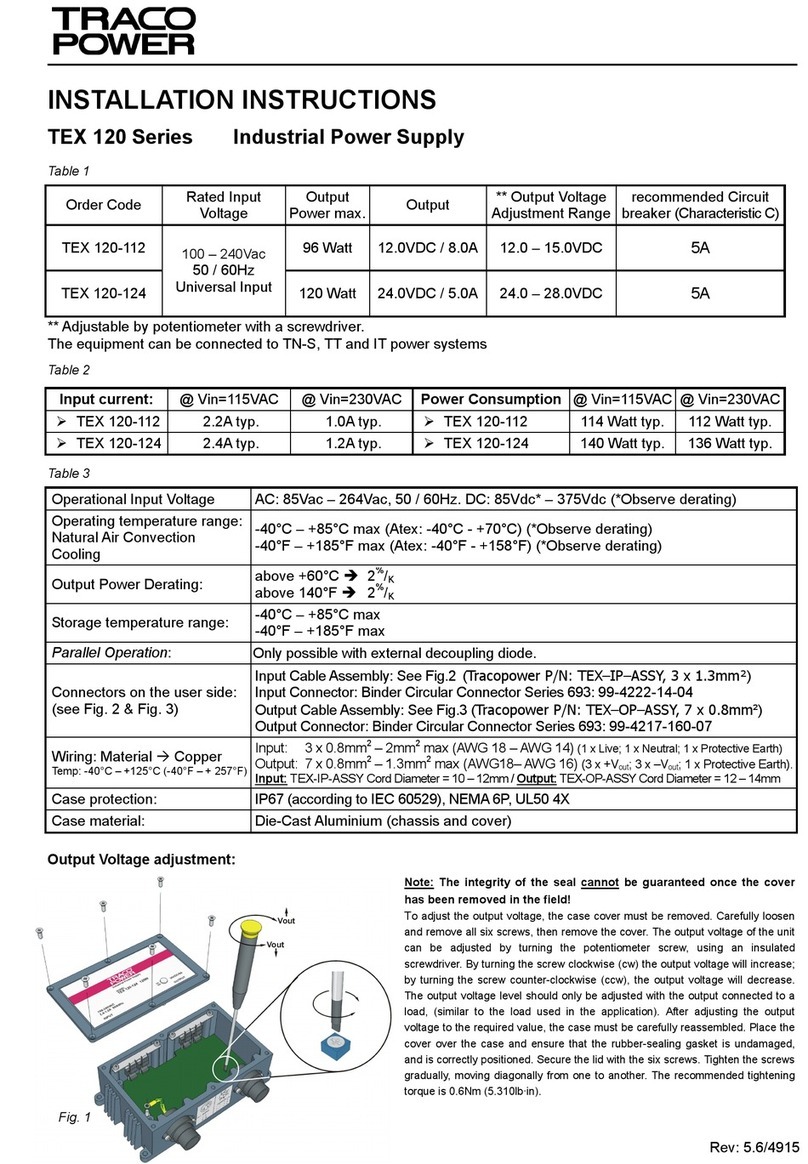
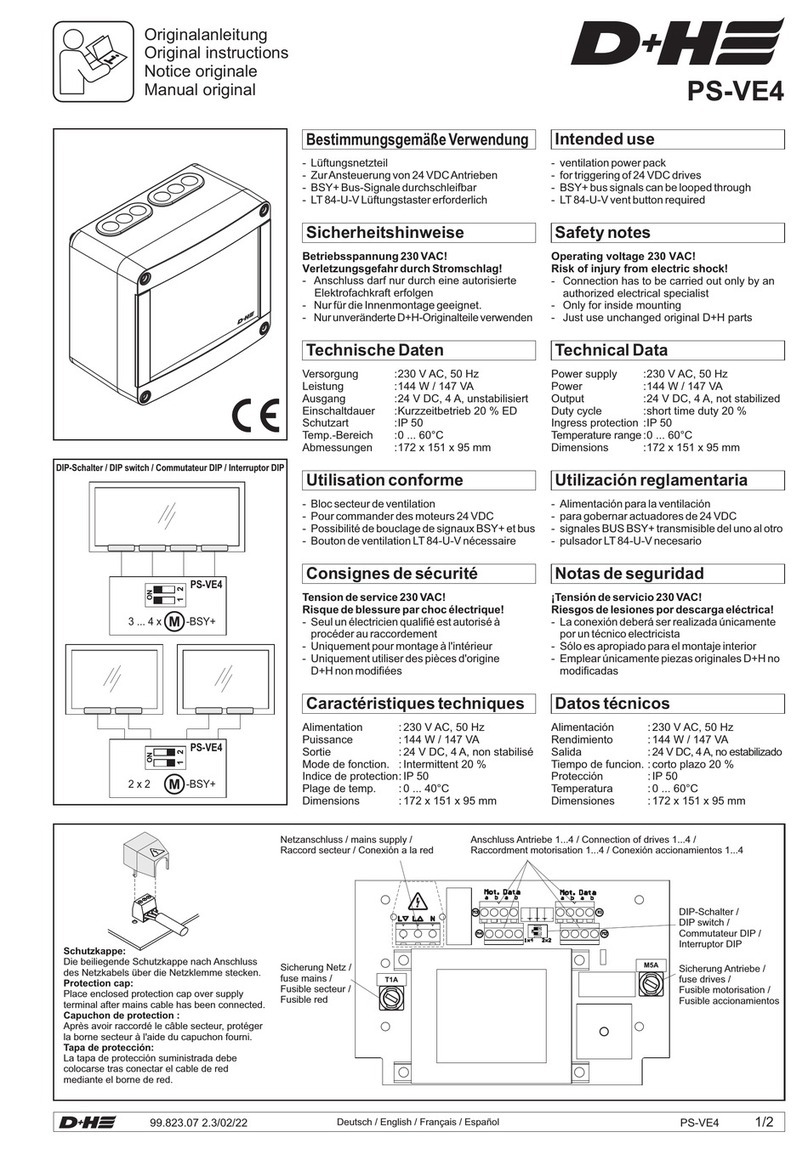
Deutsch
http://www.tracopower.com Page 5 of 8
Wird eine Justierung der Ausgangsspannung durchgeführt, so wird eine gleichmässige Stromaufteilung durch exakte Einstellung sämtlicher parallel
betriebener Stromversorgungen auf eine gleiche Ausgangsspannung gewährleistet. Für eine symmetrische Stromaufteilung empfehlen wir, alle
Kabelverbindungen von der Stromversorgung zu einer Sammelschiene in gleicher Länge und mit dem gleichen Leiterquerschnitt auszuführen!
Systembedingt sollte bei Parallelschaltung von mehr als zwei Stromversorgungen eine Schutzbeschaltung an jeden einzelnen
Stromversorgungsausgang installiert werden (z.B. Entkopplungsdioden oder DC-Sicherung). Somit werden bei einem Stromversorgungsdefekt hohe
rückwärtsgespeiste Ströme vermieden.
8.5 Redundanzbetrieb: (siehe auch TSP Datenblatt Seite 5)
Ein echter und sehr zuverlässiger Redundanzbetrieb kann mit dem Einsatz unseres Redundanzmoduls TSP-REM360 oder TSP-REM600 und zwei
Stromversorgungen aus unserer TSP Familie (TSP 070, TSP 090, TSP 140, TSP 180 und TSP 360 in Kombination mit TSP-REM360 oder TSP 600 in
Kombination mit TSP-REM600) gewährleistet werden, ohne das zusätzlich externe Komponenten angeschlossen werden müssen. Dieses Modul
sichert eine äquivalente Aufteilung des Ausgangsstroms jeder Stromversorgung. Dieses System ist wirklich redundant und stellt selbst dann noch die
volle Ausgangsleistung zur Verfügung auch wenn eine Stromversorgung ist komplett ausgefallen z.B. Kurzschluss am Ausgang. Kommt es zu einem
Stromversorgungsdefekt oder wird eine Stromversorgung abgehängt übernimmt automatisch die andere Stromversorgung unterbrechungsfrei die
vollständige Stromversorgung der Applikation. Die Redundanz des Systems ist überwacht und wenn die Redundanz nicht mehr gewährleistet ist, wird
dies mittels einem Signalausgang signalisiert.
8.6 Puffermodul: (siehe auch TSP Datenblatt Seite 5)
Das TSP-BFM24 Puffermodul hält die Ausgangsspannung konstant auf 24VDC, selbst wenn die Eingangsspannung für 10 voll 50Hz Zyklen ausfällt.
Für viele Applikationen ist dieses Modul eine ideale und kostengünstige Alternative zu einem Batterie-Backup System. Dieses Puffermodul beinhaltet
eine grosse Kondensatorenbank. Sobald die Stromversorgung eingeschaltet wird lädt sich dies Kondensatorenbank auf. Die Aufladung dieser
Kondensatorenbank dauert ca. 30 Sekunden und ein Optokoppler-Signal signalisiert wenn das Modul zum Einsatz bereit ist. Sobald die
Eingangsspannung abfällt wird die Kondensatorenbank entladen und hält die Ausgangsspannung am Puffermodul konstant auf dem nominalen Wert.
Diese Kondition wird mittels dem „Power-Fail Signal“ signalisiert. Die Überbrückungszeit beträgt typisch 200ms bei einem Ausgangsstrom von 25A und
typisch 4 Sekunden bei einem Ausgangsstrom von 1.2A. Nach 4 Sekunden schaltet das Puffermodul automatisch ab. Der Betriebsmoduls des Moduls
wird durch eine LED, in der Frontabdeckung, angezeigt. Der grosse Vorteil dieses Puffermoduls ist, das es wartungsfrei ist und die Speicherkapazität
sich über die Lebensdauer des Moduls nicht verändert.
8.7 Unterbrechungsfreies Stromversorgungssystem (UPS): (siehe auch TSP Datenblatt Seite 5)
Das TSP-BCM24 Modul sowie TSP-BCM24A stellt ein professionelles Batteriemanagementsystem, zum laden und überwachen von externen
Batterien, zur Verfügung. Mit einem Standardgerät der TSP Familie (TSP 090-124, TSP 180-124 oder TSP 360-124 in Kombination mit TSP-
BCM24 oder TSP 600-124 in Kombination mit TSP-BCM24A) zusammen kann ein perfektes DC-UPS System zusammengestellt werden. Die
angeschlossene Batterie wird durch die Stromversorgung geladen und in Schwebeladung gehalten. Bei einem Netzausfall stellt die Batterie die
Ausgangsleistung zu Verfügung, bis die Batterie entladen ist. Die Konsequenz dieses Systems ist, die Ausgangsspannung entspricht dem
Batteriespannungswert. Um eine Überladung der Batterie zu vermeiden wird die Ladespannung mittels einem Temperatursensor automatisch
justiert solange bis die eingestellte Ladespannung erreicht ist. Dadurch wird eine möglichst lange Batterielebensdauer gewährleistet.
Die Batterie ist gegen Tiefentladung geschützt. Eingangsspannung sowie der Batteriezustand wird in regelmässigen Abständen überwacht und
wird mittels LED sowie Alarmausgängen signalisiert. Um das Module sowie die Stromversorgung auszuschalten stellt das TSP-BCM24 Modul
und TSP-BCM24A Modul eine ON/OFF Schalter zur Verfügung.
8.8 Remote EIN/AUS:
Die TSP Stromversorgung stellt eine externe EIN/AUS Funktion zur Verfügung, indem der Pin 2 am Verbinder J3 (siehe Fig. 3.1, Fig. 4.1, Fig.
4.2, Fig. 4.3 und Fig. 4.4) benutzt wird. Über eine Verbindung mit einen 1k Widerstand zwischen Pin 2 Verbinder J3 (-S) und Verbinder J2,
Pin 1 (-Vout) wird die Stromversorgung ausgeschaltet. Sobald diese Verbindung unterbrochen wird, stellt die Stromversorgung die eingestellte
Ausgangsspannung wieder zur Verfügung.
9 Sicherung
10. ATEX Ergänzung zur Bedienungsanleitung
Um die ATEX Richtlinie zu erfüllen müssen folgende Installationsanweisungen beachtet werden.
1. Die Stromversorgungsgeräte Typenreihe TSP xxx-1xxEx sind in Schaltschränke oder in Schutzgehäuse einzubauen,
die den Anforderungen von EN 60079-15 oder ggf. EN 60079-0 entsprechen (Gehäuseschutzart min. IP54).
2. Der zulässige Umgebungstemperaturbereich beträgt -25°C bis +70°C.
3. Bein Einbau in Schaltschränke oder in Schutzgehäuse muss sichergestellt sein, dass an den Stromversorgungsgeräten
der Typenreihe TSP xxx-1xxEx die festgelegten maximal zulässigen Temperaturen (Ta) nicht überschritten werden.
4. Bei der Montage und Instandhaltung müssen die steckbaren Klemmen immer vollständig eingesteckt sein.
Insbesondere sind die Rastvorrichtungen an den Klemmen auf korrekte Arretierung zu überprüfen. Klemmen mit
defekten Rastervorrichtungen dürfen nicht verwendet werden.
5. Die Stromversorgungsgeräte Typenreihe TSP xxx-1xxEx sind nach RL 94/9/EG (ATEX 95) Anhang I Komponenten
(Ex-Bauteile) der Gerätegruppe II Kategorie 3G. Für den Einbau dieser Komponenten ist ein gesondertes
Konformitätsbewertungsverfahren am Endgerät, wo diese Komponenten eingebaut werden, durchzuführen.
Bei der Verwendung / Installation sind im weiteren die Anforderungen nach EN 60079-14 einzuhalten.
Modell Auslegung Beschriftung Achtung: Um einen dauernden Schutz gegen Feuergefahr zu
gewährleisten muss die Sicherung mit einer Sicherung
gleichen Typs und Wert ersetzt werden! Das Ersetzen der
Sicherung sollte nur durch autorisiertes und geschultes Personal
erfolgen, da die Sicherung eingelötet ist.
Löst die interne Sicherung aus, liegt mit hoher Wahrscheinlichkeit ein
Gerätedefekt vor. In dem Fall ist eine Überprüfung des Gerätes im
Werk erforderlich. Dazu returnieren Sie das Gerät zum lokalen
Lieferanten.
TSP 070-112 4.0 AH/250V F1 4.0 AH/250V
TSP 090-1xx(N) 4.0 AH/250V F1 4.0 AH/250V
TSP 140-112 4.0 AH/250V F1 4.0 AH/250V
TSP 180-1xx 4.0 AH/250V F1 4.0 AH/250V
TSP 360-1xx 6.3 AH/250V F1 6.3 AH/250V
TSP 600-1xx 12.0 AH/250V F1 12.0 AH/250V