RadonXTM Technical Manual and Installation Methods Guide 3
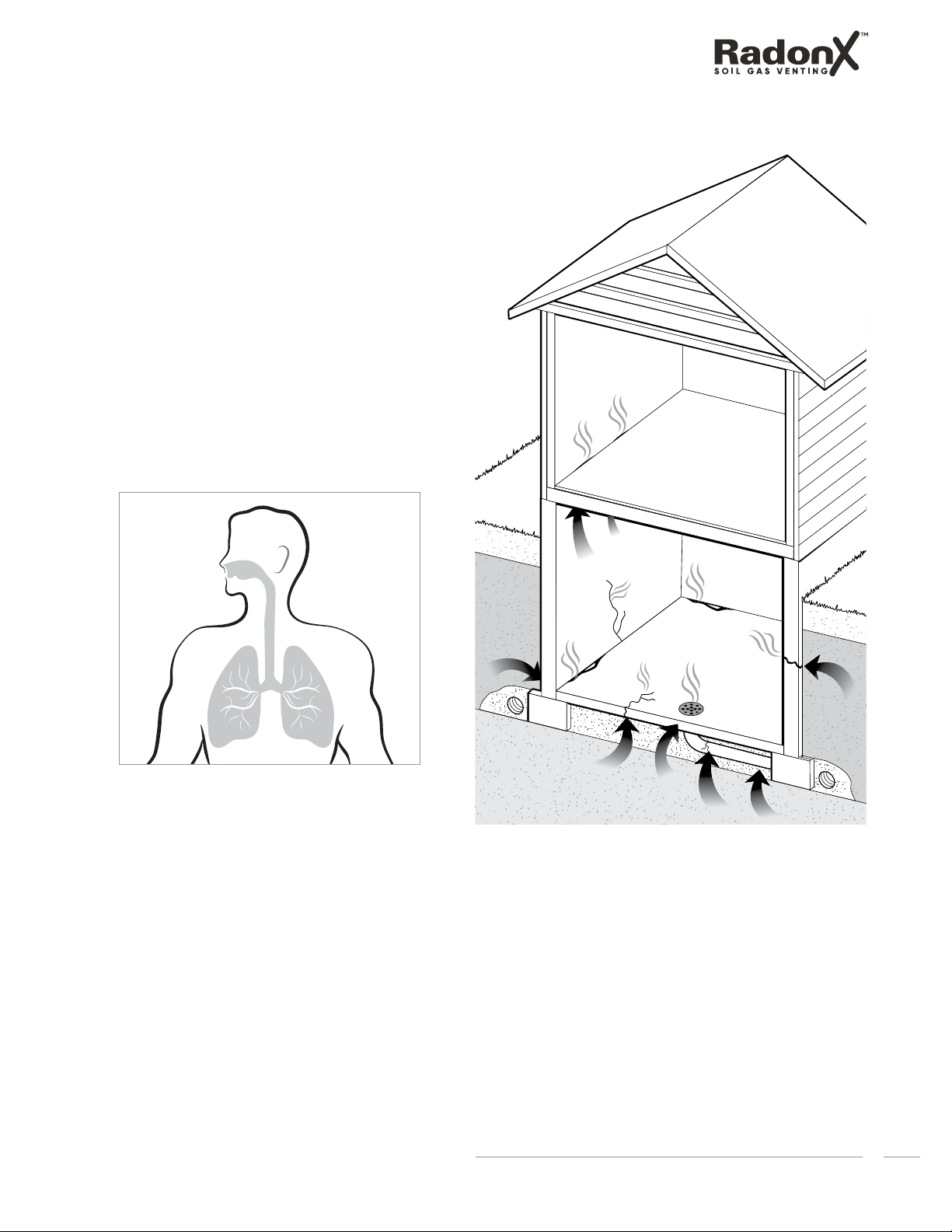
Product Application
RadonXTM Soil Gas Venting (SGV) Piping System is
intended to vent soil gases and help reduce indoor
radon concentrations in low-rise construction. RadonX
pipe and fittings satisfy the requirements of the National
Building Code 2015.
Limits of Use and Application
(a) RadonX does not treat or cure lung cancer.
(b) All RadonX soil gas venting pipe and fittings must
be carefully examined for possible damage prior
to installation. Any damaged product must be
replaced. No attempt at repairs are to be made at
the job site.
(c) Soil gas venting application will cause the piping
system to expand and contract accordingly. Proper
care must be taken to allow for this movement
through walls, ceilings, and roof penetrations. The
venting system must be supported in accordance
with these instructions.
(d) Use RadonX cement and System 636®primer to
assemble RadonX soil gas venting systems.
(e) Venting should be as direct as possible with a
minimum number of fittings.
(f) Horizontal runs should be minimized.
(g) All horizontal sections of the venting system must be
installed with a slope not less than 1% down towards
the riser in order to collect condensate and remove
condensate generated inside the line. The removal
of condensate will help reduce the possibility of ice
buildup and blockage.
(h) All framing requirements for floor and ceiling
penetrations shall be in accordance with the
local building code and/or the local regulatory
authority. All penetrations of fire rated floors and
walls in multi-unit residential shall be firestopped as
described in the Firestop section of this guide.
(i) Roof penetrations should be sealed with a
plumbing roof boot or equivalent flashing as per
the local building code, or as permitted by the local
regulatory authority.
(j) If spray foam insulation comes in contact with
RadonX, it is recommended that foam be applied in
a maximum layer thickness of 50mm (2 inches) until
the required thickness of insulation is achieved.
(k) Do not use or install perforated RadonX pipe above
ground.
(l) All RadonX piping system in unconditioned space
shall be insulated as described in the Above Grade
RadonX piping system installation section of this
guide.
DO NOT mix pipe, fittings or joining methods from
different manufacturers as they have different joint
systems and adhesives. This can result in unsafe
conditions and cause radon gas leak.
WARNING
DO NOT use or mix RadonX components with other IPEX
pipe and fittings. DO NOT use RadonX in applications
other than soil gas venting. These can result in unsafe
conditions.
WARNING
RadonX is a combustible piping system and as such
will be subjected to all conditions and limitations
of the Building Code for above-ground use in Non-
Combustible (commercial) buildings. For further
information, contact IPEX.
NOTICE
Follow IPEX solvent welding procedures as shown in
this guide, and check for proper joint construction
when joining pipe to fittings.
NOTICE
RadonX is a PVC piping system to be used in soil gas
depressurization systems to reduce indoor radon
concentrations. Once the building is occupied,
continued radon concentration measurements shall
be performed. Consult the C-NRPP, National Radon
Proficiency Program at c-nrpp.ca for details as to
frequency and guidelines to follow. If measured
radon gas concentrations exceed the Canadian
guideline level, contact a mitigation professional
certified by a C-NRPP.
WARNING