Cermetek Microelectronics, Inc. High Speed Internet Modem Family
2005 Cermetek Microelectronics, Inc. Page 3 Document No. 607-0017 Revision I1 (05/05)
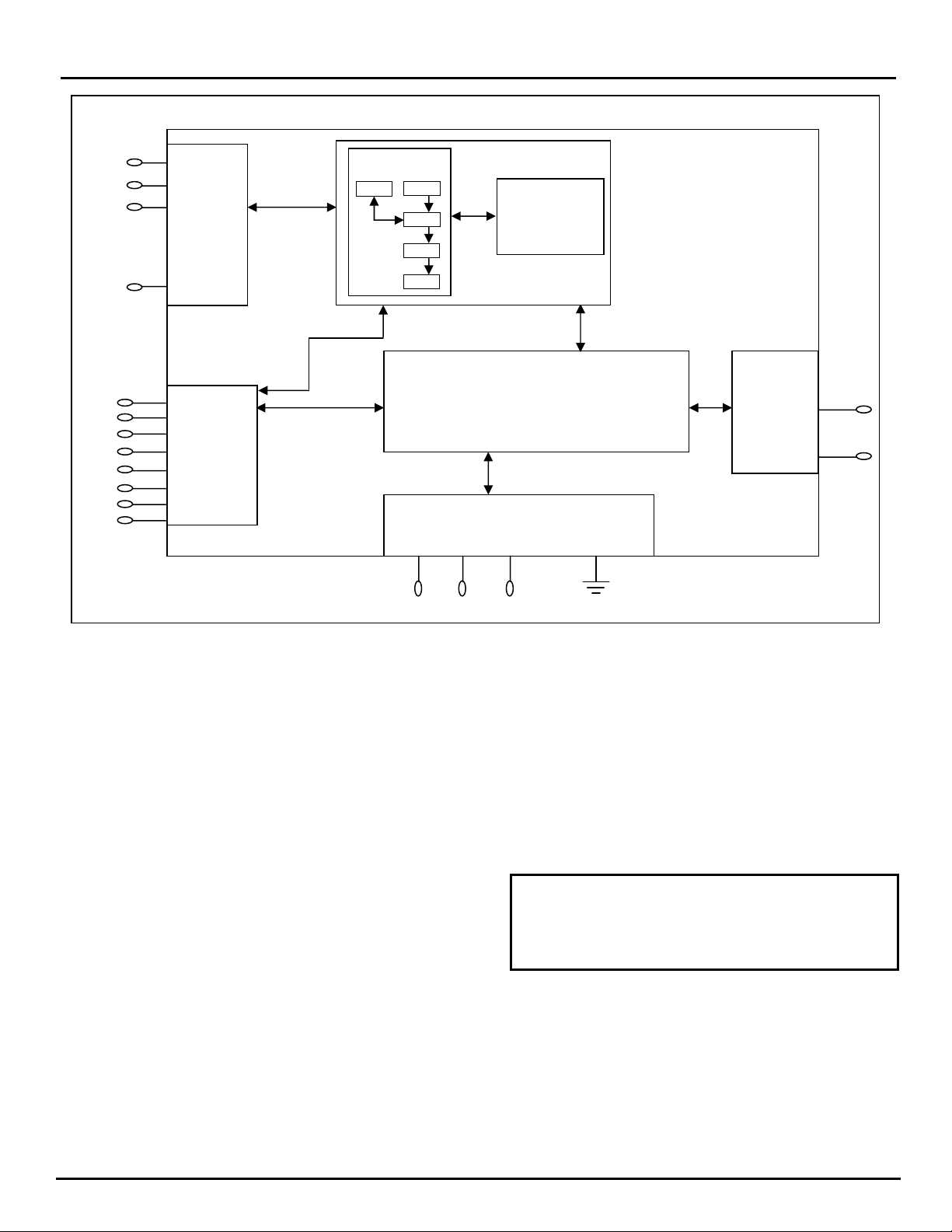
iMODEM EVALUATION BOARD
Cermetek manufactures a companion evaluation board
that is designed to simplify the hardware connections
required to program the iModem as well as providing a
reliable platform to assist with system level debugging.
Contact Cermetek and ask for the CH21XX iModem
Evaluation Board.
iMODEM CONTROL METHODOLOGIES
The iModem receives @T®commands from the host
processor or receives an event status flag on the Send
Email Control Pin (Pin #6) and proceeds to dial up the
local POP, log on to the internet, authenticate and verify
the user ID and password, and either sends or retrieves
email depending on the command/status flag received.
For CH2124/60 products, see Table 1 for a summary of
available @T®commands.
The iModem Family offers a variety of internet
communication features ranging from simple on
demand event triggered email transmission to full send
and retrieve email capability. User Control of the
internet communication activity of the iModem device
typically falls into one of the following basic control
strategies:
1. Fully Autonomous or event driven pin control
requiring no host processor intervention. A pre-
stored message is sent on a pin transition
(CH2124/60).
2. Semiautonomous control, requiring one command to
be issued from the host processor. A pre-stored
message is sent on command.
3. Complete host intervention and supervision requiring
each command to be issued from the host.
Message is constructed and sent in real time.
Fully Autonomous On Demand Event Driven
Control. This is the simplest method of operational
control. Application of a 50ms TTL Low going pulse or
level to the Send Email Control pin (Pin # 6) will cause
the CH2124/60 iModem to send an email using its
internal internet configuration profile. This profile is pre-
programmed at the factory and can be modified by the
user as necessary. No host processor intervention is
required. The DTE serial interface is not required for
fully autonomous on demand or event driven control.
The CH2124/60 iModem will abort email related
activities and return to the idle state if a low going TTL
pulse is presented to the SEND Email Control Pin (Pin
# 6) at any time during or after initiation of email send.
Semi-Autonomous Control. This method requires a
minimal amount of host processor intervention and
requires that the DTE serial port be operational. Semi-
autonomous control is a special case of full Host
Supervised Control and relies on the preprogrammed
default internet configuration profile contained within the
iModem. Initiation of an email activity occurs with the
issuance by the host processor to the iModem the
appropriate @T®command to send/retrieve/delete
email. PSTN dial-up, logon, authentication and email
transmission, retrieval, and/or deletion are performed
automatically by the iModem in the same fashion as for
the Fully Autonomous On-Demand control method
described above.
Host Supervised Control. This method is the most
flexible, but requires issuance by the host processor of
the necessary @T®commands in the required order
from the host processor. When choosing an
implementation scheme utilizing a host processor, the
host controls the iModem by using Cermetek @T®
commands. These commands are similar to the
standard Hayes AT command set.
Although the DTE serial port is required to be
operational for this method of control, an additional
feature of this method is the ability of the host to over-
ride the preprogrammed parameters (including the
email message content) by simply entering the
applicable information using the appropriate @T®
Command.
Delete Email. The user may selectively delete any
email message (by specifying the message number) or
delete all messages cached on the POP3 server.
Email and Internet Activity Status. The CH2124/60
provides activity status messages on the iModem’s
serial port. These status messages consist of a series
of ASCII characters. Some examples are: BAD
MESSAGE NUMBER, CONNECT, HANGING UP,
MESSAGE ACCEPTED, MESSAGE DELETED. For a
more detailed discussion of CH2124/60 status
messages, refer to Cermetek Application Note # 155,
@T®Command Set Description and Usage For
CH2124/60 iModems.
Back-up and Alternative POP access Phone
Numbers. Cermetek iModem products allow usage of
an alternative local access POP phone number or, if
available, a 1-800 number, should the iModem fail to
connect to the primary POP. The user can establish
the number of attempts made to the primary POP
before the back up POP is attempted.