D/F MAC User manual

INSTRUCTIONS, PARTS & SPECIFICATIONS MANUAL
D/F MACHINE SPECIALTIES, INC.
MIG & TIG Welding Products, Consumables & Accessories
Instruction Manual 653AM
MAC/MAT Long
Revised 06/2014
1750 Howard Drive, North Mankato, MN 56003
Phone: (507) 625-6200 Fax: (507) 625-6203
www.dfmachinespecialties.com
AIR COOLED MIG BARRELS
Model MAC - Collet Action (Slip-In Tip)
Model MAT - Threaded Current Tip
Shielding Gas Connection is in the Vertical
Barrel Length - 8.625”

D/F MACHINE SPECIALTIES is a world leader in the design, development, and manufacture of “MIG” (GMAW) & “TIG” (GTAW) weld-
ing products, consumables and accessories. D/F offers several types of manual Air or Water-Cooled “MIG” welding tools, and with the
increased use of automated and robotic welding systems, a demand has been created for welding tools of the highest quality, durability
and interchangeability. For over forty years, D/F welding products have been used extensively on “MIG” and “TIG” welding applications.
This experience, coupled with patented design features, unavailable on any other competitive equipment, has made D/F welding tools
the most advanced “MIG” and “TIG” welding guns and barrels for semi-automatic, automatic or robotic welding applications.
This Catalog is a guide to helping you select the proper tool for a given semi-automatic, automatic or robotic welding application. The fol-
lowing is only a partial listing of available semi-automatic, automatic and robotic guns. For further information on special “MIG” and “TIG”
requirements, please consult the factory.
Customer satisfaction and customer benets are the center
points of all strategic contents
The spirit of the D/F Machine Specialties personnel is to listen to
and to integrate the customer throughout the process, to develop
and design marketable products, to present prototypes, to carry
out pilot tests and to prepare for and be open to new technology
and tasks. We attract and carefully select talented individuals
who share our values. Together we will nurture and sustain a
work environment with two-way communication, training, men-
toring, and rewarding career opportunities.
Commitment to excellence
At D/F Machine Specialties we commit to design, build and deliver
premium products and superior customer support to quality driven
welding professionals. Customers still to this day choose D/F
over competitors because of our responsiveness and exibility.
Customers will continue to choose D/F tomorrow for our superior
hand-made products and service. To ensure this, we need cre-
ative and competent personnel in all business divisions, an inten-
sive exchange of thoughts and ideas with all users, participation
in working and study groups within the eld of welding technology
and intensive cooperation with institutes and universities.
Innovation and quality
Innovation and quality come from being receptive and willing to
learn from others. We encourage our people to be creative and
take risks in the pursuit of excellence. Innovative practices are
deeply rooted in every one of our employees, a philosophy that
leads to continuous product development and industry rsts.
Teamwork
Striving for excellence is a commitment that is an integral com-
ponent of the D/F Culture. Our team of skilled and dedicated
employees takes pride in the excellence products they produce.
Each of us willingly accepts personal responsibility for meeting
our commitments and we hold each other to a high standard of
accountability.
Progress
By remaining condent, focused, and persistent in challenging
times, we will discover opportunity. Commitment to quality and
the pursuit on innovation ensure that D/F Machine Specialties
will remain an industry leader for years to come.
Responsibility
We will continually strive to be environmentally responsible and to
support the health and safety of our employees, customers, and
neighbors. We continue to support the communities in which we
operate and the industries in which we participate.
Thank You for Choosing D/F Machine Specialties

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction, Ordering Information.................................................................................5
Required Tools List for Disassembly & Assembly.......................................................6-7
How Do I Cut, Fit, and Install a New Liner?...................................................................8
What is the Proper Use of the Nozzle Thread Chaser Tap?..........................................9
(Table I) Gas Nozzles, (Tables II) Current Tips............................................................10
Air-Cooled Machine Barrel Model MAC - Parts........................................................... 11
Air-Cooled Machine Barrel Model MAT - Parts............................................................12
(Table 3) Casings, (Table 4) Liners, (Table 5) Recommended Spare Parts ................13
Air-Cooled Machine Barrel - Remote Mounting & Utilities...........................................14
Utility Station - Air-Cooled Barrels ...............................................................................15
Wire Feeder Adapters & Inlets.....................................................................................16
Troubleshooting......................................................................................................17-20

SAFETY MEASURES - **PLEASE READ!**
Welding is not particularly hazardous when certain safety practices are followed. Anyone using this equipment should be thoroughly
trained in safe welding practices. Failure to observe safe practices may cause serious injury. Handling welding torches presents no dan-
ger if the appropriate safety regulations are strictly adhered to. For example:
• Starting-up procedures must be reserved for those fully conversant with processes relating to arc welding equipment.
• Arc welding can prove damaging to eyes, skin, and hearing! It is therefore imperative that the Accident Prevention Regulations UVV 26.0 and VGB 15 are
fully observed and that all protective clothing, eye and ear protectors specied are worn.
• The load data given are maximum limit gures. Overloading will inevitably damage the torch!
• Before changing wear parts, disconnect for the power supply.
• The operating instructions for the individual welding components - e.g. power source, wire feed and cooling unit must be followed.
• Never pull the cable assembly across sharp edges or set down close to weld spatter or on a hot workpiece.
• Those not involved in the welding process should be protected by curtains or partitions from radiation and the danger of being dazzled.
• When handling gas cylinders, consult the instructions issued by the manufacturers and the suppliers of the pressurized gas.
• Workpieces which have been degreased using chlorinated solvents must be sprayed down with clean water before welding starts to avoid the risk of
phosgene forming. For the same reason, no degreasing baths containing chlorine must be placed close to the welding point.
• All vapors given off by metals can cause harm and a special warning is attached to lead, cadmium, copper, zinc, and beryllium. If necessary, take ap-
propriate precautions (by providing adequate ventilation or an extraction system) to ensure that the legal maximum levels of toxic concentrations are not
exceeded.
For more information, refer to the following standards in their latest revisions and comply as applicable.
• ANSI Standard Z49.1, SAFETY IN WELDING AND CUTTING obtainable from the American Welding Society, 2501 N.W. 7th St., Miami, FL 33125.
• ANSI Standard Z41.1, STANDARD FOR MEN’S SAFETY - TOE FOOTWEAR obtainable from the American National Standards Institute, 1430 Broadway,
New York, NY 10018.
• ANSI Standard Z49.2, FIRE PREVENTION IN THE USE OF CUTTING AND WELDING PROCESSES obtainable from the American National Standards
Institute, 1430 Broadway, New York, NY 10018.
• OSHA, SAFETY AND HEALTH STANDARDS, 29CRF 1910, obtainable from the U.S. Government Printing Ofce, Washington, D.C. 20402.
• AWS Standard A6.0, WELDING AND CUTTING CONTAINERS WHICH HAVE HELD COMBUSTABLES obtainable from the American Welding Society,
2501 N.W. 7th St., Miami, FL 33125.
• NFPA Standard 70-1978, NATIONAL ELECTRICAL CODE obtainable from the National Fire Protection Association, 470 Atlantic Avenue, Boston, MA
02210.
• ANSI Standard Z88.2, “Practice for Respiratory Protection” obtainable from the American National Standards Institute, 1430 Broadway, New York, NY
10018.
• ANSI Standard Z87.1, SAFE PRACTICES FOR OCCUPATION AND EDUCATIONAL EYE AND FACE PROTECTION obtainable from the American
National Standards Institute, 1430 Broadway, New York, NY, 10018.
• NIOSH, SAFETY AND HEALTH IN ARC WELDING AND GAS WELDING AND CUTTING obtainable from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Printing
Ofce, Washington, D.C. 20402.
• American Welding Society Standard AWSF4.1 “Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cutting of Containers and Piping That
Have Held Hazardous Substances”, obtainable from the American Welding Society, 2501 N.W. 7th St., Miami, FL 33125.

5
INTRODUCTION
This manual covers the models MAC/MAT Air Cooled Machine Barrels for mechanized MIG welding with a barrel length
of 8.625” and a shielding gas connection in the vertical. Direct mounting is accomplished by utilizing interconnections to
the welding head or wire drive. Remote mounting is accomplished by an insulated mounting bracket and utilizing a casing/
conduit and an adapter to the wire drive.
Two models are available. The model MAC features a slip-in current tip fastened by a collet nut. The wire diameter range
includes .030”-1/16” with a current capacity of 175-275 amperes in CO2.
The model MAT uses a threaded type current tip. Current capacity is 400 amperes in CO2shielding.
For further information or help with D/F Machine Specialties products, please visit our web site at
www.dfmachinespecialties.com, or consult the factory at 1-507-625-6200.
ORDERING INFORMATION - MAC/MAT
DESCRIPTION CODE NO.
MAT-03 Th’d Tip w/ Nozzle Body 13176
MAT-04 Th’d Tip w/ Nozzle Body 13177
MAT-40 Th’d Tip w/ Nozzle Body 16383
12703
12704
12740
DESCRIPTION CODE NO.
MAC-17 Slip-in Tip w/ Nozzle Body 13176
MAC-18 Slip-in Tip w/ Nozzle Body 13177
MAC-36 Slip-in Tip w/ Nozzle Body 16383
12717
12718
12736
ORDERING INFORMATION - MODELS MAC (SLIP-IN TIP)
ORDERING INFORMATION - MODELS MAT (THREADED TIP)
TABLE 1 - SPARE PARTS
ITEM CODE NO. MIN QTY.
Gas Nozzle
Current Tip
Collet Nut
Body Liner
Insulation Tube
Insulator
To Be Selected
To Be Selected
To Be Selected
To Be Selected
To Be Selected
13163
2
25
1
2
1
1

REQUIRED TOOLS LIST FOR DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY
D/F 12111 Collet/Tip Wrench1. - This is the only tool that should ever be used to tighten the collet nut or the tip. Pressure should be 30
lbs., or as snug as hand tightened. Never use another wrench to apply more torque to this wrench.
D/F Nozzle Thread Chaser Taps (Front & Rear)2. - This is used to re-tap damaged threads that have been improperly cleaned or
cross threaded. Always blow out the nozzle and gas nozzle after changing gas cup or re-tapping. For more information on how to use
the nozzle thread chaser tap, use the following link: www.dfmachine.com/taps
3/8” Open Ended Wrench3. - This is used on the inner body’s gas hose tting to secure the gas hose to the torch’s inner body. A
crescent wrench could be used instead, but due to the large size of crescent wrenches, we prefer the smaller size of the open ended
wrenches. You never want to use excessive force by using too large of a wrench. You will use the Long 7/16” Open Ended Wrench for
the tting on the gas hose itself while using the 3/8” wrench to steady the inner body at the tting. (see #4)
Long 7/16” Open Ended Wrench4. - This is used to secure the gas hose to the torch’s inner body. (see #3)
5/8” Open Ended Wrench5. - This wrench is used to secure the adapter and jam nut that hold the current tip to the inner body. In your
left hand hold the inner body, and with your right hand thread up the adapter using the 5/8” Open Ended Wrench until it is tight. Now
place the same wrench on the jam nut and snug it up against the inner body. Keeping that wrench on the jam nut and placing it on
the table for force, take a second 5/8” Open Ended Wrench, place it on the adapter and push it down (counter-clockwise) securing
the adapter to the inner body.
Adjustable Crescent Wrench6. - A medium size adjustable crescent wrench could be used as well. CAUTION: Never use excessive
force with large wrenches, for you could twist or break parts.
Standard Flat Head Screwdriver7. - This is used to tighten or secure the torch’s body screw. Also, the screwdriver can be used to
straighten the contact tip if it is not aligned in the center of the gas cup or water-cooled nozzle CAUTION: This cannot be done unless
the spatter disc has been removed from the torch.
Long Nose Pliers8. - These are very handy when changing a slip-in contact tip.
3/32” Allen Wrench9.
This is used to secure the set screw that holds the casing in the torch’s inner body.A.
This is used on the inner body’s set screws to secure the power cable to the torch’s inner body.B.
6
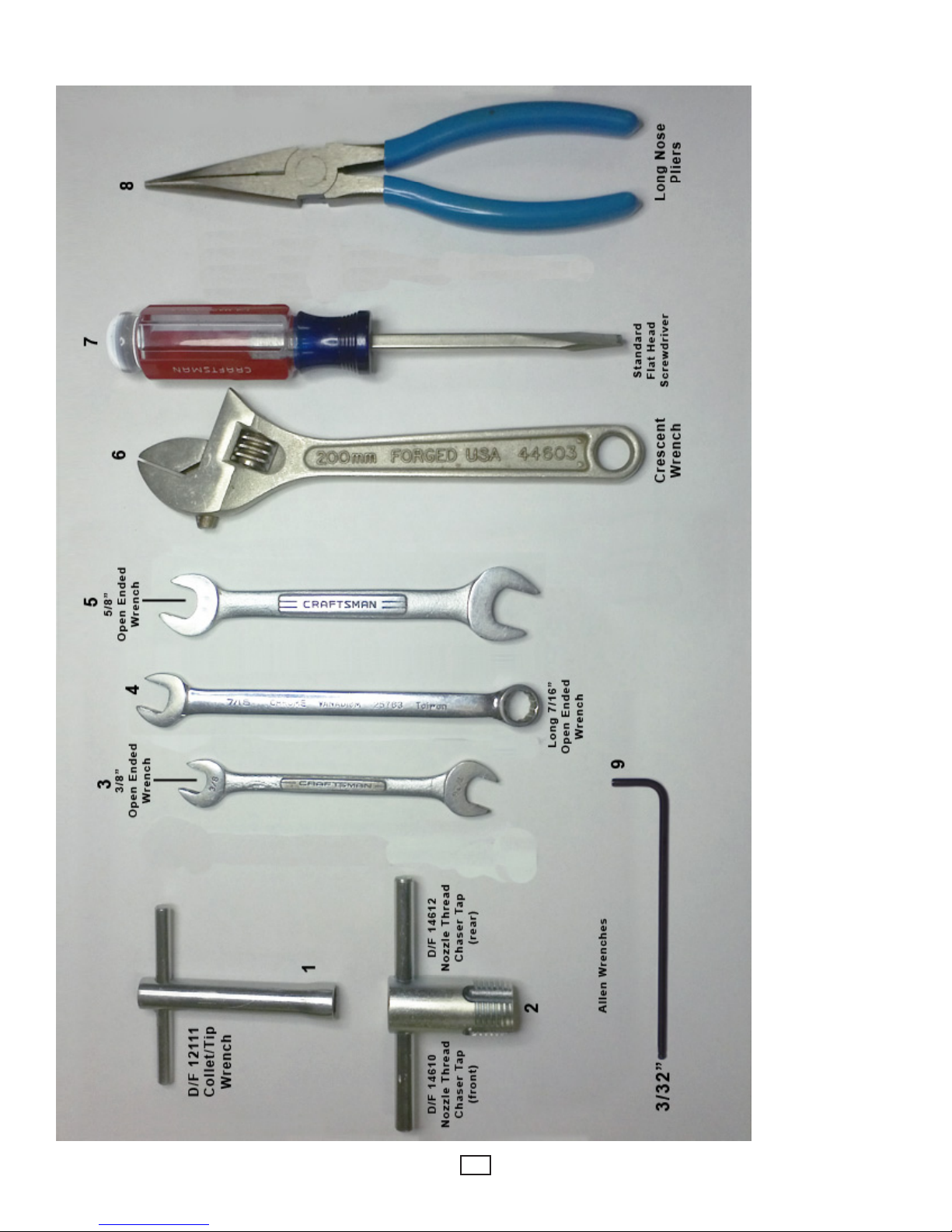
REQUIRED TOOLS LIST FOR DISASSEMBLY & ASSEMBLY
7

8
HOW DO I CUT, FIT, AND INSTALL A NEW LINER?
Be sure the MIG Gun cable is arranged in a straight line, free from twists, when installing or removing a wire liner.1.
Remove the old liner by rst removing the MIG gun’s contact tip.2.
Pull the old wire liner out of the conduit/casing assembly from the feeder connector or feeder adapter plug end. If you are using a3.
feeder adapter that has an inlet, the inlet must be removed rst. If you have any problems removing the liner you may un-thread the
feeder adapter rst this will also back the liner out of the conduit/casing.
If you know that the old liner is the correct length or is still the original liner that was cut at the factory you may hold the new liner up4.
against the old liner and cut off the new liner to the same size as the old liner.
Make sure you have a good sharp cut off with no material sticking out!5.
To get the correct length of the new liner, insert the liner into the feeder adapter and feed it through the conduit/casing.6.
Once again be sure the MIG Gun cable is arranged in a straight line, free from twists, when installing a new wire liner.7.
Sometimes on longer conduits/casings and liners it may take 2 people together; one on each end to rotate and twist the conduit/casing8.
to get the liner trough the torch.
If you have any troubles getting a liner through a torch make sure you have a good sharp cut off, and if you have to you can gently9.
sand the end of the liner on a belt sander. You can remove the cast in the aluminum liner by pre-bending and straightening the liner
before loading.
After the new liner comes out the end of the torch you want to cut the new liner off ush with the end of the copper gas nozzle or Cu 10.
gas cup.
Now you have the overall length of the liner, you still have to take out the length of the contact tip.11.
Carefully remove the liner one more time.12.
After removing the liner hold the gun end of the liner up against the tip.13.
Cut off the length off the tip plus the set back of the tip (1/8” or 3/8” tip setbacks)14.
Now that you have cut off the length of the tip plus the setback you may install the new liner and it will back up into the back of the tip15.
chamfer.
We always recommend checking the condition of the insulation tube in the front of the torch and collet nut that holds the slip-in tip.16.
We always recommend replacing the spatter disc/gas diffuser, contact tip, and nozzle, after installing a new liner.17.
Tighten the at head set screw in the inner body, or the Allen set screw in the docking spool onto the conduit/casing to prevent back-18.
ward movement or an unwanted pumping action.

9
WHAT IS THE PROPER USE OF THE NOZZLE THREAD CHASER TAP?
All D/F Nozzles are hand checked for t before and after plating, and checked again before shipping. If a nozzle has been installed on a
new complete torch, they have also been hand checked while being assembled.
The only reason to ever take a gas cup out a nozzle is to clean it. The nozzle and the gas cup must be blown out, and all of the threads
have to be wire brushed and blown out again before hand-tightening the gas cup back into the nozzle. If you can’t thread it in by hand
then something is wrong. Never force a gas cup into a nozzle.
When using the D/F Machine Specialties nozzle thread chaser taps, be sure to always follow the steps below:
Make sure that the nozzle is properly supported when tapping so it does not twist in the front of the torch body and cause damage.1.
Improper support can cause the spigots to twist off the top of the rear nozzle collar, or damage the torch internal body parts.•
Note where the water ports go down the sides of the water-cooled nozzle (following down in line with the spigots). Too much direct•
pressure on these water ports could cause them to cave in and block of the ow of water.
Best practice is to hold the water-cooled nozzle in a vice with soft jaws, perpendicular to the spigots.•
Over-tightening of the vice can cause damage in general.•
Remove the tip from the front of the torch before tapping.2.
Lightly lubricate the nozzle and nozzle thread chaser tap before tapping.3.
Be sure to start the tap very carefully. Do not cross thread the nozzle.4.
Be very careful to start threads correctly. Only tap 1/2 turn at a time, always backing up and removing chips 1/2 cycle at a time before5.
moving forward. Do not try to tap further into the water-cooled nozzle than needed or past the factory thread depth.
Blow out the nozzle after tapping. Wire brush and blow off the gas cup before threading it back into the nozzle.6.
If nozzle is badly deformed or damaged please return to the factory for a repair estimate before disposing of product (damaged parts7.
can often be repaired).
CODE NO. DESCRIPTION USED WITH
NOZZLE ASSEMBLY
USED FOR
GAS NOZZLE
14610 Nozzle Thread Chaser Tap
for Standard A/C & W/C
Nozzle Assembly Front
13197
16184
11117, 45101
11118, 45102
11119, 45103
45114
45107
NCC-N/HTC-N
NCC-LRN, HTC-LRN
10340
10359
10362
10374
14611 Nozzle Thread Chaser Tap
for BIG MIG & BIG TIG
Nozzle Assembly Front
11123 10382
10387
10389
10390
10392
14612 Nozzle Thread Chaser Tap
for Nozzle Body
Assembly Rear
13196
13197
13198
16184
14614 Nozzle Thread Chaser Tap
for Series A High-Capacity
Nozzle Assembly Front
11142, 45120
11138, 45121
45127
11132, 45129
45125
16748
16749
16750
16751
18030
18031
18032
14615 Nozzle Thread Chaser Tap
for Nozzle Body
Assembly Front
13198 10379
14617 Nozzle Thread Chaser Tap
for Tandem Nozzle
Assembly Front
41641 41667
41668
ORDERING INFORMATION - NOZZLE THREAD CHASER TAPS

10
TABLE 1 - GAS NOZZLES
Gun Model Ref. Nozzle Type O.D. I.D. Code No.
CA-C/CA-T 1
2
3
4
5
Copper Tapered
Copper Straight
Copper Full Taper
Copper Straight
Use with Nozzle Body 13198
63/64”
1”
63/64”
5/8”
1-1/16”
5/8”
3/4”
5/8”
7/16”
3/4
10362
10340
10359
10374
10379
1 2 3 4
Gun/Barrel Model Wire Size Wire Type Code No.
All NC, NCC, NCM
(Tip provides 1/8” set back)
.030”
.035”
.045”
.052”
1/16”
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
10794
10795
10796
10840
10797
All NC, NCC, NCM
(Tip provides 1/8” set back)
3/64”
1/16”
Aluminum
Aluminum
10785
10786
CURRENT TIPS - 2-1/2” SLIP-IN - 1/4” DIAMETER
5
TABLE 2 - CURRENT TIPS
Gun/Barrel Model Wire Size Wire Type Code No.
All NC, NCC, NCM
(Tip provides 1/8” set back)
.030”
.035”
.045”
.052”
1/16”
5/64”
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
10787
10788
10789
10830
10790
10792
All NC, NCC, NCM
(Tip provides 1/8” set back)
3/64”
1/16”
5/64”
3/32”
Aluminum
Aluminum
Aluminum
Aluminum
10781
10782
10823
10783
CURRENT TIPS - 1/4” DIAMETER SLIP-IN
Gun/Barrel Model Wire Size Wire Type Code No.
All NC, NCC, NCM
(Tip provides 1/8” set back)
.030”
.035”
.045”
.052”
1/16”
5/64”
3/32”
7/64”
1/8”
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
19390
19391
19392
19393
19394
19711
19726
19396
19727
All NC, NCC, NCM
(Tip provides 3/8” set back)
.035”
.045”
.052”
1/16”
5/64”
3/32”
7/64”
1/8”
Cored
Cored
Cored
Cored
Cored
Cored
Cored
Cored
19400
19401
19402
19403
19404
19405
19406
19720
All NC, NCC, NCM
(Tip provides 1/8” set back)
3/64”
1/16”
5/64”
3/32”
Aluminum
Aluminum
Aluminum
Aluminum
19407
19408
19728
19409
CURRENT TIPS - 2-1/2” SLIP-IN - 5/16” DIAMETER CURRENT TIPS - 7/16” DIAMETER THREADED
Gun/Barrel Model Wire Size Wire Type Code No.
All HT, HTC, HTM, CTW, CW-T,
MTW
(Tip provides 1/8” set back)
.035”
.045”
.052”
1/16”
5/64”
3/32”
7/64”
1/8”
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
Hard
15116
15117
15121
15118
15119
15120
15122
15105
All HT, HTC, HTM, CTW, CW-T,
MTW
(Tip provides 3/8” set back)
.035”
.045”
.052”
1/16”
5/64”
3/32”
7/64”
1/8”
Cored
Cored
Cored
Cored
Cored
Cored
Cored
Cored
15101
15106
15112
15107
15108
15109
15110
15111
All HT, HTC, HTM, CTW, CW-T,
MTW
(Tip provides 1/8” set back)
3/64”
1/16”
5/64”
3/32”
1/8”
Aluminum
Aluminum
Aluminum
Aluminum
Aluminum
15126
15125
15087
15148
15123

11
AIR-COOLED MACHINE BARREL
Model MAC - Slip-In Tip
REF. CODE NO. DESCRIPTION
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
14335
14322
14712
14111
16091
16202
13205
13209
11950
13163
16383
16384
16246
16379
16380
16381
16382
14610
16605
13176
13197
13177
13198
12111
16950
16951
16952
16953
16954
14803
14262
14090
14612
16066
Nut
Washer
Socket Set Screw
Casing Adapter
Inner Body Assembly
Adapter Jam Nut
Barrel Liner (see Table below)
Alignment Tube (see Table below)
Adapter - 1/4” Slip-In Tip
Adapter - 5/16” Slip-In Tip
Collet Nut
Current Tip (see p. 10, Table 2)
Insulator
Nozzle Body (w/ Insulator)
Nozzle Body (less insulator)
Insulator - Gas Nozzle
(used with 16379, 16380, 16381, 16382)
Gas Nozzle (.540” ID, used w/ 2.5” Tip)
Gas Nozzle (.625” ID, used w/ 2.5” Tip)
Gas Nozzle (.540” ID, used w/ 4” Tip)
Gas Nozzle (.625” ID, used w/ 4” Tip)
Nozzle Thread Chaser Tap - Nozzle Body Front
Insulator - Nozzle Body Inner Wall
Nozzle Body (w/ Insulator)
Nozzle Body (less insulator)
Gas Nozzle (see p. 10, Table 1)
Nozzle Body (w/ Insulator)
Nozzle Body (less insulator)
Gas Nozzle (see p. 10, Table 1)
Wrench
Cable/Hose Sheath 2 Ft.
Cable/Hose Sheath 3 Ft.
Cable/Hose Sheath 4 Ft.
Cable/Hose Sheath 5 Ft.
Cable/Hose Sheath 6 Ft.
Clamp
Socket Cap Screw
Mounting Bracket
Nozzle Thread Chaser Tap - Nozzle Body Rear
Sleeve - Split (used w/ 14090 Mounting Bracket)
2
1
3
4
5
7
6
8
10
9
11
12 12 12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
CODE NO. WIRE SIZE TYPE WIRE
16065
14181
14182
14201
14184
.030”-.035”
.035”-.045”
.045”-1/16”
3/64”
5/64”-3/32”
Hard
Hard
Hard
Soft
Cored
ORDERING INFORMATION - ALIGNMENT TUBES
ORDERING INFORMATION - BARREL LINERS
CODE NO. DESCRIPTION LINER WIRE SIZE
16256
16257
16257
Used with
4” Slip-In Tip
.030”-.035”
.045”-1/16”
3/64”
16440
16441
16442
Used with
2-1/2” Slip-In Tip
.030”-.035”
.045”-1/16”
3/64”
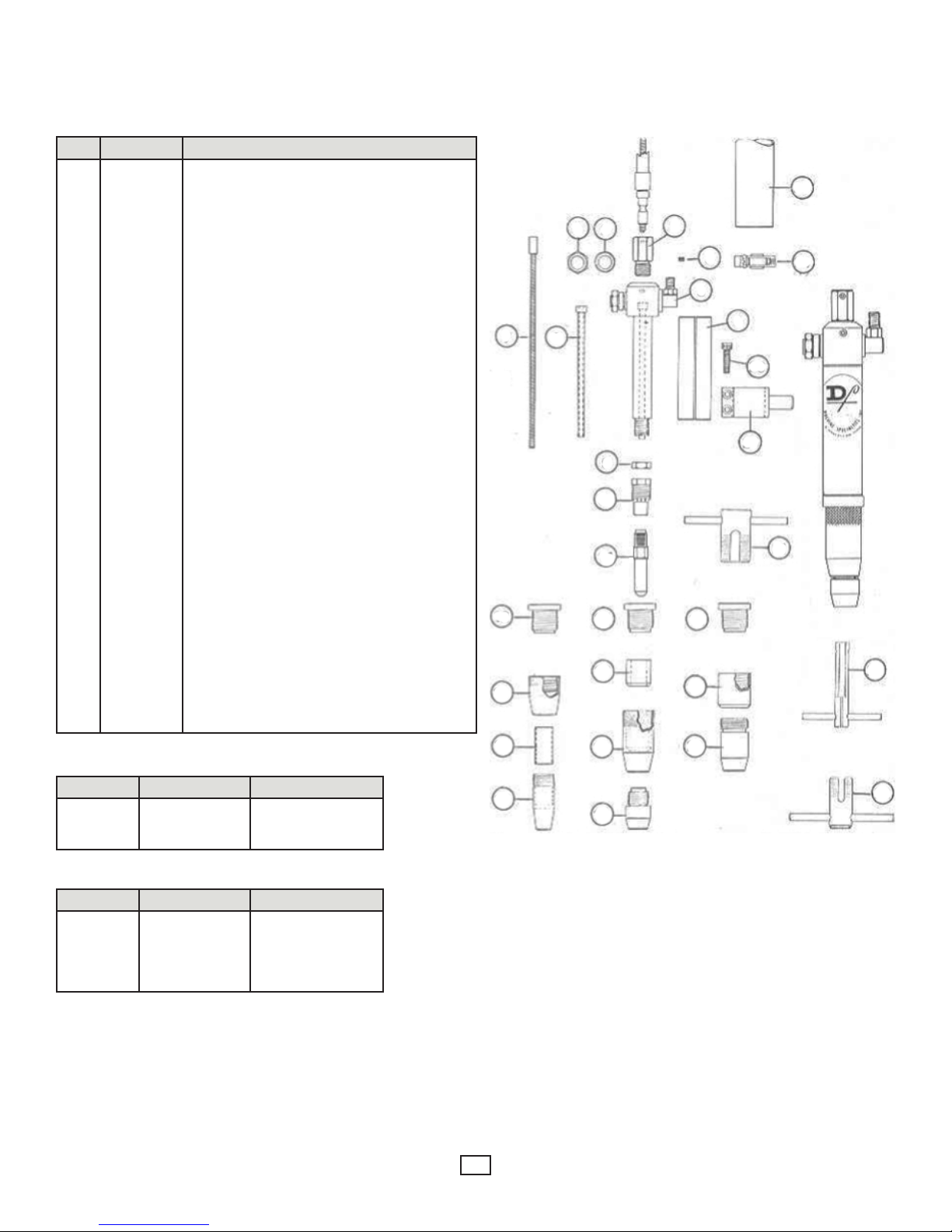
12
AIR-COOLED MACHINE BARREL
Model MAT - Threaded Tip
2
1
3
4
5
7
6
8
10
9
11
12
13
14 15
16
17
18
19
20
27
21
22
23
24
25
26
REF. CODE NO. DESCRIPTION
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
14335
14322
14712
14111
16091
16202
13205
13163
16383
16384
16246
16379
16380
16381
16382
14610
16605
13176
13197
13177
13198
16950
16951
16952
16953
16954
14803
14262
14090
14612
16066
12111
Nut
Washer
Socket Set Screw
Casing Adapter
Inner Body Assembly
Adapter Jam Nut
Barrel Liner (see Table below)
Alignment Tube (see Table below)
Adapter - 7/16” Threaded Tip
Current Tip (see p. 10, Table 2)
Insulator
Nozzle Body (w/ Insulator)
Nozzle Body (less insulator)
Insulator - Gas Nozzle
(used with 16379, 16380, 16381, 16382)
Gas Nozzle (.540” ID, used w/ 2.5” Tip)
Gas Nozzle (.625” ID, used w/ 2.5” Tip)
Gas Nozzle (.540” ID, used w/ 4” Tip)
Gas Nozzle (.625” ID, used w/ 4” Tip)
Nozzle Thread Chaser Tap - Nozzle Body Front
Insulator - Nozzle Body Inner Wall
Nozzle Body (w/ Insulator)
Nozzle Body (less insulator)
Gas Nozzle (see p. 10, Table 1)
Nozzle Body (w/ Insulator)
Nozzle Body (less insulator)
Gas Nozzle (see p. 10, Table 1)
Cable/Hose Sheath 2 Ft.
Cable/Hose Sheath 3 Ft.
Cable/Hose Sheath 4 Ft.
Cable/Hose Sheath 5 Ft.
Cable/Hose Sheath 6 Ft.
Clamp
Socket Cap Screw
Mounting Bracket
Nozzle Thread Chaser Tap - Nozzle Body Rear
Sleeve - Split (used w/ 14090 Mounting Bracket)
Wrench
11 11
CODE NO. DESCRIPTION LINER WIRE SIZE
16254
16255
16255
Used with 7/16”
Threaded Tip
.030”-.035”
.045”-1/16”
3/64”
CODE NO. WIRE SIZE TYPE WIRE
16065
14181
14182
14201
14184
.030”-.035”
.035”-.045”
.045”-1/16”
3/64”
5/64”-3/32”
Hard
Hard
Hard
Soft
Cored
ORDERING INFORMATION - ALIGNMENT TUBES
ORDERING INFORMATION - BARREL LINERS

13
TABLE 3 - LINERS
Description Wire Size 2 Ft. 3 Ft. 4 Ft. 5 Ft. 6 Ft. 7 Ft. 8 Ft. 10 Ft. 12 Ft. 15 Ft.
Hard
Hard/Cored
Hard/Cored
Stainless
Stainless
Aluminum
Aluminum
Aluminum
.030”
.035”-.045” **
.045”-1/16” **
.035”-.045” **
.045”-1/16” **
3/64” **
1/16” **
3/32” **
-
16443
16147
16154
16501
16833
16834
16835
14130
16444
16148
16155
16502
14146
14152
14158
14131
16445
16149
16156
16503
14148
14154
14160
14132
16446
16150
16157
16504
14150
14156
14162
16818
16447
16151
16158
16505
16618
14164
14165
16819
16448
16152
16159
16506
16619
16620
16769
16820
16449
16153
16160
16507
12410
12401
16602
12320
16407
16119
12336
16508
12411
12402
16602
12321
16408
16120
12337
16509
12412
12416
12417
12322
16409
16121
12338
16510
12413
12404
12426
** Liners to be used with double asterisk casing (Table 4)
TABLE 4 - CASINGS
Description Wire Size 2 Ft. 3 Ft. 4 Ft. 5 Ft. 6 Ft. 7 Ft. 8 Ft. 10 Ft. 12 Ft. 15 Ft.
Casing Assembly (Flexible)
Select Liner
Select Liner
.030”
.035”-1/16” **
14440
14444
14441
14445
14442
14446
14443
14447
12291
16173
12292
16561
12285
13565
12286
13751
12287
13757
12290
13752
Casing Assembly (Reinforced)
Single Piece
Single Piece
Single Piece
Single Piece
.035”-.045”
.045”-1/16”
5/64”-3/32”
7/64”-1/8”
16735
15750
15729
15740
16736
15751
15730
15741
16737
15752
15731
15742
16738
15753
15732
15743
16739
15754
15733
15744
16740
15755
15734
15745
16512
16513
15735
16515
15988
12380
12441
12445
15991
12383
12449
12448
16055
12386
12443
12446
TABLE 5 - RECOMMENDED SPARE PARTS
ITEM CODE NO. MIN QTY.
Gas Nozzle
Current Tip
Collet Nut
Body Liner
Insulation Tube
Insulator
To Be Selected
To Be Selected
To Be Selected
To Be Selected
To Be Selected
13163
2
25
1
2
1
1

14
AIR-COOLED MACHINE BARREL - REMOTE MOUNTING
DESCRIPTION CODE NO.
2 Ft. 3 Ft. 4 Ft. 5 Ft. 6 Ft. 8 Ft. 10 Ft.
Power Cable 1/0 16052 16039 15256 16437 15257 15258 15259
Power Cable 2/0 15232 16075 15263 16438 15264 15265 15266
Barrel
1.250” Dia.
Mounting Dia.
.625”
2.750”
8.625”
3.500”
Casings - Select from p. 13, Table 9
See Chart Below for Power Cable
ORDERING INFORMATION - POWER CABLE
1”
Description CODE NO.
2 Ft. 3 Ft. 4Ft. 5 Ft. 6 Ft. 8 Ft. 10 Ft.
Gas Hose 14500 14501 14502 14503 14504 11845 11846
ORDERING INFORMATION - GAS HOSE
See Chart Below for Gas Hose
15
Description Code No.
Utility Station - Air-Cooled Barrels 45184
UTILITY STATION 45184 - AIR-COOLED BARRELS
1/0 or 2/0
Power Cable
Shielding Gas
(3/16” Hose Shank)
1.125”
Shielding Gas
(3/16” Hose Shank)
2.75”
3.75”
5.75”
2.5”
3.125”
ORDERING INFORMATION
1/0 or 2/0
Power Cable
Gas
Hose
Base Length 3.75”
Overall Length 5.75”
Base Width 2.25”
Overall Width 2.5”
Overall Height 3.125”
Mounting Hole Center Distance 2.75”
Overall Weight 3.5 lbs.
D/F TORCH CONNECTION
CUSTOMER UTILITIES CONNECTION
DIMENSION SPECIFICATIONS
FROM LEFT: D/F TORCH CONNECTION
FROM RIGHT: CUSTOMER UTILITIES CONNECTION
UTILITY STATION SIDE VIEW WITH COVER
Gas Hose
2 ea.
1/4”-20 Screws,
Lock Washers,
Nuts
1/0 or 2/0
Power Cable
1/0 or 2/0
Power Cable

16
Wire Size Steel
Code No.
Brass
Code No.
Nylon
Code No.
.030”
.035”
.045”
.052”
1/16”
5/64”
3/32”
7/64”
1/8”
3/64” AL
1/16” AL
3/32” AL
13801
13803
13806
13844
13809
13812
13814
13816
13842
16417
16418
16419
16420
16421
16422
16422
13807
13810
13815
ORDERING INFORMATION
Each D/F gun is fully assembled and ready to in-
stall. In order to make the installation complete,
the code number, wire size & type, make/model
of wire feeder, and inlet as needed must be speci-
ed when ordering. If special welding tools or ac-
cessories other than those listed previously are
required, please consult with the factory.
FEEDER ADAPTER INLETS
Esab®, Hobart®, Lincoln®, Linde®, Miller®, OTC®, Pana-
sonic®ABB®, Fanuc®, Kuka®, Mavrix®, Motoman®, Ther-
mal Arc®, TWECO®, & Welding Alloys®are registered
trademarks of their respective companies. Names are
mentioned for reference only. D/F Machine Specialties is
in no way afliated with these companies.
WIRE FEEDER ADAPTERS & INLETS
Manufac-
turer Models Wire Diameter
Remote Mount Adapter Direct Mount
Adapter
Hard
or AL Cored Stub*
Liner
Hard
or AL Cored
ESAB®D20 (20mm) .030”-3/32” H/C/AL
5/64”-1/8” H/C
13098
13099
*
*
13096
13097
ESAB®18246 18247 18248 18249
EURO 18493 18493 18540 18540
Hobart®All
Models
.030”-3/32” H/C/AL
5/64”-1/8” H/C
13067
16087
*
*
13068
16225
Lincoln®LN-7, LN-8,
NA5-R
.030”-3/32” H/C/AL
5/64”-1/8” H/C
13110
13112
*
*
13113
13116
LN-9 .030”-3/32” H/C/AL
5/64”-1/8” H/C
16581
16582
*
*
16528
16529
NA3, NA5 .030”-3/32” H/C/AL
5/64”-1/8” H/C
16879
16878
*
*
16880
16881
“BIG MIG” NA3, NA5 .030”-3/32” H/C/AL
5/64”-1/8” H/C
16879
16878
*
*
16888
16888
Lincoln®Power-Feed
10, LF-72,
LF-74
.030”-3/32” H/C/AL
5/64”-1/8” H/C
13479
13469
*
*
13480
13468
Linde®SWM31
SWM34
SWM37
SWM38
EH8
Casing to Feeder
(Accepts Linde®
Outlet Guide)
13046 13046
D/F Insert
.035”-.045” Hard
.045”-1/16” Hard
5/64”-3/32” Cored
3/64”-1/16” AL
13047
13048
13050
13049
13047
13048
13050
13049
EH10 .030”-3/32” H/C/AL
5/64”-1/8” H/C
13043
13052
*
*
13080
13079
Mavrix®PA-10 .030”-3/32” H/C/AL
5/64”-1/8” H/C
16556
16568
Requires
Inlet
Miller®
(50 Series)
.030”-3/32” H/C/AL
5/64”-1/8” H/C
16557
16559
*
*
16558
16560
OTC®Requires
Insert
.030”-1/8”
.030”-1/8”
18268 *
* 18275
CMRE-741 18282 18282
Panasonic®PME-12X
YW50AKW1
.030”-1/16”
.030”-1/16”
13090
13466 Requires Inlet
TWECO®#4 .030”-3/32” H/C/AL
5/64”-1/8” H/C
13479
13469
*
*
13480
13468
Welding
Alloys®
.030”-3/32” H/C/AL
5/64”-1/8” H/C
Requires Liner
Requires Inlet
13486
13486
*Stub liners only required in feeder adapter when single-piece casing is used.

17
Causes of Porosity
BASE METAL CONTAMINATION
Impurities on base metal
FILLER METAL CONTAMINATION
Impurities on ller metal (wire)
ATMOSPHERIC CONTAMINATION
Drafts, wind, fans, etc.
GAS MIXING APPARATUS
1. Too high a gas ow, causing turbulence, and/or sucking air
at hose connections; creating the venturi effect at end of gas
nozzle
2. Too low a gas ow, causing insufcient gas coverage
3. Damaged or kinked gas lines
4. Too high an oxygen content
5. Leaks in gas distribution system
6. Other impurities in gas - moisture, etc.
7. Inconsistent gas ow (cfh) at the torch connection
GAS TURBULENCE
1. Excessive spatter build-up in gas nozzle and on current tip
2. Nozzle damage, causing uneven gas coverage
3. Torch gas ports clogged or deformed
4. Super-heated nozzle, causing shielding gas to expand rap-
idly and create return effect at end of nozzle
5.Gas diffuser/nozzle insulator missing
6. Too high a gas ow causing the venturi effect
WELDING PARAMETERS, ETC.
1. Too long a wire stick-out; gas nozzle too far from weld
puddle
2. Bad torch position - too sharp a torch incline causing the
venturi effect at the end of the nozzle leading to atmospheric
contamination
3. Excessively wide weld pool for nozzle I.D.
4. Arc voltage too high
5. Too high a travel speed
TROUBLESHOOTING: POROSITY (SUMMARY)
NOTE: Most POROSITY is caused by gas problems, followed by base metal contamination.
Possible Solutions
a. Remove contamination; clean surfaces
b. Use of specic wire/gas mix for specic types of impurities
a. Replace wire
b. Install wire-cleaning system
c. Prevent industrial dust/dirt/grit from contaminating wire dur-
ing storage or use
d. Prevent build-up of aluminum oxide on exposed aluminum
wire surface by using up quickly
e. Remove wire from wire drive unit and store in a sealed plas-
tic bag when not in use for long periods
a. Protect weld from drafts (curtains/screens)
b. Use tapered or bottleneck gas nozzles when drafts cannot
be avoided
1a. Reduce gas ow
1b. Tighten all hose connection points
2. Increase gas ow
3. Repair or replace
4. Adjust mixer
5. Repair leaks
6. Overhaul system; t lters and/or dryers
7. Regulate pressure into ow meter for consistent cfh delivery
of gas
1. Clean nozzle and tip regularly; spray with anti-spatter uid
2. Replace nozzle
3. Clean or replace
4. Check duty cycle rating of torch
5. Replace
6. Reduce gas ow
1. Use longer nozzle or adjust stick-out (3/8” minimum or 15
times wire diameter)
2. Correct torch angle
3. Width of the weld pool should be 1.3 times the nozzle I.D.;
use suitable wider gas nozzle
4. Reduce voltage
5. Reduce speed

Problems/Causes
SPATTER
Too fast or too slow wire feed for the arc voltage
Too long an arc
Damaged current tip
Inclination of welding gun too great
Faulty power source
Incorrect start
Incorrect pulse parameters
Uneven wire feed
Impurities on the base metal
Poor ground contact
Too long stick-out (short-arc welding)
Incorrect polarity
TROUBLESHOOTING: SPATTER
Possible Solutions
Set the wire feed rate and voltage in accordance with good weld-
ing practices as recommended by a qualied welding engineer.
Adjust the wire feed and voltage so that the arc is in accordance
with good welding practice for the joint to be welded. The dis-
tance from the current tip to the workpiece should be 15 times
the welding wire diameter. If the arc is too long there will be spat-
ter, usually in the direction of the weld.
If the current tip becomes worn the welding wire will not be in
constant contact with the tip and the arc will become unstable.
A current tip contaminated with spatter will cause uneven wire
feed resulting in further spatter.
The angle of the gas nozzle relative to the workpiece should be
between 45 and 90 degrees. If the angle is too small, the wire
runs parallel to the weld pool, resulting in spatter in the direction
of the welding.
Have the power source checked for faulty conditions such as
broken wires and faulty contacts.
A great deal of spatter occurs if the stick-out is too great and if
the welding gun is held too far from the workpiece when striking
the arc. Try to start with as short a stick-out as possible and with
the welding gun as close to the starting point as possible. If a
large ball end is formed on the end of the welding wire, remove
it by cutting the wire with sharp wire cutters. It is helpful if the
wire is cut to a point. Always remove the ball end before striking
an aluminum arc. Check the welding ground connection.
Check the user manual for your power supply or consult a quali-
ed welding engineer.
Uneven wire feed gives rise to heavy spatter. Find the cause of
the disturbance and correct the condition before proceeding.
Paint, mill scale, rust and other contamination on the base metal
form an insulating layer causing an unstable arc that results in
heavy spatter. Clean the surfaces to be welded.
Inspect ground cable for loose connections, fraying and cuts.
Correct any problem areas found and attach the ground cable
directly to the workpiece after having cleaned the contact sur-
face rst. POOR GROUND CONTACT IS THE MOST COM-
MON CAUSE OF UNSTABLE MIG WELDING CONDITIONS.
The stick-out should be 15 times the diameter of the wire elec-
trode being used. With increasing stick-out, the current is re-
duced and the arc voltage rises, giving a longer unstable arc
and increased spatter.
Check for correct polarity. Follow the electrode manufacturer’s
recommendations.
18

Problems/Causes
ERRATIC WIRE FEED
Slipping feed rolls
Clogged or worn gun liner
Liners too long or too short
Spatter on the wire
Coil brake incorrectly adjusted
UNSTABLE ARC
Incorrect setting of voltage and/or current
Problems in wire feeding: worn current tip
Impurities on the base metal
Poor contact between ground cable and work-
piece or loose power connection
Stick-out too long
TROUBLESHOOTING: GENERAL GUIDE
Possible Solutions
Check that the feed roll size is correct for the wire size being used. Increase the
drive roll pressure until the wire feed is even. Do not apply excessive pressure as
this can damage the wire surface, causing copper coating to loosen from steel
wires or metal shavings to be formed from soft wires like aluminum. These metal
fragments or shavings can be drawn into the wire feed conduit and will rapidly
clog the liner. When welding with ux-cored wires, excessive drive roll pressure
may open the wire seam and allow ux or metal powders to escape.
a. Dust, particles of copper, drawing lubricants, metal or ux and other forms of
contamination can all clog the liner so that the wire feed is slowed or impeded. A
liner that has been in use for an extended period of time becomes worn and lled
with dirt and must be replaced.
b. When changing the welding wire, remove the tip from the front end of the
gun and blow out the body liner with clean, dry compressed air from the back of
the gun. Repeat with the casing and liner assembly. Note: Wear safety goggles
when using compressed air to clean the liners. Make sure proper safety proce-
dures are followed in order to avoid possible serious eye injury.
Check the lengths of the liners and trim or replace if too long or too short. The
efcient feeding of the welding wire is dependent on the liners tting correctly.
An unprotected coil of wire quickly collects dust and other airborne contamina-
tion. If grinding is being performed in the vicinity, particles can become attached
to the wire, severely interfering with the wire feed. Replace with clean wire and
keep it protected with a cover. Make sure spare wire rolls are stored in a clean,
dry place.
Set the brake so that the coil immediately stops rotating as soon as welding is
interrupted. If the brake is applied too hard it will cause the feed rolls to slip,
resulting in uneven wire feed. If it is too loose, overrun of the wire will occur,
causing wire tangles, inconsistent tension on the feed mechanism and irregular
arc characteristics.
Set the wire feed in relation to the arc voltage in such a way that the arc is stable
and burns evenly. In spray arc welding, set the wire feed so that there are no
short circuits and the ller metal is transferred in a spray across the arc. Find the
cause of the interference and correct it. (See ERRATIC WIRE FEED above)
When the internal diameter of the current tip becomes worn from the passage
of wire through it, the wire may no longer stay in continuous electrical contact
with the tip. This results in an unstable arc and an increase in spatter. Paint, mill
scale, silicon scale, rust or ux deposits from previous weld runs may form an
insulating layer causing an unstable arc. Clean the surfaces to be welded.
Securely attach the ground cable as close to the point of welding as possible on
the workpiece. Clean the surfaces thoroughly to ensure good contact.
Check to insure the welding power connection on the power source is tight, the
and workpiece. Connection on the wire feeder is tight, the connection to the
adaptor block is tight, Loose power connection and the connection of the gun to
the adaptor block is tight.
Adjust the current tip to work distance to a minimum of 3/8” for short arc welding.
A more precise distance is 15 times the wire diameter.
19

TROUBLESHOOTING: GENERAL GUIDE
20
Problems/Causes
AIR-COOLED GUN RUNNING TOO HOT
Poor ground
Loose power connection
Consumable items loose or worn
Capacity of gun being exceeded
Dirty connection
Possible Solutions
Inspect ground cable for loose connections, fraying and cuts. Correct any prob-
lem areas found. Clean clamping area to insure good contact. Securely attach
the ground cable to the workpiece, as close as possible to the point of welding.
Make sure there is a good connection to the welding power source.
Check to make sure the power connection on the power source is tight, the con-
nection on the wire feeder is tight, the connection to the adaptor block is tight,
and the connection of the gun to the adaptor block is tight.
Remove nozzle from gun and inspect current tip, collet nut (tip holder) and spat-
ter disc (gas diffuser) for wear and tightness; replace or tighten as necessary.
Note complete weld parameters, including welding current (Amps), welding volt-
age, wire feed speed, type and size of wire, type of gas and ow rate of gas and
consult your local Authorized D/F Machine Specialties Distributor or contact the
factory.
Remove torch and inspect parts for dirt build-up. Periodic cleaning is neces-
sary.
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Popular Welding Accessories manuals by other brands

Sundstrom
Sundstrom SR 592 Instructions for use

Bug-O Systems
Bug-O Systems K-BUG 6050 instructions

Lincoln Electric
Lincoln Electric VIKING 3350 Series Operator's manual

ArcOne
ArcOne 1000FcF User instruction manual

Kemppi
Kemppi A3 MIG Rail System 2500 operating manual

Abicor Binzel
Abicor Binzel SR 9 operating instructions











