VA41620/VA41630 Evaluation Board User’s Manual
V1.0
1
Contents
1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................... 2
1.1 Purpose of Document .................................................................................................... 2
1.2 Overview of Hardware and Software components ........................................................ 2
1.3 Key components included on the PEB1 evaluation kit (subject to change depending on
availability). ................................................................................................................................ 2
1.4 PEB1 MCU board component placement diagram ........................................................ 5
1.5 Connector pin assignment table for MCU board ........................................................... 6
1.6 Materials List .................................................................................................................. 7
1.7 Board connectivity ......................................................................................................... 7
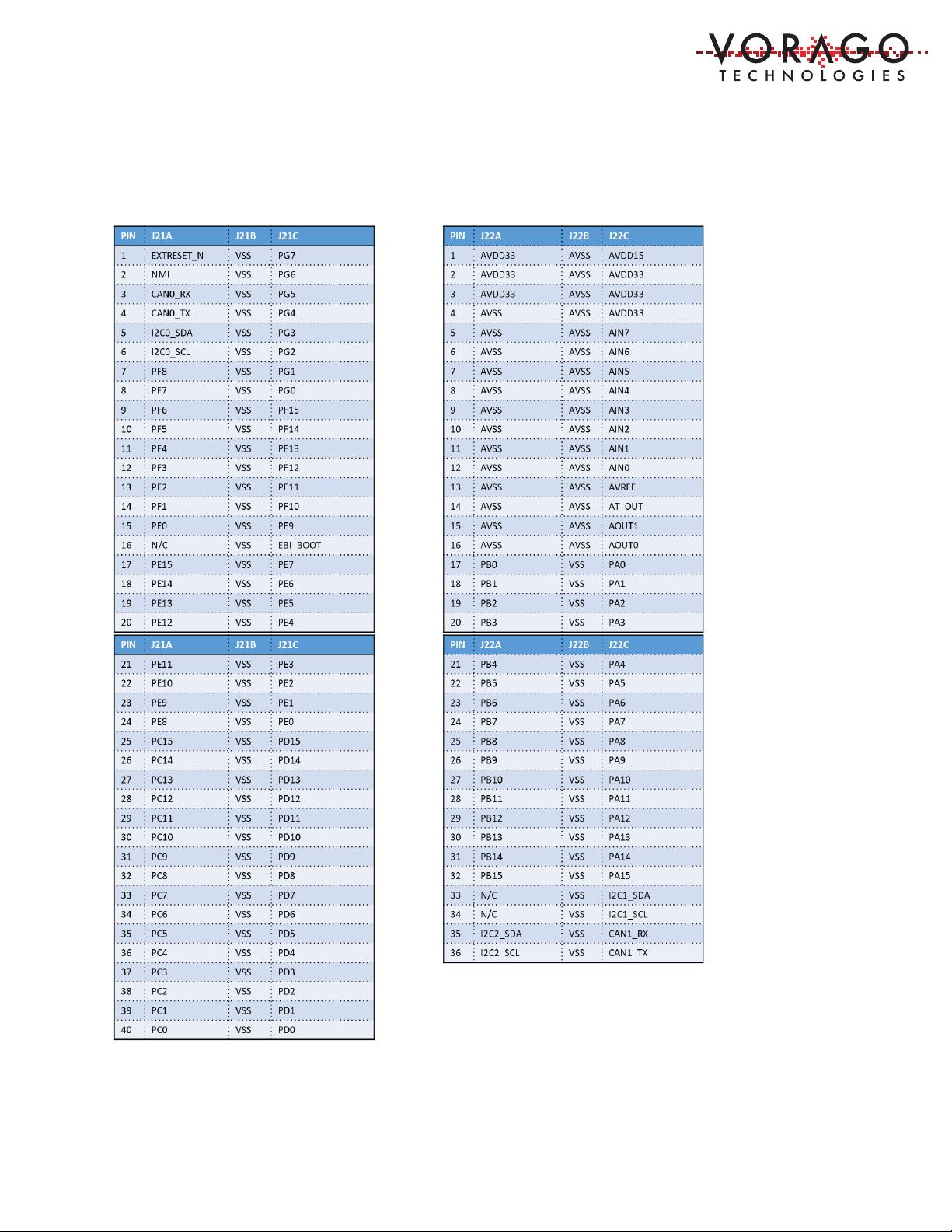
1.8 Connector pin assignment table for GPIO board ........................................................... 8
1.9 Support ......................................................................................................................... 13
2 Software Setup ..................................................................................................................... 13
2.1 Required Downloads .................................................................................................... 14
3 Hardware check ................................................................................................................... 17
3.1 Powering up the board ................................................................................................. 17
4 Command line control of the EVK ........................................................................................ 17
4.1 J-Link OB and RTT (Real Time Terminal) ....................................................................... 20
5 Starting an IDE and building a program ............................................................................... 23
5.1 Keil IDE – ....................................................................................................................... 23
5.2 Programming procedure (Keil Specific) ........................................................................ 31
6 Software Development Kit ................................................................................................... 33
6.1 Project organization ..................................................................................................... 33
6.2 CMSIS compatible driver .............................................................................................. 34
6.3 Preprocessor directives ................................................................................................ 34
7 Commonly asked questions ................................................................................................. 35
8 Other resources for VA416x0 code ...................................................................................... 36
9 Revision history .................................................................................................................... 36