5
ATIM_1GATE_INDUS2_UG_EN_V1.2
Waste disposal by users in private households within the European Union. This symbol appears on a product or
its packaging to indicate that the product may not be discarded with other household waste. Rather, it is your
responsibility to dispose of this product by bringing it to a designated collection point for the recycling of
electrical and electronic devices. Collection and recycling waste separately at the time you dispose of it helps
to conserve natural resources and ensure a recycling process that respects human health and the environment.
For more information on the recycling center closest to your home, contact your closest local government office,
your local waste management service or the business from which you purchased the product.
Radio
Modems in the ACW line are radio-communication modems that use the ISM (industrial, scientific and medical) bands,
which may be used freely (at no cost and with no authorization required) for industrial, scientific and medical
applications.
IMPORTANT NOTE
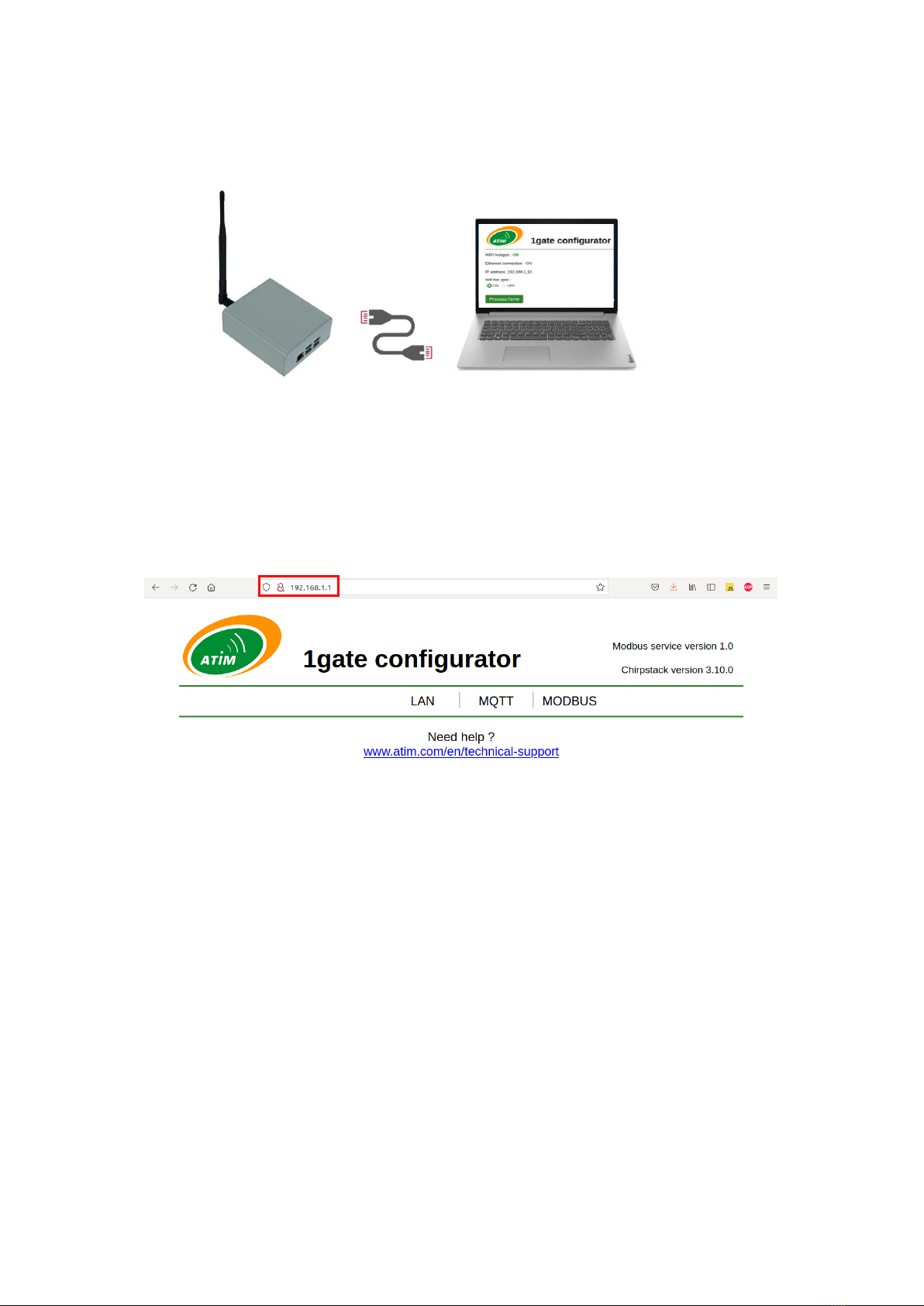
- Basic IT network knowledge is required to set up ATIM LoRaWAN gateways.
- Contact your IT service before installing the gateway.
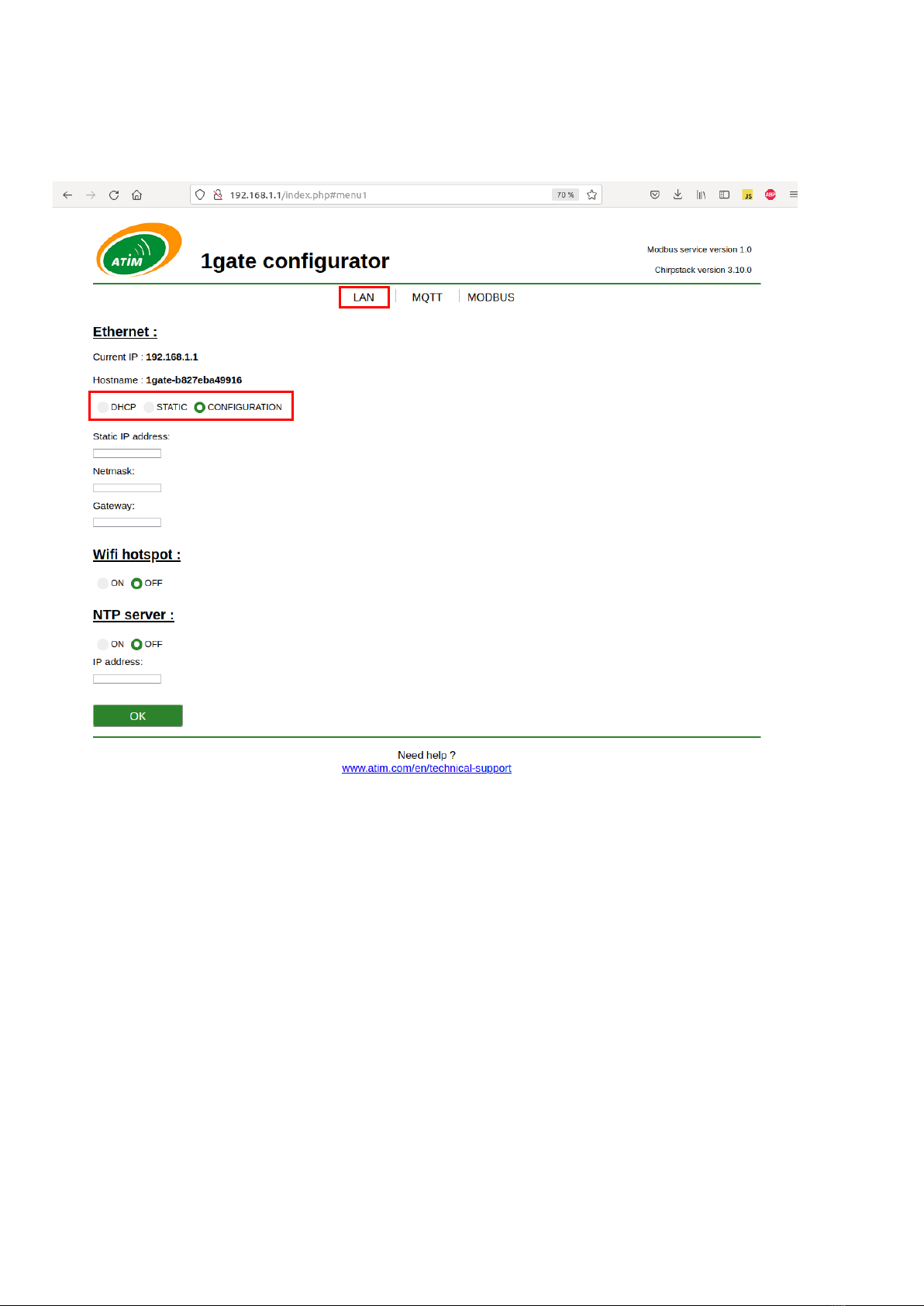
- Configuration options are explained in this document.
- Further details about Chirpstack network server are available on https://www.chirpstack.io/
- Gateway power supply is 5VDC 2,5A max.
LoRaWAN 868 MHz antenna should be connected to SMA connector before starting the gateway.