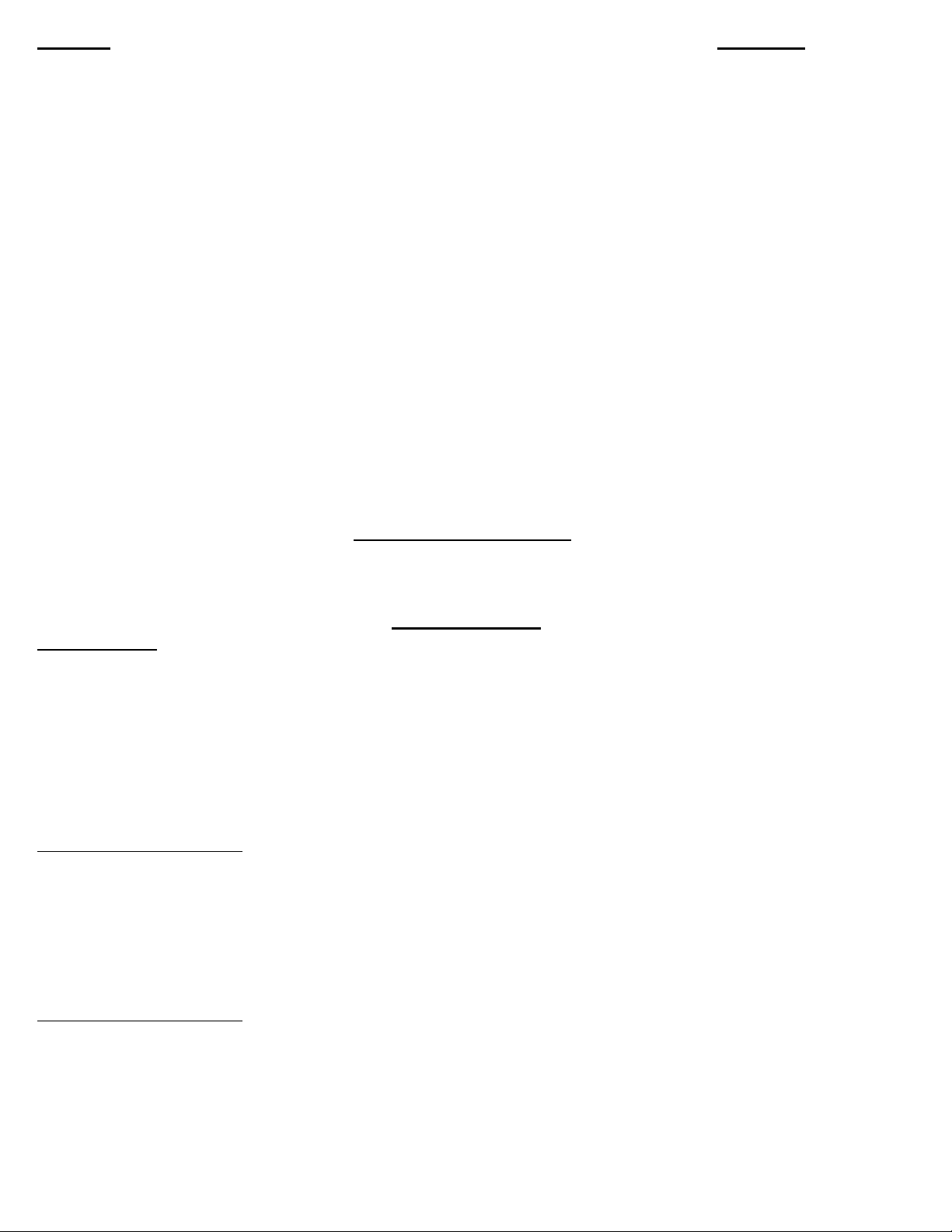Installation and Set Up:
The CTD saw you have purchased is designed to cut wood, aluminum, plastic and steel, with of course the proper
blades and conditions. For the material you are cutting, please refer to the cutting instructions for each type. The machine
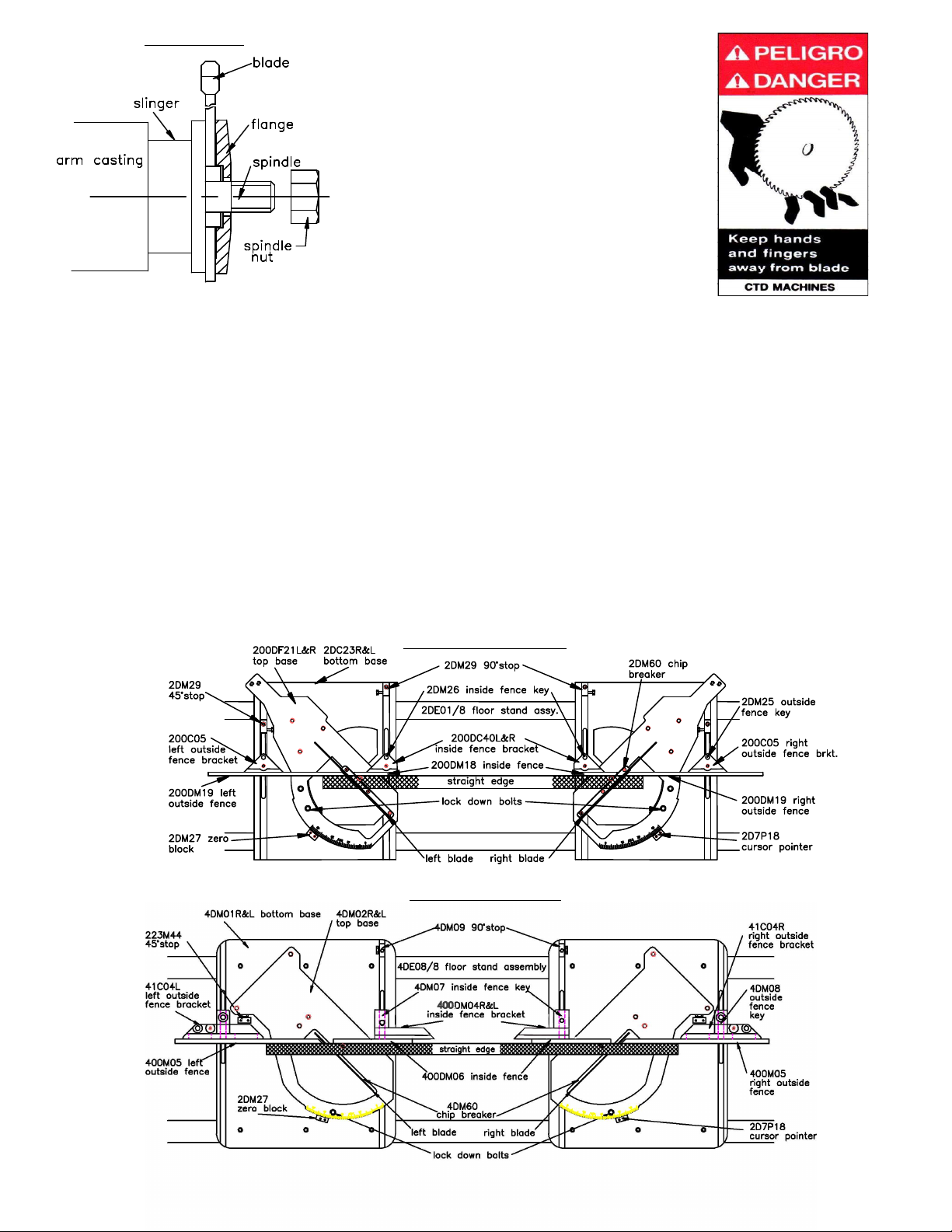
must be leveled and framed in or bolted to the floor. See “Alignment of Saw “on page 5.
The Model DM200R uses NEMA 56 Frame 2 H.P., 3450 RPM, 60 Hertz TEFC Motors.
The DM400 uses NEMA 213T or 215T Frame 8 H.P. or 10 H.P., 1725 RPM, or 15 H.P., 3450 RPM, 60 Hertz TEFC
Motors. CTD uses a speed up drive so that the blade will run at approximately 12,500 SFPM on a 16” blade and 14,000
SFPM on a 20” blade.
IMPORTANT: Before operating the saw, please be sure to read the “SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS TO THE
OPERATOR” (see Page No. 7).
Blade Installation: (for model DM200R)
Before setting blades on spindle, always shut off or disconnect air supply. The model DM200R uses a lower rotating
blade guard. With Motor OFF and Power Disconnected, rotate Lower Blade Guard (p/n 200A270) up into main
blade guard. Slide link puller (p/n 200M360Lor R) off screw and bushing through large hole in slot. Loosen and remove
four machine nuts on Blade Guard Cover (p/n 200F250Lor R) and remove entire Blade Guard Cover Assembly (p/n
200E250Lor R). The entire Blade Guard Cover Assembly, consisting of Bearing Housing, Lower Blade Guard and Link
Puller with Pawl (p/n 200M261) will come off as one piece, exposing spindle nut and flange. (Refer to Page No. 18.)
After blade has been placed on spindle and tightened (see Blade Installation below), replace Blade Guard Cover Assem-
bly with Housing and Link Puller by reversing the sequence.
For DM400 loosen wing nut on bottom blade guard strap and swing down.
Now lift main blade guard, exposing spindle assembly.
To install or remove blade:
1. Hold blade in hand with a rag covering sharp tips, or lower blade into a piece of wood so it will not
rotate. Push down with wrench on spindle nut. Remove spindle nut and outer flange.
2. Place blade on spindle with tips pointing down. Make sure slinger (inner flange) and blade surface are
CLEAN before putting blade on spindle. This is a critical surface and is ground within .0005 flatness.
Any debris or dust will wear this surface. Wipe both surfaces (blade and slinger) with a clean rag.
A. The blade must ALWAYS rotate to the rear of the machine on the underside of the blade
Always check rotation before cutting a piece of material.
3. Replace outer flange and nut as before and tighten (refer to Diagram “A” on Page 5). Pull up with your wrench.
Do not over tighten. Snugging the blade is all that is necessary. Replace Blade Guard parts as before or close
door to cover the blade.
If blades were purchased from CTD, your machine has been set with your blades. If a chip breaker is included on your
machine, it has been cut with the blades purchased from CTD. If not, blade diameters and widths vary and your chip breaker
has not been cut. Cut chip breaker using your blades VERY SLOWLY the first cut through.
Note: Also make sure blades do not contact top base in the down position. Adjust downstop if necessary.
-4-
Blade Guard:
DM200R: The blade and belt drive are enclosed. When the saw arms are lowered, the lower blade guard rotates up into the
main blade guard. The blade continues through the work as the lower blade guard rotates up, via linkage arm. Cut only
material that fits into the cutting capacity of the machine. Damage to the blade guard will result if too large
material is attempted to be cut.
DM400: When the saw arms are lowered, the Blade Guard Bearing, P/N 2B2P05 contacts Blade Guard Guide, P/N
4BM68. The blade continues through the work as the blade guard rides forward on the guide. Always keep the blade
guard guide as close as possible to the material for maximum protection to the operator.