CONTENTS
SVM Series Operating & Instruction Manual Page iv
GENERAL ................................................................................................................................................. 1
Noise levels .......................................................................................................................................... 1
Area of operation ................................................................................................................................. 2
Spare parts ........................................................................................................................................... 2
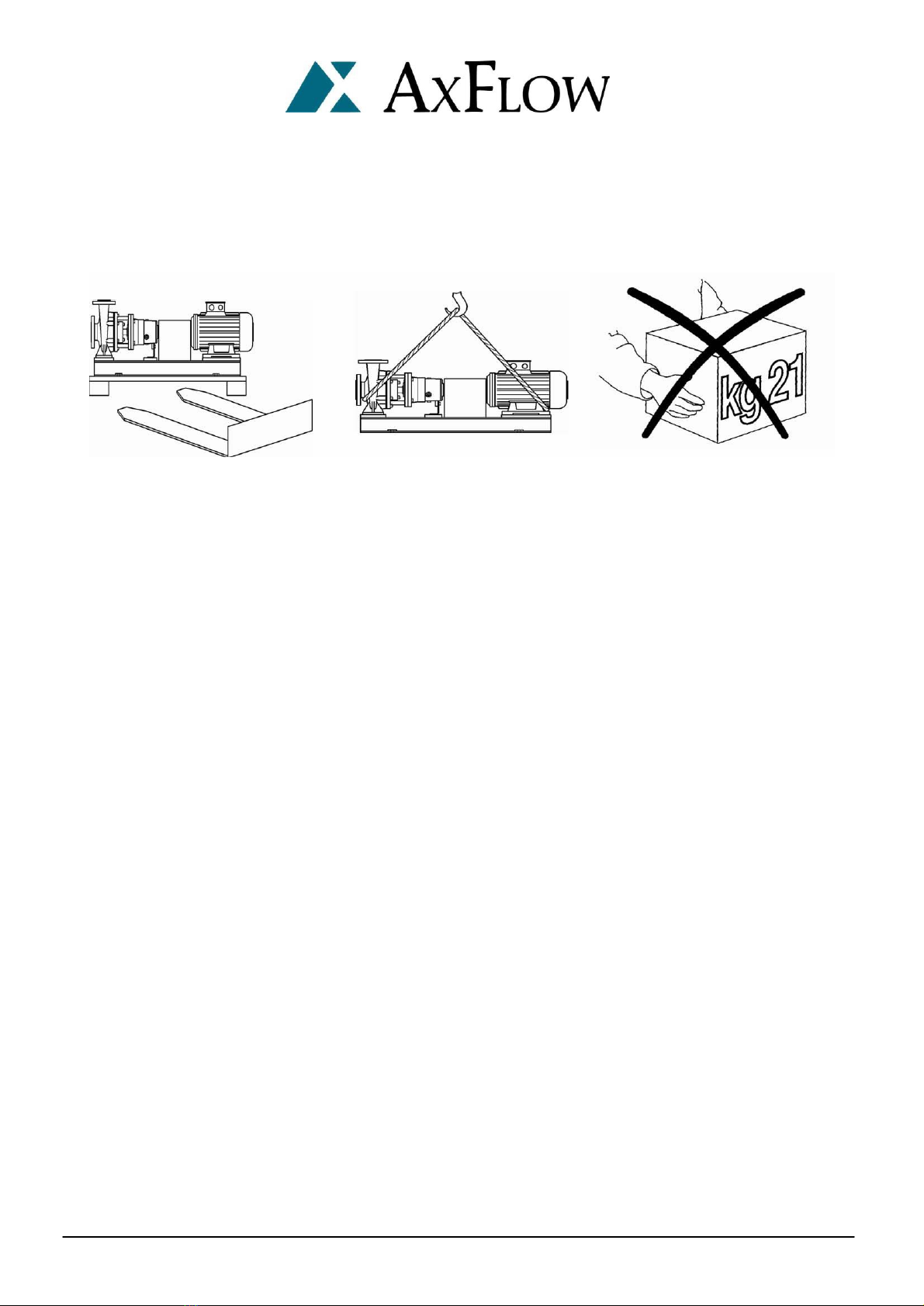
Transport ............................................................................................................................................. 3
Storage ................................................................................................................................................ 3
Drivers ..................................................................................................................................................4
INSTALLATION........................................................................................................................................ 5
Foundations ......................................................................................................................................... 5
Close-coupled motor-pump unit without baseplate ......................................................................... 5
Motor-pump units on baseplates...................................................................................................... 5
Pump and motor alignment .................................................................................................................6
Methods of checking alignment ........................................................................................................... 7
Straight edge.................................................................................................................................... 7
Dial gauge ("clocking") ..................................................................................................................... 8
Optical methods ............................................................................................................................... 8
Location and piping .............................................................................................................................. 8
Admissible external forces and torques on pump flanges .................................................................. 11
Protecting the pump against Dry Running ......................................................................................... 12
Loss of liquid supply ....................................................................................................................... 12
Low inlet pressure .......................................................................................................................... 12
`Dead-heading'............................................................................................................................... 12
Electronic dry running protection ....................................................................................................... 12
Electrical connection .......................................................................................................................... 13
Connecting the electric motor ........................................................................................................ 13
Check direction of rotation ................................................................................................................. 14
Long-coupled pumps only .............................................................................................................. 14
Direction of rotation ....................................................................................................................... 15
OPERATION .......................................................................................................................................... 16
Supervision ........................................................................................................................................ 16
Essential running precautions ............................................................................................................ 16
Priming the pump .............................................................................................................................. 19
Pump operation ................................................................................................................................. 20
MAINTENANCE ..................................................................................................................................... 22
Supply isolation .................................................................................................................................. 22
Maintenance schedule ....................................................................................................................... 22
DISASSEMBLY ....................................................................................................................................... 23
Strong magnet essential precautions ................................................................................................. 23
Decommissioning the pump .............................................................................................................. 24
Disassembling the pump .................................................................................................................... 24