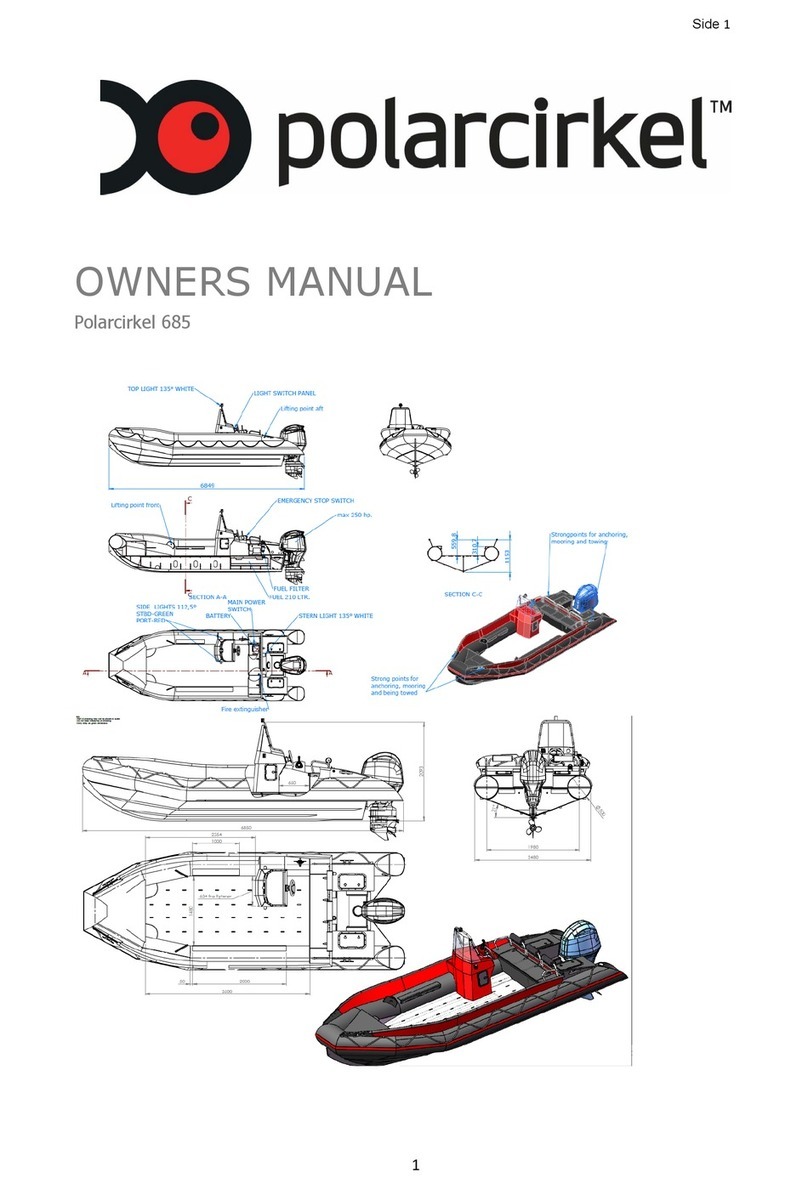
6
6 20of
DOCUMENT PART:DOCUMENT NO:
10001800DC10000901 C
REVISION NO:
2 ABOUT AKVA SUBSEA FEEDER
The AKVA Subsea Feeder is manufactured by Nærøysund Aquaservice AS, who has the following
business address: Marøystrand Næringsområde, Marøystrandvegen 29, NO-7900 Rørvik,
Norway. Telephone: + 47 51 77 85 03. E-mail: supportakvasmart@akvagroup.com
Variants of the AKVA Subsea Feeder: AKVA Subsea Feeder Long (13 m +)
AKVA Subsea Feeder Standard (7 m)
AKVA Subsea Feeder Short (4 m)
The AKVA Subsea Feeder is a feeding system designed for sea-based sh farming sites. It
enables underwater feeding at a maximum depth down to 20 m. The purpose of feeding sh
deeper in the water column is to keep the sh at a certain depth and prevent lice from attaching,
and also enhance growth of the sh. Lice thrive near the surface, which is why keeping the sh
at a deeper level reduces the spread of lice in the cage.
Feed pellets are delivered to the cage through a normal air hose and enters the cyclone at the
top of the feeder tangentially, where the pellet speed is reduced. A spiral motion circulates the
pellets down into the cyclone until they reach the water level at the top of the main pipe and
then sink. The pellets are transported down into the distribution chamber and then distributed
evenly via a cone shape out to the sh through 12 branching pipes that spread the feed across
an area with a circumference of about 17 m. The feed is transported at a speed of up to 50 kg
per minute, and experience has shown that bird nets are not necessary when feeding with the
AKVA Subsea Feeder.
When using an long feeder (13 meter feeding depth or deeper) or using smolt feed, we
recommend creating a current in the water column in the main pipe. This is achieved by using
a pump to collect water from a deeper level, and pumping it up into the distribution chamber,
where an ejector generates negative pressure in the main pipe. Water from the same depth
as the pump is transported into the top of the main pipe to create a downward pressure that
forces the water down through the pipe. This downward motion is maintained as the pellet-and-
water mixture moves down through the main pipe. This motion ensures that the branching pipes
distribute the feed to the sh evenly at the correct depth.
Pellets are transported to the cage through a feed pipe, and enters the cyclone at the top of the
AKVA Subsea Feeder tangentially. Here, water is also added in the same tangential direction.
The water and feed combine and generates a cyclonic motion, that is maintained as the mixture
travels down through the main pipe and out in the desired depth. The water intake pipe is tted
with a lter to prevent planctonic stages of salmon lice from entering the feeding system.
The sinker tube that encircles the branching pipes is weighted to provide stability.
The AKVA Subsea Feeder pump requires 230 V/50 Hz – 970 W and is delivered with a power
cable that reaches the edge of the cage, where the user then ensures sucient power supply.
The feeder may be used without the pump, but in such case, we recommend removing the lter
in the riser pipe to avoid pellet build-ups. Choosing not to use a pump will require monitoring the
process with extra care, particularly for large doses.