Cirrus Logic CS2000-OTP Operating and maintenance instructions

Cirrus Logic Confidential
Copyright Cirrus Logic, Inc. 2009–2015
(All Rights Reserved)
http://www.cirrus.com
Fractional-N Clock Synthesizer & Clock Multiplier
Features
Delta-Sigma Fractional-N Frequency Synthesis
– Generates a Low Jitter 6 - 75 MHz Clock
from an 8 - 75 MHz Reference Clock
Clock Multiplier / Jitter Reduction
– Generates a Low Jitter 6 - 75 MHz Clock
from a Jittery 50 Hz to 30 MHz Clock
Source
Highly Accurate PLL Multiplication Factor
– Maximum Error Less Than 1 PPM in High-
Resolution Mode
One-Time Programmability
– Configurable Hardware Control Pins
– Configurable Auxiliary Output
Flexible Sourcing of Reference Clock
– External Oscillator or Clock Source
– Supports Inexpensive Local Crystal
Minimal Board Space Required
– No External Analog Loop-filter
Components
General Description
The CS2000-OTP is an extremely versatile system
clocking device that utilizes a programmable phase lock
loop. The CS2000-OTP is based on a hybrid analog-
digital PLL architecture comprised of a unique combina-
tion of a Delta-Sigma Fractional-N Frequency
Synthesizer and a Digital PLL. This architecture allows
for both frequency synthesis/clock generation from a
stable reference clock as well as generation of a low-jit-
ter clock relative to an external noisy synchronization
clock with frequencies as low as 50 Hz. The CS2000-
OTP has many configuration options which are set once
prior to runtime. At runtime there are three hardware
configuration pins available for mode and feature
selection.
The CS2000-OTP is available in a 10-pin MSOP pack-
age in Commercial (-10°C to +70°C) and Automotive-D
(-40°C to +85°C) and Automotive-E (-40°C to +105°C)
grades. Customer development kits are also available
for custom device prototyping, small production pro-
gramming, and device evaluation. Please see “Ordering
Information” on page 29 for complete details.
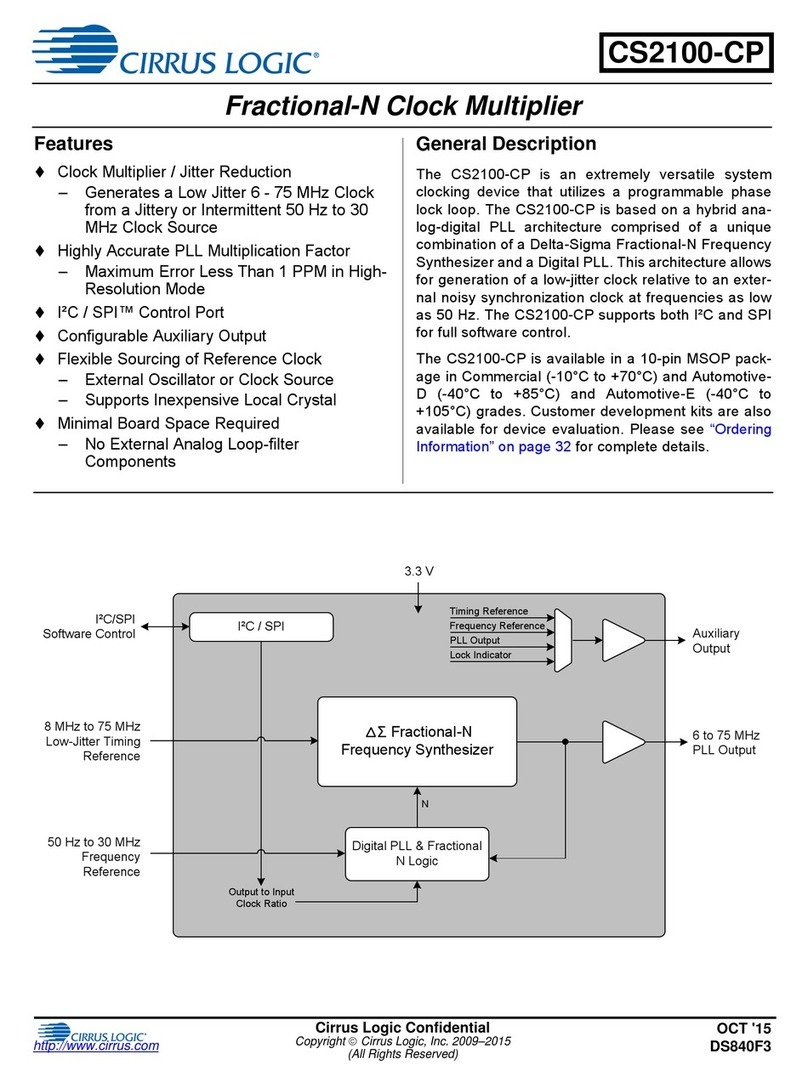
Hardware Configuration Auxiliary
Output
6 to 75 MHz
PLL Output
Frequency Reference
3.3 V
Hardware Control
8 MHz to 75 MHz
Low-Jitter Timing Reference
Fractional-N
Frequency Synthesizer
Digital PLL & Fractional
N Logic
Output to Input
Clock Ratio
N
Timing Reference
PLL Output
Lock Indicator
50 Hz to 30 MHz
Frequency Reference
Output to Input
Clock Ratio
OCT '15
DS758F3
CS2000-OTP

CS2000-OTP
DS758F3 2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. PIN DESCRIPTION ................................................................................................................................. 4
2. TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM ..................................................................................................... 5
3. CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS ...................................................................................... 6
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS .................................................................................... 6
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS ........................................................................................................ 6
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ................................................................................................ 6
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ................................................................................................ 7
PLL PERFORMANCE PLOTS ............................................................................................................... 8
4. ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW ............................................................................................................... 9
4.1 Delta-Sigma Fractional-N Frequency Synthesizer ........................................................................... 9
4.2 Hybrid Analog-Digital Phase Locked Loop ...................................................................................... 9
4.2.1 Fractional-N Source Selection for the Frequency Synthesizer .............................................. 10
5. APPLICATIONS ................................................................................................................................... 11
5.1 One Time Programmability ............................................................................................................ 11
5.2 Timing Reference Clock Input ........................................................................................................ 11
5.2.1 Internal Timing Reference Clock Divider ............................................................................... 11
5.2.2 Crystal Connections (XTI and XTO) ...................................................................................... 12
5.2.3 External Reference Clock (REF_CLK) .................................................................................. 12
5.3 Frequency Reference Clock Input, CLK_IN ................................................................................... 12
5.3.1 Adjusting the Minimum Loop Bandwidth for CLK_IN ............................................................ 13
5.4 Output to Input Frequency Ratio Configuration ............................................................................. 14
5.4.1 User Defined Ratio (RUD), Frequency Synthesizer Mode .................................................... 14
5.4.2 User Defined Ratio (RUD), Hybrid PLL Mode ....................................................................... 14
5.4.3 Ratio Modifier (R-Mod) .......................................................................................................... 15
5.4.4 Effective Ratio (REFF) .......................................................................................................... 15
5.4.5 Fractional-N Source Selection ............................................................................................... 15
5.4.5.1 Manual Fractional-N Source Selection for the Frequency Synthesizer ..................... 16
5.4.5.2 Automatic Fractional-N Source Selection for the Frequency Synthesizer ................. 16
5.4.6 Ratio Configuration Summary ............................................................................................... 17
5.5 PLL Clock Output ........................................................................................................................... 18
5.6 Auxiliary Output .............................................................................................................................. 18
5.7 Mode Pin Functionality ................................................................................................................... 19
5.7.1 M1 and M0 Mode Pin Functionality ....................................................................................... 19
5.7.2 M2 Mode Pin Functionality .................................................................................................... 19
5.7.2.1 M2 Configured as Output Disable .............................................................................. 19
5.7.2.2 M2 Configured as R-Mod Enable .............................................................................. 19
5.7.2.3 M2 Configured as Auto Fractional-N Source Selection Disable ................................ 20
5.7.2.4 M2 Configured as Fractional-N Source Select .......................................................... 20
5.7.2.5 M2 Configured as AuxOutSrc Override ..................................................................... 20
5.8 Clock Output Stability Considerations ............................................................................................ 20
5.8.1 Output Switching ................................................................................................................... 20
5.8.2 PLL Unlock Conditions .......................................................................................................... 21
5.9 Required Power Up Sequencing for Programmed Devices ........................................................... 21
6. PARAMETER DESCRIPTIONS ........................................................................................................... 22
6.1 Modal Configuration Sets ............................................................................................................... 22
6.1.1 R-Mod Selection (RModSel[1:0]) ...........................................................................................22
6.1.2 Auxiliary Output Source Selection (AuxOutSrc[1:0]) ............................................................. 23
6.1.3 Lock Clock Ratio (LockClk[1:0]) ............................................................................................ 23
6.1.4 Fractional-N Source for Frequency Synthesizer (FracNSrc) ................................................. 23
6.2 Ratio 0 - 3 ...................................................................................................................................... 23
6.3 Global Configuration Parameters ................................................................................................... 24
6.3.1 AUX PLL Lock Output Configuration (AuxLockCfg) .............................................................. 24

CS2000-OTP
DS758F3 3
6.3.2 Reference Clock Input Divider (RefClkDiv[1:0]) .................................................................... 24
6.3.3 Enable PLL Clock Output on Unlock (ClkOutUnl) ................................................................. 24
6.3.4 Low-Frequency Ratio Configuration (LFRatioCfg) ................................................................ 24
6.3.5 M2 Pin Configuration (M2Config[2:0]) ................................................................................... 25
6.3.6 Clock Input Bandwidth (ClkIn_BW[2:0]) ................................................................................ 25
7. CALCULATING THE USER DEFINED RATIO .................................................................................... 26
7.1 High Resolution 12.20 Format ....................................................................................................... 26
7.2 High Multiplication 20.12 Format ................................................................................................... 26
8. PROGRAMMING INFORMATION ........................................................................................................ 27
9. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS .................................................................................................................... 28
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS ......................................................................................................... 28
10. ORDERING INFORMATION .............................................................................................................. 29
11. REVISION HISTORY .......................................................................................................................... 29
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1. Typical Connection Diagram ........................................................................................................ 5
Figure 2. CLK_IN Sinusoidal Jitter Tolerance ............................................................................................. 8
Figure 3. CLK_IN Sinusoidal Jitter Transfer ................................................................................................ 8
Figure 4. CLK_IN Random Jitter Rejection and Tolerance .........................................................................8
Figure 5. Delta-Sigma Fractional-N Frequency Synthesizer .......................................................................9
Figure 6. Hybrid Analog-Digital PLL .......................................................................................................... 10
Figure 7. Fractional-N Source Selection Overview ................................................................................... 10
Figure 8. Internal Timing Reference Clock Divider ................................................................................... 11
Figure 9. REF_CLK Frequency vs. a Fixed CLK_OUT ............................................................................. 12
Figure 10. External Component Requirements for Crystal Circuit ............................................................ 12
Figure 11. Low bandwidth and new clock domain .................................................................................... 13
Figure 12. High bandwidth with CLK_IN domain re-use ........................................................................... 13
Figure 13. Ratio Feature Summary ........................................................................................................... 17
Figure 14. PLL Clock Output Options ....................................................................................................... 18
Figure 15. Auxiliary Output Selection ........................................................................................................ 18
Figure 16. M2 Mapping Options ................................................................................................................ 19
Figure 17. Parameter Configuration Sets .................................................................................................. 22
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1. Modal and Global Configuration .................................................................................................. 11
Table 2. Ratio Modifier .............................................................................................................................. 15
Table 3. Example 12.20 R-Values ............................................................................................................ 26
Table 4. Example 20.12 R-Values ............................................................................................................ 26

CS2000-OTP
4DS758F3
1. PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin Name # Pin Description
VD 1 Digital Power (Input) - Positive power supply for the digital and analog sections.
GND 2 Ground (Input) - Ground reference.
CLK_OUT 3 PLL Clock Output (Output) - PLL clock output.
AUX_OUT 4 Auxiliary Output (Output) - This pin outputs a buffered version of one of the input or output clocks,
or a status signal, depending on configuration.
CLK_IN 5 Frequency Reference Clock Input (Input) - Clock input for the Digital PLL frequency reference.
XTO
XTI/REF_CLK
6
7
Crystal Connections (XTI/XTO) / Timing Reference Clock Input (REF_CLK) (Input/Output) -
XTI/XTO are I/O pins for an external crystal which may be used to generate the low-jitter PLL input
clock. REF_CLK is an input for an externally generated low-jitter reference clock.
M2 8 Mode Select (Input) - M2 is a configurable mode selection pin.
M1 9 Mode Select (Input) - M1 is a configurable mode selection pin.
M0 10 Mode Select (Input) - M0 is a configurable mode selection pin.
1
2
3
4
56
7
8
9
10
XTO
CLK_OUT
GND
VD
XTI/REF_CLK
M2
M1
M0
AUX_OUT
CLK_IN

CS2000-OTP
DS758F3 5
2. TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM
2
1
GND
M2
M1
XTI/REF_CLK
Frequency Reference CLK_IN
XTO
CLK_OUT
AUX_OUT
0.1 µF
VD
+3.3 V
M0
Low-Jitter
Timing Reference
System Microcontroller
1 µF
1
or
2
REF_CLK
XTO
XTI
XTO
or
40 pF
x
40 pF
Crystal
To circuitry which requires
a low-jitter clock
N.C.
To other circuitry or
Microcontroller
Figure 1. Typical Connection Diagram
CS2000-OTP

CS2000-OTP
6DS758F3
3. CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
GND = 0 V; all voltages with respect to ground. (Note 1)
Notes: 1. Device functionality is not guaranteed or implied outside of these limits. Operation outside of these limits
may adversely affect device reliability.
2. CLK_IN must not be applied when these conditions are not met, including during power up. See section
5.9 on page 21 for required power up procedure.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
GND = 0 V; all voltages with respect to ground.
WARNING:Operation at or beyond these limits may result in permanent damage to the device.
Notes: 3. The maximum over/under voltage is limited by the input current except on the power supply pin.
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Test Conditions (unless otherwise specified): VD = 3.1 V to 3.5 V; TA= -10°C to +70°C (Commercial Grade);
TA= -40°C to +85°C (Automotive-D Grade); TA= -40°C to +105°C (Automotive-E Grade).
Notes: 4. To calculate the additional current consumption due to loading (per output pin), multiply clock output
frequency by load capacitance and power supply voltage.
For example, fCLK_OUT (49.152 MHz) * CL (15 pF) * VD (3.3 V) = 2.4 mA of additional current due to
these loading conditions on CLK_OUT.
Parameters Symbol Min Typ Max Units
DC Power Supply (Note 2) VD 3.1 3.3 3.5 V
Ambient Operating Temperature (Power Applied)
Commercial Grade
Automotive-D Grade
Automotive-E Grade
TAC
TAD
TAE
-10
-40
-40
-
-
-
+70
+85
+105
°C
°C
°C
Parameters Symbol Min Max Units
DC Power Supply VD -0.3 6.0 V
Input Current IIN -±10mA
Digital Input Voltage (Note 3)V
IN -0.3 VD + 0.4 V
Ambient Operating Temperature (Power Applied) TA-55 125 °C
Storage Temperature Tstg -65 150 °C
Parameters Symbol Min Typ Max Units
Power Supply Current - Unloaded (Note 4)I
D-1218mA
Power Dissipation - Unloaded (Note 4)P
D-4060mW
Input Leakage Current IIN --±10µA
Input Capacitance IC-8-pF
High-Level Input Voltage VIH 70% - - VD
Low-Level Input Voltage VIL --30%VD
High-Level Output Voltage (IOH = -1.2 mA) VOH 80% - - VD
Low-Level Output Voltage (IOH = 1.2 mA) VOL --20%VD

CS2000-OTP
DS758F3 7
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Test Conditions (unless otherwise specified): VD = 3.1 V to 3.5 V; TA= -10°C to +70°C (Commercial Grade);
TA= -40°C to +85°C (Automotive-D Grade); TA= -40°C to +105°C (Automotive-E Grade); CL=15pF.
Notes: 5. 1 UI (unit interval) corresponds to tSYS_CLK or 1/fSYS_CLK.
6. fCLK_OUT is ratio-limited when fCLK_IN is below 72 Hz.
7. fCLK_OUT = 24.576 MHz; Sample size = 10,000 points; AuxOutSrc[1:0] =11.
8. In accordance with AES-12id-2006 section 3.4.2. Measurements are Time Interval Error taken with 3rd
order 100 Hz to 40 kHz bandpass filter.
9. In accordance with AES-12id-2006 section 3.4.1. Measurements are Time Interval Error taken with 3rd
order 100 Hz Highpass filter.
10. 1 UI (unit interval) corresponds to tCLK_IN or 1/fCLK_IN.
11. The frequency accuracy of the PLL clock output is directly proportional to the frequency accuracy of the
reference clock.
Parameters Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Crystal Frequency
Fundamental Mode XTAL
fXTAL RefClkDiv[1:0] = 10
RefClkDiv[1:0] = 01
RefClkDiv[1:0] = 00
8
16
32
-
-
-
14
28
50
MHz
MHz
MHz
Reference Clock Input Frequency fREF_CLK RefClkDiv[1:0] = 10
RefClkDiv[1:0] = 01
RefClkDiv[1:0] = 00
8
16
32
-
-
-
14
28
56
MHz
MHz
MHz
Reference Clock Input Duty Cycle DREF_CLK 45 - 55 %
Internal System Clock Frequency fSYS_CLK 814MHz
Clock Input Frequency fCLK_IN 50 Hz - 30 MHz
Clock Input Pulse Width (Note 5)pw
CLK_IN fCLK_IN < fSYS_CLK/96
fCLK_IN > fSYS_CLK/96
2
10
-
-
-
-
UI
ns
PLL Clock Output Frequency fCLK_OUT (Note 6)6-75MHz
PLL Clock Output Duty Cycle tOD Measured at VD/2 45 50 55 %
Clock Output Rise Time tOR 20% to 80% of VD - 1.7 3.0 ns
Clock Output Fall Time tOF 80% to 20% of VD - 1.7 3.0 ns
Period Jitter tJIT (Note 7) - 70 - ps rms
Base Band Jitter (100 Hz to 40 kHz) (Notes 7, 8) - 50 - ps rms
Wide Band JItter (100 Hz Corner) (Notes 7, 9) - 175 - ps rms
PLL Lock Time - CLK_IN (Note 10)t
LC fCLK_IN < 200 kHz
fCLK_IN > 200 kHz
-
-
100
1
200
3
UI
ms
PLL Lock Time - REF_CLK tLR fREF_CLK = 8 to 75 MHz - 1 3 ms
Output Frequency Synthesis Resolution (Note 11)f
err High Resolution
High Multiplication
0
0
-
-
±0.5
±112
ppm
ppm

CS2000-OTP
8DS758F3
PLL PERFORMANCE PLOTS
Test Conditions (unless otherwise specified): VD = 3.3 V; TA=25°C;C
L=15pF;f
CLK_OUT = 12.288 MHz;
fCLK_IN = 12.288 MHz; Sample size = 10,000 points; Base Band Jitter (100 Hz to 40 kHz); AuxOutSrc[1:0] =11.
110 100 1,000 10,000
0.1
1
10
100
1,000
10,000
Input Jitter Frequency (Hz)
Max Input Jitter Level (usec)
1 Hz Bandwidth
128 Hz Bandwidth
110 100 1000 10000
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
10
Input Jitter Frequency (Hz)
Jitter Transfer (dB)
1 Hz Bandwidth
128 Hz Bandwidth
Figure 2. CLK_IN Sinusoidal Jitter Tolerance Figure 3. CLK_IN Sinusoidal Jitter Transfer
Samples size = 2.5M points; Base Band Jitter (100Hz to 40kHz). Samples size = 2.5M points; Base Band Jitter (100Hz to 40kHz).
Figure 4. CLK_IN Random Jitter Rejection and Tolerance
0.01 0.1 110 100 1000
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
1000
Input Jitter Level (nsec)
Output Jitter Level (nsec)
1 Hz Bandwidth
128 Hz Bandwidth
Unlock
Unlock

CS2000-OTP
DS758F3 9
4. ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW
4.1 Delta-Sigma Fractional-N Frequency Synthesizer
The core of the CS2000 is a Delta-Sigma Fractional-N Frequency Synthesizer which has very high-resolu-
tion for Input/Output clock ratios, low phase noise, very wide range of output frequencies and the ability to
quickly tune to a new frequency. In very simplistic terms, the Fractional-N Frequency Synthesizer multiplies
the Timing Reference Clock by the value of N to generate the PLL output clock. The desired output to input
clock ratio is the value of N that is applied to the delta-sigma modulator (see Figure 5).
The analog PLL based frequency synthesizer uses a low-jitter timing reference clock as a time and phase
reference for the internal voltage controlled oscillator (VCO). The phase comparator compares the fraction-
al-N divided clock with the original timing reference and generates a control signal. The control signal is fil-
tered by the internal loop filter to generate the VCO’s control voltage which sets its output frequency. The
delta-sigma modulator modulates the loop integer divide ratio to get the desired fractional ratio between the
reference clock and the VCO output (thus the duty cycle of the modulator sets the fractional value). This
allows the design to be optimized for very fast lock times for a wide range of output frequencies without the
need for external filter components. As with any Fractional-N Frequency Synthesizer the timing reference
clock should be stable and jitter-free.
Figure 5. Delta-Sigma Fractional-N Frequency Synthesizer
4.2 Hybrid Analog-Digital Phase Locked Loop
The addition of the Digital PLL and Fractional-N Logic (shown in Figure 6) to the Fractional-N Frequency
Synthesizer creates the Hybrid Analog-Digital Phase Locked Loop with many advantages over classical an-
alog PLL techniques. These advantages include the ability to operate over extremely wide frequency ranges
without the need to change external loop filter components while maintaining impressive jitter reduction per-
formance. In the Hybrid architecture, the Digital PLL calculates the ratio of the PLL output clock to the fre-
quency reference and compares that to the desired ratio. The digital logic generates a value of N which is
then applied to the Fractional-N frequency synthesizer to generate the desired PLL output frequency. Notice
that the frequency and phase of the timing reference signal do not affect the output of the PLL since the
digital control loop will correct for the PLL output. A major advantage of the Digital PLL is the ease with which
the loop filter bandwidth can be altered. The PLL bandwidth is set to a wide-bandwidth mode to quickly
achieve lock and then reduced for optimal jitter rejection.
Fractional-N
Divider
Timing Reference
Clock PLL Output
Voltage Controlled
Oscillator
Internal
Loop Filter
Phase
Comparator
N
Delta-Sigma
Modulator

CS2000-OTP
10 DS758F3
Figure 6. Hybrid Analog-Digital PLL
4.2.1 Fractional-N Source Selection for the Frequency Synthesizer
The fractional-N value for the frequency synthesizer can be sourced from either a static ratio or a dynamic
ratio generated from the digital PLL (see Figure 7). This allows for the selection between operating in the
static ratio based Frequency Synthesizer Mode as a simple frequency synthesizer (for frequency gener-
ation from the Timing Reference Clock) and in the dynamic ratio based Hybrid PLL Mode (for jitter reduc-
tion and clock multiplication). Selection between these two modes can either be made automatically
based on the presence of the Frequency Reference Clock or manually through the mode select pins.
Figure 7. Fractional-N Source Selection Overview
N
Digital Filter
Frequency
Comparator for
Frac-N Generation
Frequency Reference
Clock
Delta-Sigma Fractional-N Frequency Synthesizer
Digital PLL and Fractional-N Logic
Output to Input Ratio for Hybrid mode
Fractional-N
Divider
Timing Reference
Clock PLL Output
Voltage Controlled
Oscillator
Internal
Loop Filter
Phase
Comparator
Delta-Sigma
Modulator
Frequency Reference Clock
Output to Input ratio for Hybrid Mode
Timing Reference Clock PLL Output
Fractional-N
Frequency Synthesizer
Digital PLL & Fractional-N Logic
Output to Input Ratio for Synthesizer Mode
N

CS2000-OTP
DS758F3 11
5. APPLICATIONS
5.1 One Time Programmability
The one time programmable (OTP) circuitry in the CS2000-OTP allows for pre-configuration of the device
prior to use in a system. There are two types of parameters that are used for device pre-configuration: modal
and global. The modal parameters are features which, when grouped together, create a modal configuration
set (see Figure 17 on page 22). Up to four modal configuration sets can be permanently stored and then
dynamically selected using the M[1:0] mode select pins (see Table 1). The global parameters are the re-
maining configuration settings which do not change with the mode select pins. The modal and global pa-
rameters can be pre-set at the factory or user programmed using the customer development kit, CDK2000;
Please see “Programming Information” on page 27 for more details.
Table 1. Modal and Global Configuration
5.2 Timing Reference Clock Input
The low jitter timing reference clock (RefClk) can be provided by either an external reference clock or an
external crystal in conjunction with the internal oscillator. In order to maintain a stable and low-jitter PLL out-
put the timing reference clock must also be stable and low-jitter; the quality of the timing reference clock
directly affects the performance of the PLL and hence the quality of the PLL output.
5.2.1 Internal Timing Reference Clock Divider
The Internal Timing Reference Clock (SysClk) is limited to a lower maximum frequency than that allowed
on the XTI/REF_CLK pin. The CS2000-OTP supports the wider external frequency range by offering an
internal divider for RefClk. The RefClkDiv[1:0] global parameter should be configured such that SysClk,
the divided RefClk, then falls within the valid range as indicated in “AC Electrical Characteristics” on
page 7.
It should be noted that the maximum allowable input frequency of the XTI/REF_CLK pin is dependent
upon its configuration as either a crystal connection or external clock input. See the “AC Electrical Char-
acteristics” on page 7 for more details.
For the lowest possible output jitter, attention should be paid to the absolute frequency of the Timing Ref-
erence Clock relative to the PLL Output frequency (CLK_OUT). To minimize output jitter, the Timing Ref-
erence Clock frequency should be chosen such that fRefClk is at least +/-15 kHz from fCLK_OUT*N/32
where N is an integer. Figure 9 shows the effect of varying the RefClk frequency around fCLK_OUT*N/32.
It should be noted that there will be a jitter null at the zero point when N = 32 (not shown in Figure 9). An
Parameter Type M[1:0] pins = 00 M[1:0] pins = 01 M[1:0] pins = 10 M[1:0] pins = 11
Modal Configuration Set 0
Ratio 0
Configuration Set 1
Ratio 1
Configuration Set 2
Ratio 2
Configuration Set 3
Ratio 3
Global Configuration settings set once for all modes.
Figure 8. Internal Timing Reference Clock Divider
N
Internal Timing
Reference Clock
PLL Output
Fractional-N
Frequency
Synthesizer
Timing Reference
Clock Divider
1
2
4
XTI/REF_CLK
RefClkDiv[1:0]
8 MHz < SysClk < 14 MHz
8 MHz < RefClk <
Timing Reference Clock
50 MHz (XTI)
58 MHz (REF_CLK)

CS2000-OTP
12 DS758F3
example of how to determine the range of RefClk frequencies around 12 MHz to be used in order to
achieve the lowest jitter PLL output at a frequency of 12.288 MHz is as follows:
where:
and
5.2.2 Crystal Connections (XTI and XTO)
An external crystal may be used to generate RefClk. To accomplish this, a 20 pF fundamental mode par-
allel resonant crystal must be connected between the XTI and XTO pins as shown in Figure 10. As shown,
nothing other than the crystal and its load capacitors should be connected to XTI and XTO. Please refer
to the “AC Electrical Characteristics” on page 7 for the allowed crystal frequency range.
5.2.3 External Reference Clock (REF_CLK)
For operation with an externally generated REF_CLK signal, XTI/REF_CLK should be connected to the
reference clock source and XTO should be left unconnected or terminated through a 47 kresistor to
GND.
5.3 Frequency Reference Clock Input, CLK_IN
The frequency reference clock input (CLK_IN) is used in Hybrid PLL Mode by the Digital PLL and Fractional-
N Logic block to dynamically generate a fractional-N value for the Frequency Synthesizer (see “Hybrid An-
alog-Digital PLL” on page 10). The Digital PLL first compares the CLK_IN frequency to the PLL output. The
Fractional-N logic block then translates the desired ratio based off of CLK_IN to one based off of the internal
timing reference clock (SysClk). This allows the low-jitter timing reference clock to be used as the clock
Referenced Control Parameter Definition
RefClkDiv[1:0] .......................“Reference Clock Input Divider (RefClkDiv[1:0])” on page 24
-80 -60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
Normalized REF__CLK Frequency (kHz)
Typical Base Band Jitter (psec)
CLK__OUT Jit ter
-15 kHz +15 kHz
CLK__OUT
f *32/N
Figure 9. REF_CLK Frequency vs. a Fixed CLK_OUT
fLfRefClk fH
fLfCLK_OUT 31
32
------15kHz+=
12.288MHz 0.96875 15kHz+=
11.919MHz=
fHfCLK_OUT 32
32
------15kHz–=
12.288MHz 115kHz+=
12.273MHz=
XTI XTO
40 pF 40 pF
Figure 10. External Component Requirements for Crystal Circuit

CS2000-OTP
DS758F3 13
which the Frequency Synthesizer multiplies while maintaining synchronicity with the frequency reference
clock through the Digital PLL. The allowable frequency range for CLK_IN is found in the “AC Electrical Char-
acteristics” on page 7.
5.3.1 Adjusting the Minimum Loop Bandwidth for CLK_IN
The CS2000 allows the minimum loop bandwidth of the Digital PLL to be adjusted between 1 Hz and
128 Hz using the ClkIn_BW[2:0] global parameter. The minimum loop bandwidth of the Digital PLL direct-
ly affects the jitter transfer function; specifically, jitter frequencies below the loop bandwidth corner are
passed from the PLL input directly to the PLL output without attenuation. In some applications it is desir-
able to have a very low minimum loop bandwidth to reject very low jitter frequencies, commonly referred
to as wander. In others it may be preferable to remove only higher frequency jitter, allowing the input wan-
der to pass through the PLL without attenuation.
Typically, applications in which the PLL_OUT signal creates a new clock domain from which all other sys-
tem clocks and associated data are derived will benefit from the maximum jitter and wander rejection of
the lowest PLL bandwidth setting. See Figure 11.
Systems in which some clocks and data are derived from the PLL_OUT signal while other clocks and data
are derived from the CLK_IN signal will often require phase alignment of all the clocks and data in the
system. See Figure 12. If there is substantial wander on the CLK_IN signal in these applications, it may
be necessary to increase the minimum loop bandwidth allowing this wander to pass through to the
CLK_OUT signal in order to maintain phase alignment. For these applications, it is advised to experiment
with the loop bandwidth settings and choose the lowest bandwidth setting that does not produce system
timing errors due to wandering between the clocks and data synchronous to the CLK_IN domain and
those synchronous to the PLL_OUT domain.
Figure 11. Low bandwidth and new clock domain
LRCK
SCLK
SDATA
MCLK
MCLK
Wander > 1 Hz
Wander and Jitter > 1 Hz Rejected
D0 D1
LRCK
SCLK
SDATA
Subclocks generated
from new clock domain.
or
PLL
BW = 1 Hz
CLK_IN PLL_OUT
D0 D1
Jitter
Figure 12. High bandwidth with CLK_IN domain re-use
D0 D1
LRCK
SCLK
SDATA
MCLK
MCLK
Wander < 128 Hz
Jitter > 128 Hz Rejected
Wander < 128 Hz Passed to Output
LRCK
SCLK
SDATA
or
PLL
BW = 128 Hz
CLK_IN PLL_OUT
Subclocks and data re-used
from previous clock domain.
Jitter
D0 D1

CS2000-OTP
14 DS758F3
While acquiring lock, the digital loop bandwidth is automatically set to a large value. Once lock is
achieved, the digital loop bandwidth will settle to the minimum value selected by the ClkIn_BW[2:0] pa-
rameter.
5.4 Output to Input Frequency Ratio Configuration
5.4.1 User Defined Ratio (RUD), Frequency Synthesizer Mode
The User Defined Ratio, RUD, is a 32-bit un-signed fixed-point number which determines the basis for the
desired input to output clock ratio. Up to four different ratios, Ratio0-3, can be stored in the CS2000’s one
time programmable memory. Selection between the four ratios is achieved by the M[1:0] mode select
pins. The 32-bit RUD is represented in a high-resolution 12.20 format where the 12 MSBs represent the
integer binary portion while the remaining 20 LSBs represent the fractional binary portion. The maximum
multiplication factor is approximately 4096 with a resolution of 0.954 PPM in this configuration. See “Cal-
culating the User Defined Ratio” on page 26 for more information.
The status of internal dividers, such as the internal timing reference clock divider, are automatically taken
into account. Therefore RUD is simply the desired ratio of the output to input clock frequencies.
5.4.2 User Defined Ratio (RUD), Hybrid PLL Mode
The same four ratio locations, Ratio0-3, are used to store the User Defined Ratios for Hybrid PLL Mode.
Selection of the User Defined Ratio for the dynamic ratio based Hybrid PLL Mode is made with the M[1:0]
pins (unless auto fractional N source selection is enabled; see section 5.4.5 on page 15).
In addition to the High-Resolution ratio format, a High-Multiplication format is also available. In the High-
Multiplication format mode, the 32-bit fixed-point number for RUD is represented in a 20.12 format where
the 20 MSBs represent the integer binary portion while the remaining 12 LSBs represent the fractional
binary portion. In this configuration, the maximum multiplication factor is approximately 1,048,575 with a
resolution of 244 PPM.
The 20.12 format is enabled by the LFRatioCfg global parameter. The 20.12 ratio format is only available
when the device is running in Hybrid PLL Mode. In Auto Fractional-N Source Selection Mode (see section
5.4.5.2 on page 16) when CLK_IN is not present the LFRatioCfg parameter is ignored and the ratio format
is 12.20.
It is recommended that the 12.20 High-Resolution format be utilized whenever the desired ratio is less
than 4096 since the output frequency accuracy of the PLL is directly proportional to the accuracy of the
timing reference clock and the resolution of the RUD.
Referenced Control Parameter Definition
ClkIn_BW[2:0] ....................... “Clock Input Bandwidth (ClkIn_BW[2:0])” on page 25
Referenced Control Parameter Definition
Ratio 0-3................................“Ratio 0 - 3” on page 23
M[1:0] ....................................“M1 and M0 Mode Pin Functionality” on page 19
Referenced Control Parameter Definition
LockClk[1:0] ..........................“Lock Clock Ratio (LockClk[1:0])” section on page 23
LFRatioCfg ............................ “Low-Frequency Ratio Configuration (LFRatioCfg)” on page 24
FracNSrc ............................... “Fractional-N Source for Frequency Synthesizer (FracNSrc)” section on page 23

CS2000-OTP
DS758F3 15
5.4.3 Ratio Modifier (R-Mod)
The Ratio Modifier is used to internally multiply/divide the currently addressed RUD (Ratio0-3 stored in the
register space remain unchanged). The available options for R-Mod are summarized in Table 2 on
page 15. R-Mod is enabled via the M2 pin in conjunction with the appropriate setting of the M2Config[2:0]
global parameter (see Section 5.7.2 on page 19).
Table 2. Ratio Modifier
5.4.4 Effective Ratio (REFF)
The Effective Ratio (REFF) is an internal calculation comprised of RUD and the appropriate modifiers, as
previously described. REFF is calculated as follows:
REFF = RUD R-Mod
To simplify operation the device handles some of the ratio calculation functions automatically (such as
when the internal timing reference clock divider is set). For this reason, the Effective Ratio does not need
to be altered to account for internal dividers.
Ratio modifiers which would produce an overflow or truncation of REFF should not be used. In all cases,
the maximum and minimum allowable values for REFF are dictated by the frequency limits for both the
input and output clocks as shown in the “AC Electrical Characteristics” on page 7.
Selection of the user defined ratio from the four stored ratios is made by using the M[1:0] pins unless auto
clock switching is enabled in which case the LockClk[1:0] modal parameter also selects the ratio (see
“Fractional-N Source Selection” on page 15).
5.4.5 Fractional-N Source Selection
To select between the static ratio based Frequency Synthesizer Mode and the dynamic ratio based Hybrid
PLL Mode, the source for the fractional-N value for the Frequency Synthesizer must be changed. The
Fractional-N value can either be sourced directly from the Effective Ratio (static ratio) or from the output
of the Digital PLL (dynamic ratio) (see Figure 13 on page 17). The setting of this function can be made
manual or automatically depending on the presence of CLK_IN.
RModSel[1:0] R Modifier
00 0.5
01 0.25
10 0.125
11 0.0625
Referenced Control Parameter Definition
Ratio 0-3................................“Ratio 0 - 3” on page 23
RModSel[1:0] ........................“R-Mod Selection (RModSel[1:0])” section on page 22
M2Config[2:0]........................“M2 Pin Configuration (M2Config[2:0])” on page 25
Referenced Control Parameter Definition
M[1:0] pins.............................“M1 and M0 Mode Pin Functionality” on page 19
LockClk[1:0] ..........................“Lock Clock Ratio (LockClk[1:0])” section on page 23

CS2000-OTP
16 DS758F3
5.4.5.1 Manual Fractional-N Source Selection for the Frequency Synthesizer
Manual selection of the fractional-N source for the frequency synthesizer can be done in one of two
ways. The FracNSrc modal parameter can be set to the desired setting for each available configu-
ration mode and then the Fractional N source is selected by the M1 and M0 pins. In order for this
manual selection to work, the LockClk[1:0] modal parameter (even if unused) must be set to the
same value as the modal ratio (Ratio 0 for Mode 0, Ratio 1 for Mode 1, etc.), see Section 5.4.5.2
on page 16. Alternatively, the M2 pin in conjunction with the M2Config[2:0] global parameter can
be set to control the fractional N source directly and thus override the FracNSrc modal parameter
(see Section 5.7.2.4 on page 20 for details).
5.4.5.2 Automatic Fractional-N Source Selection for the Frequency Synthesizer
Automatic source selection allows for the selection of the frequency synthesizer’s fractional-N value
to be made dependent on the presence of the CLK_IN signal. When CLK_IN is present the device
will use the dynamic ratio generated from the Digital PLL and CLK_IN for Hybrid PLL Mode. When
CLK_IN is not present, the device will use RefClk and the static ratio for Frequency Synthesizer
Mode. After losing CLK_IN, the CS2000-OTP will wait for 223 SysClk cycles before switching to Sy-
sClk and re-acquiring lock, during which time the PLL is unlocked
The modal ratio location (see Table 1 on page 11) should contain the desired CLK_OUT to RefClk
ratio to be used when CLK_IN is not present. The User Defined Ratio pointed to by LockClk[1:0]
should contain the desired CLK_OUT to CLK_IN ratio to be used when CLK_IN is present. Auto-
matic source selection is enabled when the LockClk[1:0] modal parameter is set to a different User
Defined Ratio from the modal ratio location.
When automatic source selection is enabled, the FracNSrc modal parameter (used for manual
clock selection) will be ignored.
The automatic source selection feature can be disabled by setting the LockClk[1:0] modal param-
eter to the modal ratio location. The FracNSrc modal parameter must then be used to select the
desired clock used for the PLL’s frequency reference. The automatic source selection feature can
also be disabled by using the M2 pin in conjunction with the M2Config[2:0] global parameter.
Referenced Control Parameter Definition
M[1:0] pins ............................ “M1 and M0 Mode Pin Functionality” on page 19
LockClk[1:0] .......................... “Lock Clock Ratio (LockClk[1:0])” section on page 23
FracNSrc............................... “Fractional-N Source for Frequency Synthesizer (FracNSrc)” section on page 23
M2Config[2:0] ....................... “M2 Pin Configuration (M2Config[2:0])” on page 25
Referenced Control Parameter Definition
M[1:0] pins ............................ “M1 and M0 Mode Pin Functionality” on page 19
LockClk[1:0] .......................... “Lock Clock Ratio (LockClk[1:0])” section on page 23
FracNSrc............................... “Fractional-N Source for Frequency Synthesizer (FracNSrc)” section on page 23
M2Config[2:0] ....................... “M2 Pin Configuration (M2Config[2:0])” on page 25

CS2000-OTP
DS758F3 17
5.4.6 Ratio Configuration Summary
The RUD is the user defined ratio for which up to four different values (Ratio0-3) can be stored in the one
time programmable memory. The M[1:0] pins or LockClk[1:0] modal parameter then select the user de-
fined ratio to be used (depending on if static or dynamic ratio mode is to be used). The resolution for the
RUD is selectable for the dynamic ratio mode. R-Mod is applied accordingly. The user defined ratio, ratio
modifier, and automatic ratio modifier make up the effective ratio REFF, the final calculation used to deter-
mine the output to input clock ratio. The effective ratio is then corrected for the internal dividers. The fre-
quency synthesizer’s fractional-N source selection is made between the static ratio (in frequency
synthesizer mode) or the dynamic ratio generated from the digital PLL (in Hybrid PLL mode) by either the
FracNSrc modal parameter for manual mode or the presence of CLK_IN in automatic mode. The concep-
tual diagram in Figure 13 summarizes the features involved in the calculation of the ratio values used to
generate the fractional-N value which controls the Frequency Synthesizer. The subscript ‘4’ indicates the
modal parameters.
Figure 13. Ratio Feature Summary
Referenced Control Parameter Definition
Ratio 0-3................................“Ratio 0 - 3” on page 23
M[1:0] pins.............................“M1 and M0 Mode Pin Functionality” on page 19
LockClk[1:0] ..........................“Lock Clock Ratio (LockClk[1:0])” section on page 23
LFRatioCfg ............................ “Low-Frequency Ratio Configuration (LFRatioCfg)” on page 24
RModSel[1:0] ........................“R-Mod Selection (RModSel[1:0])” section on page 22
RefClkDiv[1:0] .......................“Reference Clock Input Divider (RefClkDiv[1:0])” on page 24
FracNSrc ............................... “Fractional-N Source for Frequency Synthesizer (FracNSrc)” section on page 23
Effective Ratio REFF
Ratio Format
Frequency Reference Clock
(CLK_IN)
SysClk PLL Output
Frequency
Synthesizer
Digital PLL &
Fractional N Logic
R Correction N
Ratio 0
Ratio 1
Ratio 2
Ratio 3
12.20
20.12
12.20
only
M[1:0] pins
LockClk[1:0]4
LFRatioCfg
Ratio
Modifier
RModSel[1:0]4
Ratio
Modifier
Auto Selection
(CLK_IN sense)
Manual Selection
(FracNSrc4or M2 pin)
R Correction
RefClkDiv[1:0]
Timing Reference Clock
(XTI/REF_CLK)
Divide
RefClkDiv[1:0]
Static Ratio
Dynamic Ratio
User Defined Ratio RUD
M2 pin force Manual
or
M[1:0] pins =? LockClk[1:0]
=
M2 pin

CS2000-OTP
18 DS758F3
5.5 PLL Clock Output
The PLL clock output pin (CLK_OUT) provides a buffered version of the output of the frequency synthesizer.
The driver can be set to high-impedance with the M2 pin when the M2Config[1:0] global parameter is set to
either 000 or 010. The output from the PLL automatically drives a static low condition while the PLL is un-
locked (when the clock may be unreliable). This feature can be disabled by setting the ClkOutUnl global
parameter, however the state CLK_OUT may then be unreliable during an unlock condition.
Figure 14. PLL Clock Output Options
5.6 Auxiliary Output
The auxiliary output pin (AUX_OUT) can be mapped, as shown in Figure 15, to one of four signals: refer-
ence clock (RefClk), input clock (CLK_IN), additional PLL clock output (CLK_OUT), or a PLL lock indicator
(Lock). The mux is controlled via the AuxOutSrc[1:0] modal parameter. If AUX_OUT is set to Lock, the Aux-
LockCfg global parameter is then used to control the output driver type and polarity of the LOCK signal (see
section 6.3.1 on page 24). In order to indicate an unlock condition, REF_CLK must be present. If AUX_OUT
is set to CLK_OUT, the phase of the PLL Clock Output signal on AUX_OUT may differ from the CLK_OUT
pin. The driver for the pin can be set to high-impedance using the M2 pin when the M2Config[1:0] global
parameter is set to either 001 or 010.
Figure 15. Auxiliary Output Selection
Referenced Control Parameter Definition
ClkOutUnl..............................“Enable PLL Clock Output on Unlock (ClkOutUnl)” on page 24
ClkOutDis .............................. “M2 Configured as Output Disable” on page 19
M2Config[2:0]........................“M2 Pin Configuration (M2Config[2:0])” on page 25
Referenced Control Parameter Definition
AuxOutSrc[1:0]......................“Auxiliary Output Source Selection (AuxOutSrc[1:0])” on page 23
AuxOutDis ............................. “M2 Configured as Output Disable” on page 19
AuxLockCfg...........................“AUX PLL Lock Output Configuration (AuxLockCfg)” section on page 24
M2Config[2:0]........................“M2 Pin Configuration (M2Config[2:0])” on page 25
PLL Locked/Unlocked
PLL Output
2:1 Mux
M2 pin with
M2Config[1:0] = 000, 010
2:1 Mux
ClkOutUnl
0
PLL Clock Output Pin
(CLK_OUT)
0
1
0
1
PLL Clock Output
PLLClkOut
Frequency Reference Clock
(CLK_IN)
PLL Lock/Unlock Indication
(Lock)
Timing Reference Clock
(RefClk)
PLL Clock Output
(PLLClkOut)
4:1 Mux Auxiliary Output Pin
(AUX_OUT)
AuxOutSrc[1:0]
AuxLockCfg
M2 pin with
M2Config[1:0] = 001, 010

CS2000-OTP
DS758F3 19
5.7 Mode Pin Functionality
5.7.1 M1 and M0 Mode Pin Functionality
M[1:0] determine the functional mode of the device and select both the default User Defined Ratio and
the set of modal parameters. The modal parameters are RModSel[1:0], AuxOutSrc[1:0], LockClk[1:0], and
FracNSrc. By modifying one or more of the modal parameters between the 4 sets, different functional con-
figurations can be achieved. However, global parameters are fixed and the same value will be applied to
each functional configuration. Figure 17 on page 22 provides a summary of all parameters used by the
device.
5.7.2 M2 Mode Pin Functionality
M2 usage is mapped to one of the optional special functions via the M2Config[2:0] global parameter. De-
pending on what M2 is mapped to, it will either act as an output enable/disable pin or override certain mod-
al parameters. Figure 16 summarizes the available options and the following sections will describe each
option in more detail.
Figure 16. M2 Mapping Options
5.7.2.1 M2 Configured as Output Disable
If M2Config[2:0] is set to either ‘000’, ‘001’, or ‘010’, M2 becomes an output disable pin for one or
both output pins. If M2 is driven ‘low’, the corresponding output(s) will be enabled, if M2 is driven
‘high’, the corresponding output(s) will be disabled.
5.7.2.2 M2 Configured as R-Mod Enable
If M2Config[2:0] is set to ‘011’, M2 becomes the R-Mod enable pin. It should be noted that M2 is
the only way to enable R-Mod. Even though the RModSel[1:0] modal parameter can be set arbi-
trarily for each configuration set, it will not take effect unless enabled via M2. If M2 is driven ‘low’,
R-Mod will be disabled, if M2 is driven ‘high’ R-Mod will be enabled.
M2 pin
Disable CLK_OUT and AUX_OUT pins
Disable AUX_OUT pin
Disable CLK_OUT pin
RModSel[1:0] Modal Parameter Enable
Force AuxOutSel[1:0] = 10 (PLL Clock Out)
Reserved
Force Manual Fractional N Source Selection
M2Config[2:0] global parameter
000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
FracNSrc Modal Parameter Override

CS2000-OTP
20 DS758F3
5.7.2.3 M2 Configured as Auto Fractional-N Source Selection Disable
If M2Config[2:0] is set to ‘100’, M2 becomes a disable pin for the auto fractional-N source selection
functionality. If auto fractional-N source selection is enabled (see section 5.4.5 on page 15), driving
M2 ‘high’ will disable the auto fractional-N source selection and revert control over the fractional-N
source to the FracNSrc modal parameter, regardless of the LockClk[1:0] modal parameter and the
presence of a clock on CLK_IN. If auto fractional-N source selection is not enabled, toggling M2 will
have no effect in this case.
5.7.2.4 M2 Configured as Fractional-N Source Select
If M2Config[2:0] is set to ‘110’, M2 becomes the Fractional-N Source Select pin and will override
the FracNSrc modal parameter. It should be noted that overriding FracNSrc has no effect when
auto clock switching is enabled (see section 5.4.5 on page 15). If M2 is driven ‘low’, the fractional-
N value will be the Static Ratio sourced directly from REFF for Frequency Synthesizer Mode. If M2
is driven ‘high’ the fractional-N value will be the Dynamic Ratio sourced from the Digital PLL for Hy-
brid PLL Mode.
5.7.2.5 M2 Configured as AuxOutSrc Override
If M2Config[2:0] is set to ‘111’, M2 when driven ‘high’ will override the AuxOutSrc[1:0] modal pa-
rameter and force the AUX_OUT source to PLL Clock Output. When M2 is driven ‘low’, AUX_OUT
will function according to AuxOutSrc[1:0].
5.8 Clock Output Stability Considerations
5.8.1 Output Switching
The CS2000-OTP is designed such that re-configuration of the clock routing functions do not result in a
partial clock period on any of the active outputs (CLK_OUT and/or AUX_OUT). In particular, enabling or
disabling an output, changing the auxiliary output source between REF_CLK and CLK_OUT, changing
between Frequency Synthesizer and Hybrid PLL Mode, and the automatic disabling of the output(s)
during unlock will not cause a runt or partial clock period.
The following exceptions/limitations exist:
• Enabling/disabling AUX_OUT when AuxOutSrc[1:0] = 11 (unlock indicator).
• Switching AuxOutSrc[1:0] to or from 01 (CLK_IN) and to or from 11 (unlock indicator)
(Transitions between AuxOutSrc[1:0] = [00,10] will not produce a glitch).
When any of these exceptions occur, a partial clock period on the output may result.
Table of contents
Other Cirrus Logic Synthesizer manuals