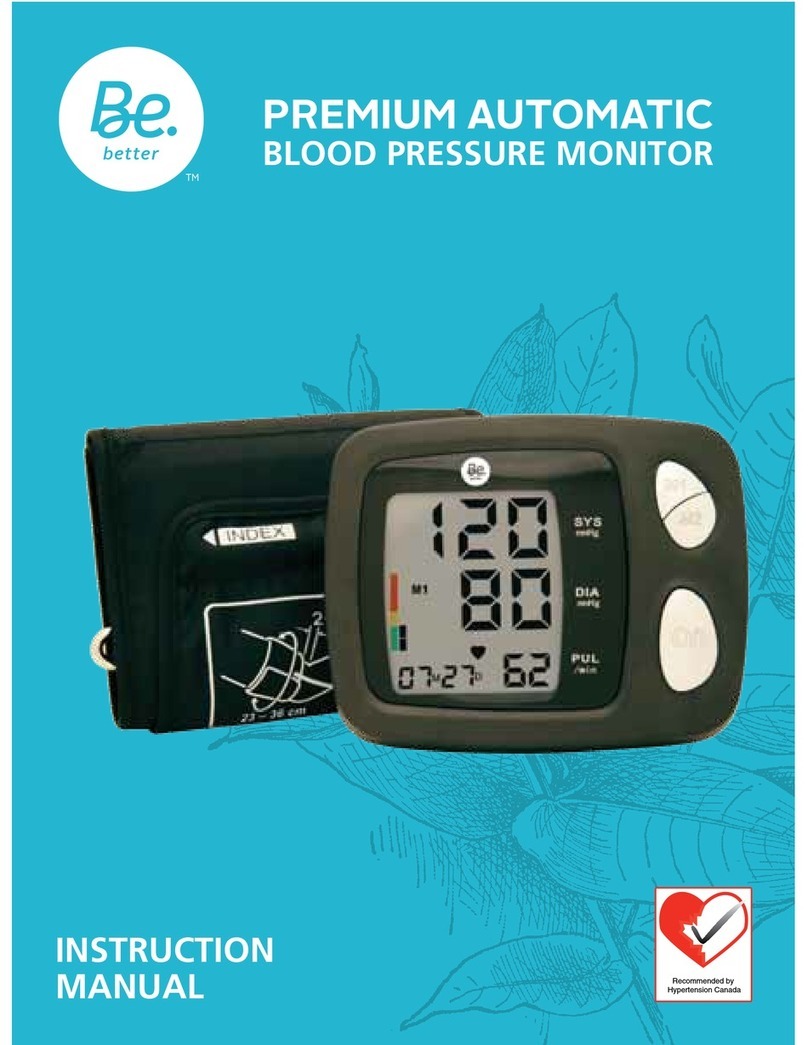
Be.Better PREMIUM PLUS BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR User manual

INSTRUCTION
MANUAL
UCTION
AL
Recommended by
Hypertension Canada
R
PREMIUM PLUS
BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR

1
Advanced Blood Pressure Monitor - Instruction Manual
Table of contents
1. Introduction
1.1. Features of your blood pressure monitor
1.2. Important information about self measurement
2. Important Information on Blood Pressure and its Measurement
2.1. How does high/low blood pressure arise?
2.2. Which values are normal?
2.3. What can be done if regular high/low values are obtained?
3. Components of your Blood Pressure Monitor
4. Using your Monitor for the First Time
4.1. Installing the batteries
4.2. Setting the date and time
4.3. Cuff tube connection
4.4. Select the measuring mode: Standard or Averaging Mode
4.5. Select the user
4.6. Averaging Mode
5. Measurement Procedure
5.1. Before measurement
5.2. Common sources of error
5.3. Fitting the cuff
5.4. Measuring procedure
5.5. PAD - Pulse Arrythmia Detection
5.6. Traffic Light Indicator
5.7. Memory - Displaying the last 120 measurements
5.8. Discontinuing a measurement
5.9. Setting the Medication Reminder
5.10. Battery Indicator
5.11. Using the AC Adapter
6. Software Functions
6.1. Installation and data transmission
7. Error Messages/Troubleshooting
8. Care and Maintenance
9. Lifetime Warranty
10. Certifications
11. Technical Specifications

2
1. Introduction
1.1.Features of your Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor
Your blood pressure monitor with Averaging Mode, Pulse Arrythmia Detection, and PC
Link Blood Pressure Analyzer Software is a fully automatic digital blood pressure
measuring device for use by adults on the upper arm at home or in your doctor’s/nurse’s
office. It enables very fast and reliable measurement of systolic and diastolic blood
pressure as well as pulse through the oscillometric method. This device offers clinically
proven accuracy and has been designed to be user friendly.
Before using, please read this instruction manual carefully and then keep it in a safe
place. Please contact your doctor for further questions on the subject of blood pressure
and its measurement.
Attention!
1.2.Important information about self-measurement
• Self-measurement means control, not diagnosis or treatment. Unusual values must
always be discussed with your doctor. Under no circumstances should you alter
the dosages of any drugs prescribed by your doctor.
•The pulse display is not suitable for checking the frequency of heart pacemakers!
•In cases of irregular heartbeat, measurements made with this instrument should only
be evaluated after consultation with your doctor.
Electromagnetic interference:
The device contains sensitive electronic components. Avoid strong electrical or
electromagnetic fields in the direct vicinity of the device (e.g. mobile telephones,
microwave ovens). These can lead to temporary impairment of the measuring accuracy.
2. Important Information on Blood Pressure and its Measurement
2.1. How does high or low blood pressure arise?
Your level of blood pressure is determined in the circulatory center of the brain and
adjusts to a variety of situations through feedback from the nervous system. To adjust
blood pressure, the strength and speed of the heart (Pulse), as well as the width of
circulatory blood vessels is altered. Blood vessel width is controlled by fine muscles in the
blood vessel walls.
Your level of arterial blood pressure changes periodically during heart activity: During the
“blood ejection” (Systole) the value is highest (systolic blood pressure value). At the end
of the heart’s “rest period” (Diastole) pressure is lowest (diastolic blood pressure value).
3
Blood pressure values must lie within certain normal ranges in order to prevent particular
diseases.
2.2. Which values are normal?
Blood pressure is very high if your diastolic pressure is above 100 mmHg and/or your
systolic blood pressure is over 160 mmHg, while at rest. In this case, please
consult your physician immediately. Long-term values at this level endanger your
health due to continual damage to the blood vessels in your body.
If your systolic blood pressure values are between 140 mmHg and 159 mmHg and/or
the diastolic blood pressure values between 90 mmHg and 99 mmHg, consult your
physician. Regular self-checks are necessary.
If you have blood pressure values that are too low, (i.e., systolic values under
105 mmHg and/or diastolic values under 60 mmHg), consult your physician.
Even with normal blood pressure values, a regular self-check with your blood
pressure monitor is recommended. You can detect possible changes in your values
early and react appropriately.
If you are undergoing medical treatment to control your blood pressure, keep a
record of values along with time of day and date. Show these values to your
physician. Never use the results of your measurements to independently alter
the drug doses prescribed by your physician.
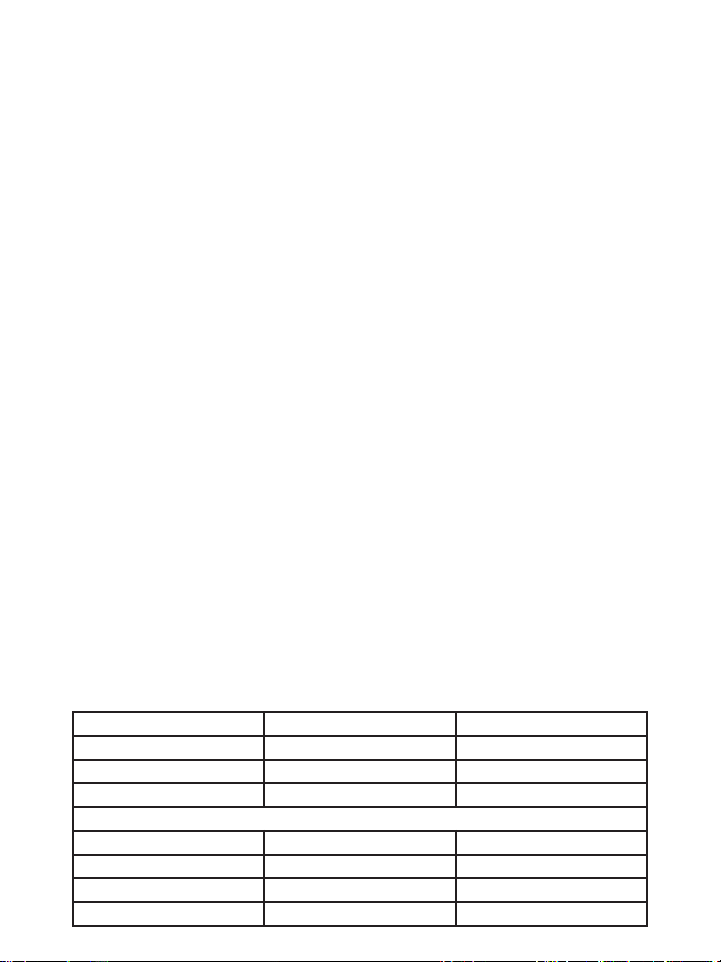
Which values are normal?
The following standards for assessing high blood pressure (without regard to age)
have been established by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2003.
Category Systolic (mmHg) Diastolic (mmHg)
Optimal <120 <80
Normal <130 <85
High Normal 130 - 139 85 - 89
Hypertension
• Stage 1: Mild 140-159 90-99
• Stage 2: Hypertension 160 - 179 100 - 109
• Stage 3: Severe >180 >110
Isolated Systolic Hypertension >140 <90

4
Further information
• If your values are mostly normal under resting conditions but exceptionally high under
conditions of physical or psychological stress, it is possible that you are suffering from
so-called “labile hypertension.” Consult your doctor.
•Correctly measured diastolic blood pressure values above 120 mmHg require
immediate medical treatment.
2.3. What can be done if regular high or low values are obtained?
a) Consult your doctor.
b) Increased blood pressure values (various forms of hypertension) are associated with
considerable health risks over time. Arterial blood vessels in your body are endangered
due to constriction caused by deposits in the vessel walls (Arteriosclerosis). A deficient
supply of blood to important organs (heart, brain, muscles) can result from
arteriosclerosis. Furthermore, the heart will become structurally damaged with
increased blood pressure values.
c) There are many different causes of high blood pressure. We differentiate between the
common primary (essential) hypertension, and secondary hypertension. The latter
group can be ascribed to specific organ malfunctions. Please consult your doctor for
information about the possible origins of your own increased blood pressure values.
d) There are measures which you can take to reduce and even prevent high blood
pressure. These measures must be permanent lifestyle changes.
A) Eating habits
• Strive for a normal weight corresponding to your age. See your doctor for your ideal
weight.
• Avoid excessive consumption of common salt.
• Avoid fatty foods.
B) Previous illnesses
• Consistently follow all medical instructions for treating illness such as:
• Diabetes (Diabetes mellitus or sugar diabetes)
• Fat metabolism disorder
• Gout
C) Habits
• Give up smoking completely.
• Drink only moderate amounts of alcohol.
• Restrict your caffeine consumption (coffee, tea, chocolate).
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Other Be.Better Blood Pressure Monitor manuals