Victor V30-RA User manual
Other Victor Calculator manuals

Victor
Victor V10 User manual

Victor
Victor 1230-4 Series User manual

Victor
Victor 1100-2 User manual

Victor
Victor 1208-2 Series User manual

Victor
Victor 1225-3A Series User manual

Victor
Victor VCT11802 User manual

Victor
Victor 1260-3 User manual

Victor
Victor 1205-4 User manual

Victor
Victor 1212-3A Series User manual

Victor
Victor 1260-3 User manual
Victor
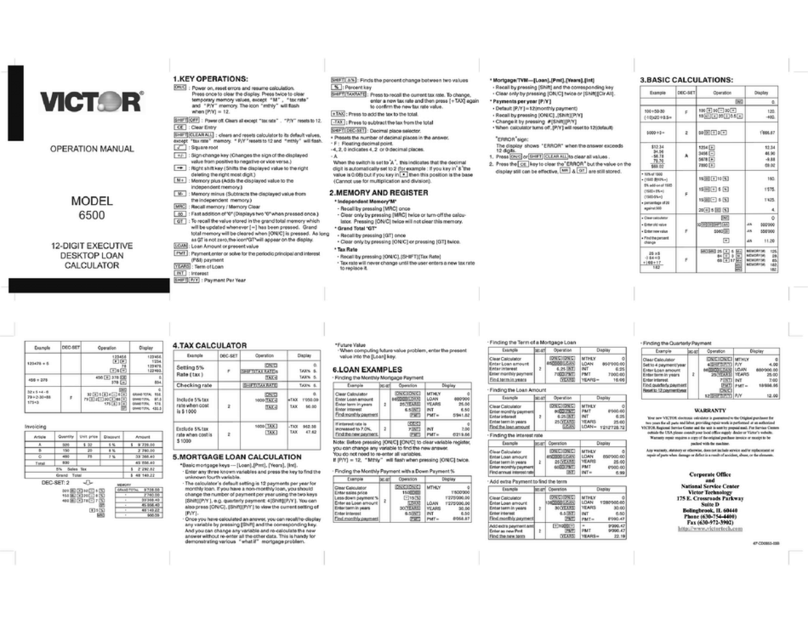
Victor 6500 User manual

Victor
Victor 1225-3A Series User manual

Victor
Victor 1170 User manual

Victor
Victor Big Print 1310 User manual

Victor
Victor VCT700 User manual

Victor
Victor V12 User manual

Victor
Victor 1228-2 Series User manual

Victor
Victor C5000 User manual

Victor
Victor PL3000 User manual

Victor
Victor 1212-2 Series User manual
Popular Calculator manuals by other brands

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments BA II Plus user guide

Kompernass
Kompernass KH 2283 instruction manual

Helwett Packard
Helwett Packard 9100A Operating and programming manual

Calculated Industries
Calculated Industries 3423 user guide

Calculated Industries
Calculated Industries Qualifier Plus IIcx user guide

HP
HP 35s Instruction guide