WVD100
Product Manual
WVD100, Rev 2.5E Page 9
EZ Loop
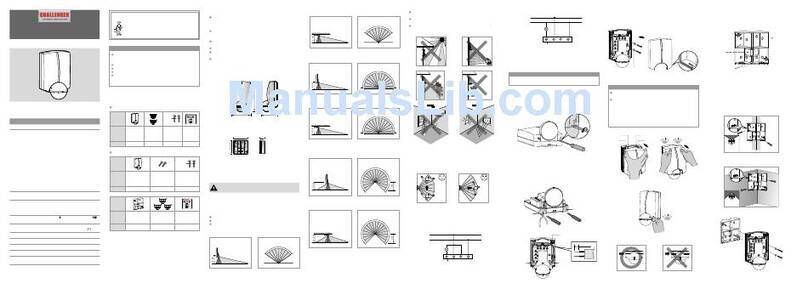
Sensor Slide Gate Layout:
The following diagram shows a typical slide gate application for
two-way traffic with a free exit. For one-way traffic, the exit
sensor is not needed. (This diagram is a basic layout and does not
show safety devices, pedestrian gate, fencing, etc. Refer to the
gate operator manual for proper details).
Most slide gate applications
will use a Reverse Sensor on
the outside and inside of the
gate, and an Exit/Open Sensor
further down the driveway.
Reverse Sensors are used to
keep the gate from timing out.
When a vehicle is over a
Reverse Sensor, the gate
operator should remain open
until the Reverse Sensor is
cleared and then the gate
operator should time out and
close. A Reverse Sensor is
used on the outside and inside
of the gate so that a vehicle in
the path of the gate should be
within the detection range of
either the outside or inside
Reverse Sensor. Only
installing one Reverse Sensor
will not offer proper detection
coverage.
An Exit/Open Sensor can be
used inside the gate and
further down the driveway as a
convenient way to
automatically open the gate
when a vehicle is leaving the
property. An Exit/Open Sensor
can be up to 20-25ft away
using the S200P Sensor or up
to 75ft using the Above
Ground Cap.
To layout a standard slide gate application:
1. Place the sensor in the center of the traffic lane.
2. Determine if one or multiple sensors will be needed for full detection
across a wide traffic lane.
3. Place the sensor far enough away from the gate so the moving gate
does not activate the sensor. This is usually 8-10 feet from the gate.
4. Mark the location of where each sensor will be installed.
Sensor Swing Gate Layout:
The following diagram shows a typical swing gate application for
two-way traffic with a free exit. For one-way traffic, the exit
sensor is not needed. (This diagram is a basic layout and does not
show safety devices, pedestrian gate, fencing, etc. Refer to the
gate operator manual for proper details).
Most swing gate applications will
use a Reverse Sensor on the
outside and inside of the gate,
and an Exit/Open Sensor down
the driveway. Some applications
will use a Shadow Sensor to cover
the swing area of the gate.
Reverse Sensors are used to keep
the gate from timing out. When a
vehicle is over a Reverse Sensor,
the gate operator should remain
open until the Reverse Sensor is
cleared, then the gate operator
should time out and close. A
Reverse Sensor is used on the
outside and inside of the gate so
that a vehicle in the path of the
gate should be within the
detection range of either the
outside or inside Reverse Sensor.
Only installing one Reverse Sensor
will not offer proper detection
coverage and the addition of a
Shadow Sensor may be needed.
A Shadow Sensor is used to cover
the swing area of the gate when
the Reverse Sensors are too far
apart to cover a vehicle in
between. Test the Shadow Sensor
prior to installing to make sure it
does not pickup the gate.
An Exit/Open Sensor can be used
inside the gate and further down
the driveway as a convenient way
to automatically open the gate
when a vehicle is leaving the
property. An Exit/Open Sensor
can be up to 20-25ft away using
the S200P Sensor or up to 75ft
using the Above Ground Cap.
To layout a standard swing gate
application:
1. Place the sensor in the center of
the traffic lane.
2. Determine if one or multiple sensors will be needed for full detection
across a wide traffic lane.
3. Place the sensor far enough away from the gate so the moving gate
does not activate the sensor. This is usually 8-10 feet from the gate.
Note: The Reverse Sensor near the swing of the gate should be 8-10
feet from the swing path of the gate.
4. Mark the location of where each sensor will be installed.
Vehicular Gate Only
8-10
Feet
2-3
Feet
Reverse
2-3
Feet
Exit/Open
8-10
Feet
Reverse
2-3
Feet
8-10
Feet
Vehicular Gate Only
Shadow
8-10
Feet
Reverse
2-3
Feet
Reverse
2-3
Feet
Exit
2-3
Feet