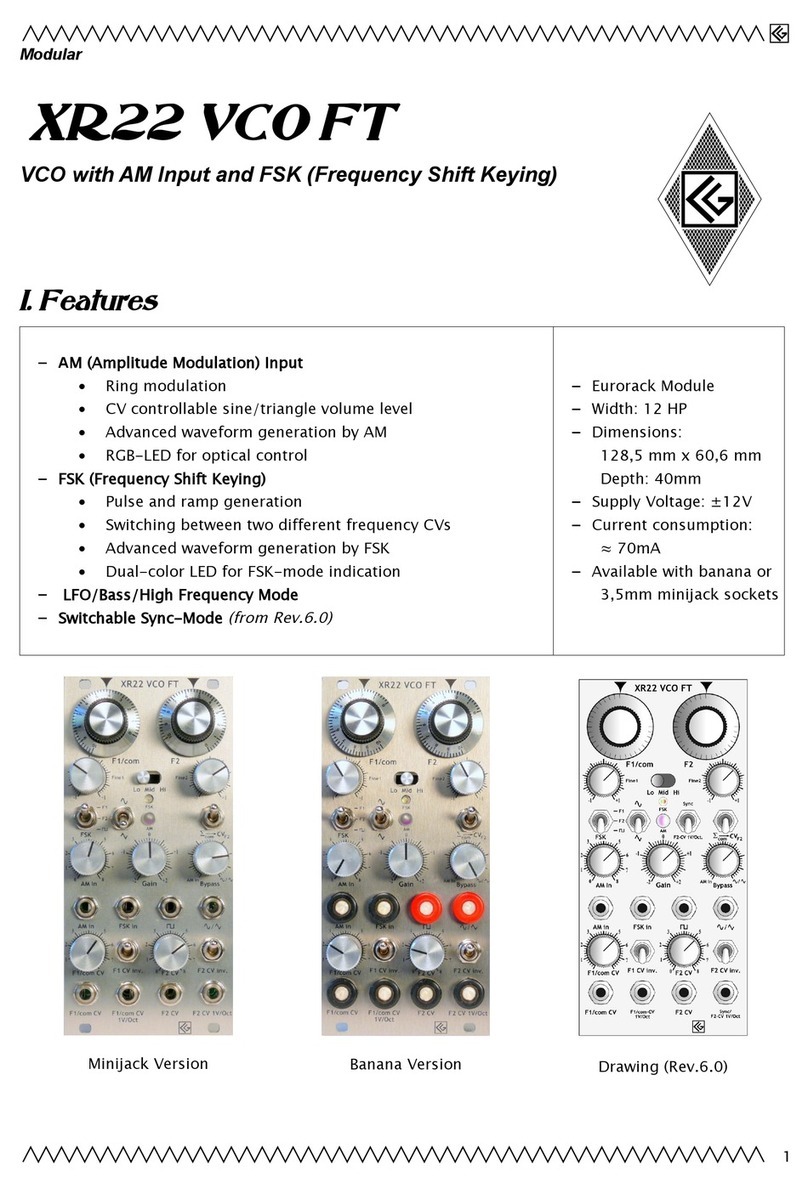
CG Products XR1-E User manual

XR1-E
Ring Modulation Oscillator
Analog Effect Device
Berlin 2013
The XR1-E is an analog ring modulator device with fixed sinus/triangle ring modulation
oscillator, suitable for both instrument or microphone input.
The oscillator pitch is adjustable by manual control over a wide range. n addition, the
frequency can be modulated by the integrated envelope follower (the oscillator pitch
changes dependent from the volume of the input signal) and LFO (low frequency oscillator)
as well as by an external CV signal or pedal. Original and effect signal are miscible by
controller, but the XR1-E also provides a footswitch input for external switching between
effect and original. Further, the ability of battery operation makes the instrument
independent from external power.
The XR1-E is based on an ancient function generator chip, which am using since many
years for musical purposes due to its warm and smooth sound.
Low noise high impedance preamp
Ring modulation oscillator frequency range:
High: 18Hz – 18000 Hz
Low: 0.1 Hz – 120Hz
Envelope follower and LFO for frequency modulation
Frequency CV input (1V/oct adjustable), also suitable for pedal use
Optional footswitch control
Output attenuator switch
Battery operation or external DC power supply (wide voltage range: 6-1 V)
Power dissipation: ca 600mW
1

Quick start guide
1. Insert batteries or accus (6x AA Mignon) or connect a power adaptor . Set the power
switch upwards to "On". Connect an amplifier, mixer etc. to the output . Set the
attenuator switch for instrument amplifiers in the lower position "low" , for line-in input
at a mixer to the upper "high" position. Connect an instrument or microphone to the
instrument input .
2. Set the frequency selector switch on "Hi". Turn the "Frequency" knob in middle
position.Turn the bypass pot in fully right position : "100%". Turn the envelope and LFO
modulation knobs , in fully left position: "0".
By turning the "Carrier Surpression" pot while listening to the oscillator tone, adjust the
tone to its minimum (≈ "0" on the scale; you may also use the green LED for indication).
Adjust the "Preamp" input gain controller while playing your instrument and listen for
optimal performance.
NOTE: It is not possible to eleminate the carrier (oscillator) tone completely. There will
always remain some overtone frequencies. Try to set the input pot on a high level (but
without distortion) to achieve best operation.
3. After you have detected the basic settings you can start to experiment, e.g. with different
oscillator frequencies , , ; add some frequency modulation with the LFO: for LFO
speed and for modulation depth, or activate the envelope modulation by turning knob
clockwise, etc.etc..
2

In-/Outputs and Control Elements
①On/Off Switch
Switches the power supply on or off.
ote: In combination with an external power adaptor only the XR1-E will be switched off
and not the power adaptor itself. This means that the power adaptor still may consume
some current for its own ("stand-by"). It is recommended to disconnect the adaptor
completly from public power supply if the XR1-E is not in use for a of longer time .
②External Power Supply nput
Allows the operation with an external standard DC power adaptor. The connection is a
standard DC plug with 2.1mm diameter hole. By using the external power supply input ,
the internal batteries will be switched off. The input voltage may range from 6V – 1 V.
Max. current dissipation is ca. 100mA (at 9V: ≈ 70mA). Take care on right polarity: The
"+"pole must be the outer contact.
③Output
Connect to an amplifier etc. The output voltage can be selected by the attenuator switch
for best adaption to the consecutive stage (e.g. line-in or instrument amplifier)
④Output Attenuator Switch
High: max. 8Vpp output voltage made for analog synthesizer inputs, line-in (mixer) inputs
etc..
Low: max. 0.8Vpp output voltage for instrumental amplifier inputs etc.
⑤nstrument nput
Input jack for instrument or microphone. Impedance: ca 2MΩ; max. input voltage: ≤3. Vpp.
⑥Preamp Gain Control
Adjustment of the amplification of the input preamp.
⑦Carrier Surpression Control
Controller for adjusting the oscillator (carrier) tone to its minimum. The "0" position in the
middle of the scale may be used as reference point, as well as the green LED – when dark
(and without input signal) – is suitable for indication of a minimum carrier tone amount.
ote: There will always remain a little bit of the oscillator sound (2nd harmonics etc.). For
best performance, make sure that the input signal level is high.
⑧Bypass Control
Ratio between input signal (preamplified) and effect signal. Turning the knob fully left will
provide the preamplified input signal only; by turning the knob clockwise the effect signal
will increase more and more and the original (dry) signal will disappear.Fully right position
= "100%": the pure ring modulation effect signal.
⑨Footswitch nput
Input jack for external bypass control, e.g. by a footswitch
•Switch opened: The dry preamplified input signal
•Switch closed: The effect signal (also depending on postion of the "Bypass" control
pot )
The switching also can be controlled by an external logic signal (0V = effect , + V = dry),
e.g. a gate signal from a synthesizer.
3

⑩Oscillator Frequency High/Low Switch
Hi: ≈ 18Hz – 18000 Hz (Audio range)
Lo: ≈ 0.1 Hz – 120 Hz
In "Hi" position, the oscillator is working in audio range. The amplitude modulation e.g.
will generate additional audio frequencies – sum and difference tones of the input signal
and the oscillator frequency.
In "Lo" position, the oscillator is working with subaudio frequencies. The amplitude
modulation effect is more like a" tremolo" sound. Volume of the input signal will change
constantly with the oscillator frequency.
⑪Oscillator Frequency Control
Rough adjustment of the amplitude modulation (AM) oscillator frequency.
⑫Oscillator Frequency Fine Adjustment Control
Fine adjustment of the oscillation frequency. Range is about 4 – semitones (quarte).
⑬Oscillator Waveform Switch
The oscillator waveform can be selected between sinewave and triangle. In " " (sine)
position, the effect is a more smooth sound with less overtones; in " " (triangle) mode the
generated sounds are rougher.
⑭LFO Frequency Control
Speed control of the internal LFO device (low frequency oscillator) for frequency
modulation of the ring modulation oscillator. Frequency is from ≈0.06Hz (left position ) to
≈ 44Hz (right position)
The LFO frequency is also displayed by the orange LED for easy visual confirmation.
⑮LFO Modulation Depth Control
Amount of LFO modulation depth
⑯LFO Waveform Switch
The LFO waveform can be selected between triangle (" ") and square (" ")." " will
provide a continously up-and down gliding pitch, while " " makes the oscillator shifting
between two tones.
⑰Envelope Follower/ext. CV Modulation Depth Control
The internal envelope follower converts the volume of the input signal into a control
voltage modulating the oscillator frequency. Amount of modulation can be varied by this
knob.
If the external frequency CV (= Control Voltage) input is in use, the envelope follower
will be switched off and instead the signal on will control the frequency and will be
adjusted by this pot.
⑱Envelope Follower Modulation: nversion Switch
Switches the the modulation (from envelope follower or external source) from positive to
negative. If the switch is in upper position, the pitch of the AM oscillator will increase with
higher volume of the input signal. switch in lower position (= " nversion") the pitch will
decrease with higher input volume. The inversion switch works also for a control voltage
signal connected to .
4

⑲External Frequency Control nput
Allows to control the oscillator pitch by an external control voltage (CV) or an external
resistor. By connecting a jack to this input, the internal envelope follower device will be
shut off and instead the fed in control voltage is adjusted by knob , regulating the
amount of pitch control by the CV.
The modulation CV also can be inverted by switch . Normally, a higher voltage will cause
an increasing pitch and vice versa. With in lower postion ("Inversion") a higher voltage
will cause a decreasing pitch and vice versa.
Further, a + V voltage (via 10kΩ resistor) is provided on , available on the middle
connector of a 3pole jack plugged in . Thus may be useful, for example, in combination
with a sensor or a pedal. In the latter case, a common passive foot pedal with 3pole jack
should work.
In combination with analog synthesizer equipment (e.g. sequencers, monophone
keyboards), it is possible to calibrate the XR1-E on 1V/Oct. by adjusting knob .
To calibrate on 1V/Oct for tracking with other instruments, connect the
external CV source to and set the pointer of the "Envelope/
ext.Modulation" controller to nearby "7" on the scale. This is a good base.
Then adjust by listening with different CV values until the pitch matches
with the pitch of your instrument.
Envelope/ext.Modulation
1
2
3
4
5
0
6
7
8
17

About Ring Modulation
Ring modulation is the multiplication of two bipolar audio signals by each other. Each value of a
carrier signal, C, is multiplied by a modulator signal, M, to create a new ring-modulated signal, R:
R(t) = C(t) x M(t)
(from: http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Sound_Synthesis_Theory/Modulation_Synthesis)
It is referred to as "ring" modulation because the analog circuit of diodes originally used to
implement this technique took the shape of a ring (Wikipedia).
For example: If one or both of the input signals C or M is 0V, the output R will be also 0V.
ote: In the case of the XR1-E the carrier signal is or , provided by the internal oscillator.
Examples
nput (=modulator) signal frequency >> oscillator (carrier) frequency ( ):
Input signal: metallophone
The volume of the metallophone sound varies with the oscillator amplitude.
nput (=modulator) signal frequency << oscillator (carrier) frequency ( )
Input signal: "Base drum" from rhythm machine The generated effect signal
The volume of the oscillator sound varies with the amplitude of the input signal
nput (=modulator) signal frequency ≤ or ≥ oscillator (carrier) frequency ( )
Input signal: "Mid tom" from rhythm machine
Complexe sound structures are generated, depending on the oscillator pitch.
6

Circuit Diagram
7
Other manuals for XR1-E
2
Table of contents
Other CG Products Modulator manuals
Popular Modulator manuals by other brands

Radio Shack
Radio Shack Video RF Modulator owner's manual

dig-MOD
dig-MOD HD-1605 User guide & installation manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments UM1381 operating guide

axing
axing UIM 1-00 Operation instructions

Pico Macom
Pico Macom M860 Installation and operation manual

Marmitek
Marmitek MEGAVIDEO 55 operating instructions