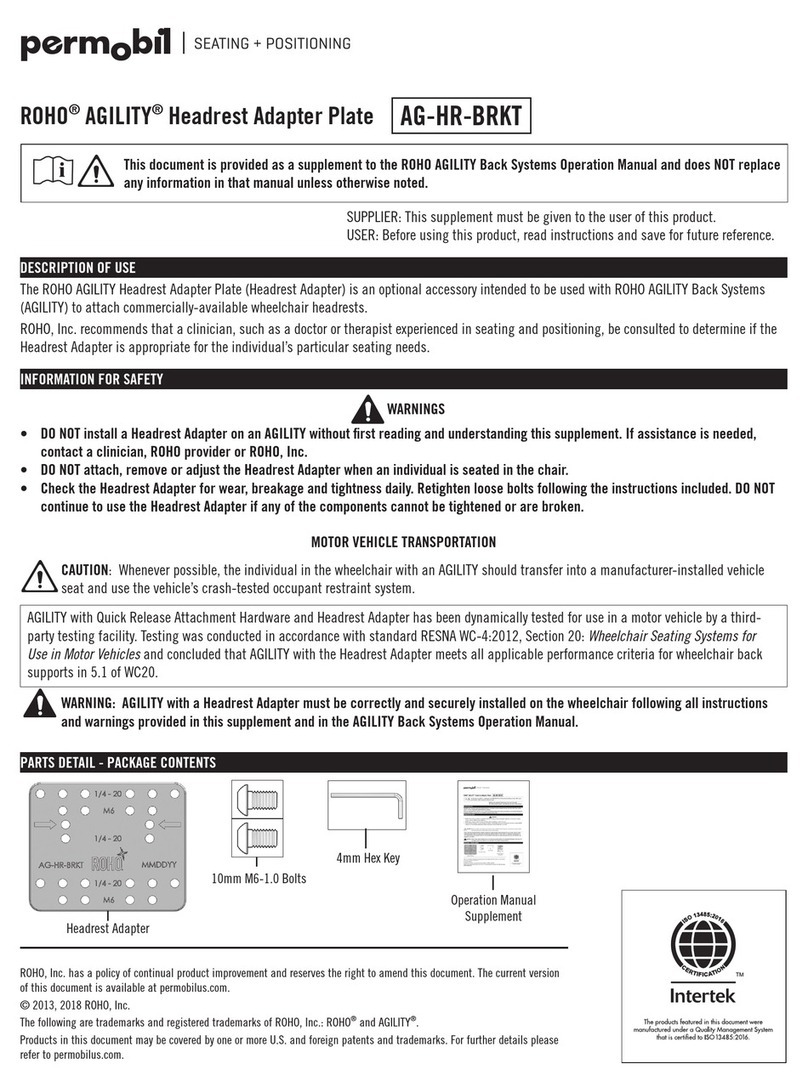
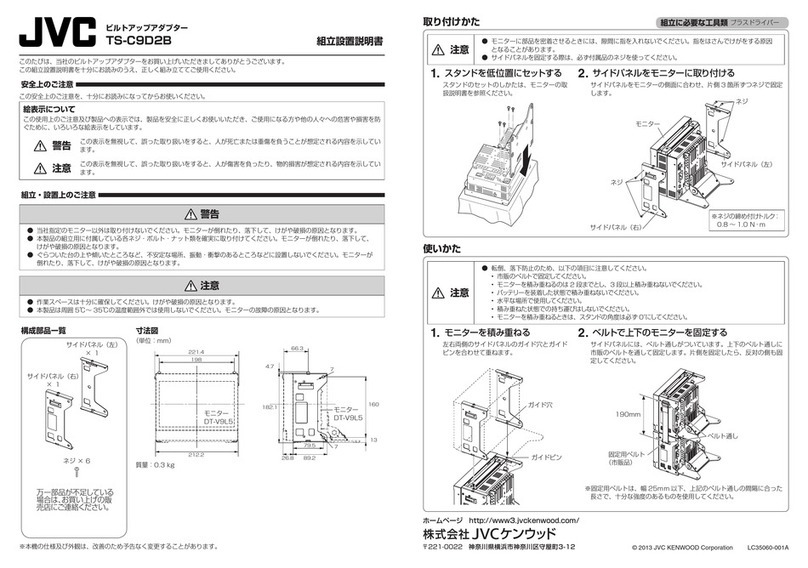
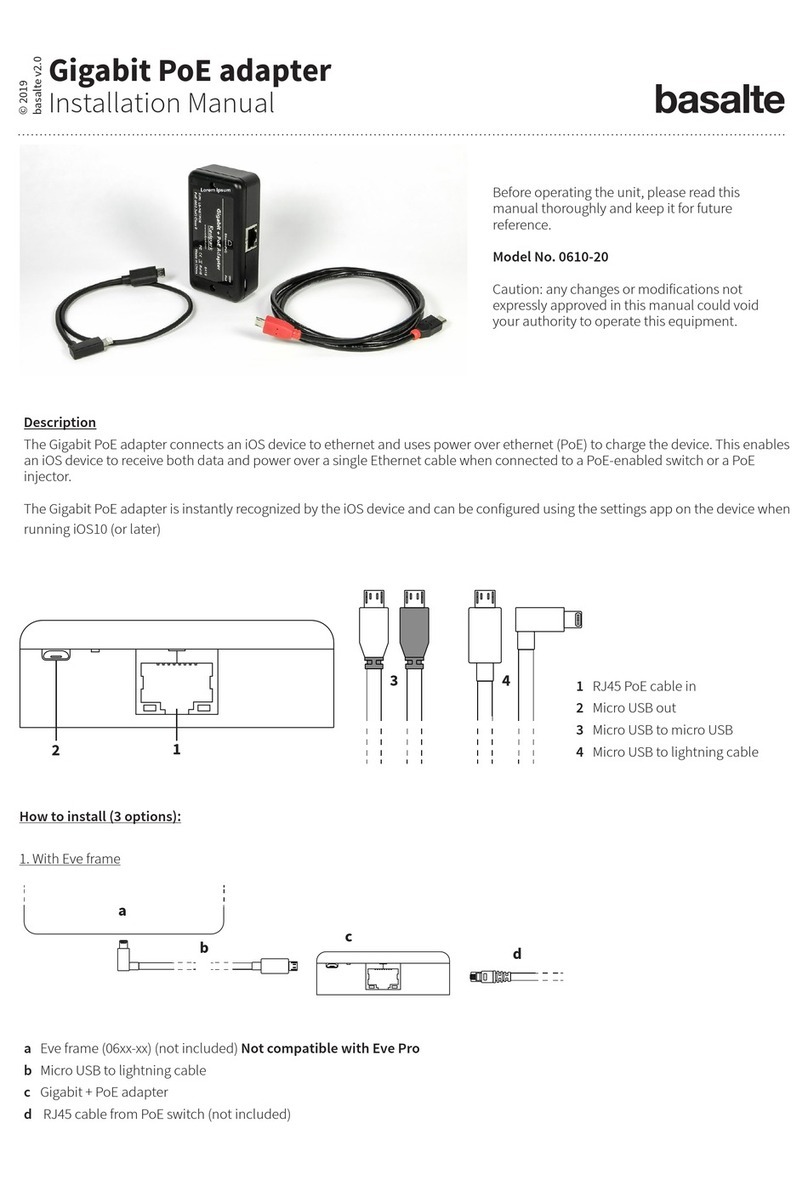
6
Wireless Basics
Wireless users can use the same applications they use on a wired network.
Wireless adapter cards used on laptop and desktop systems support the same
protocols as Ethernet adapter cards.
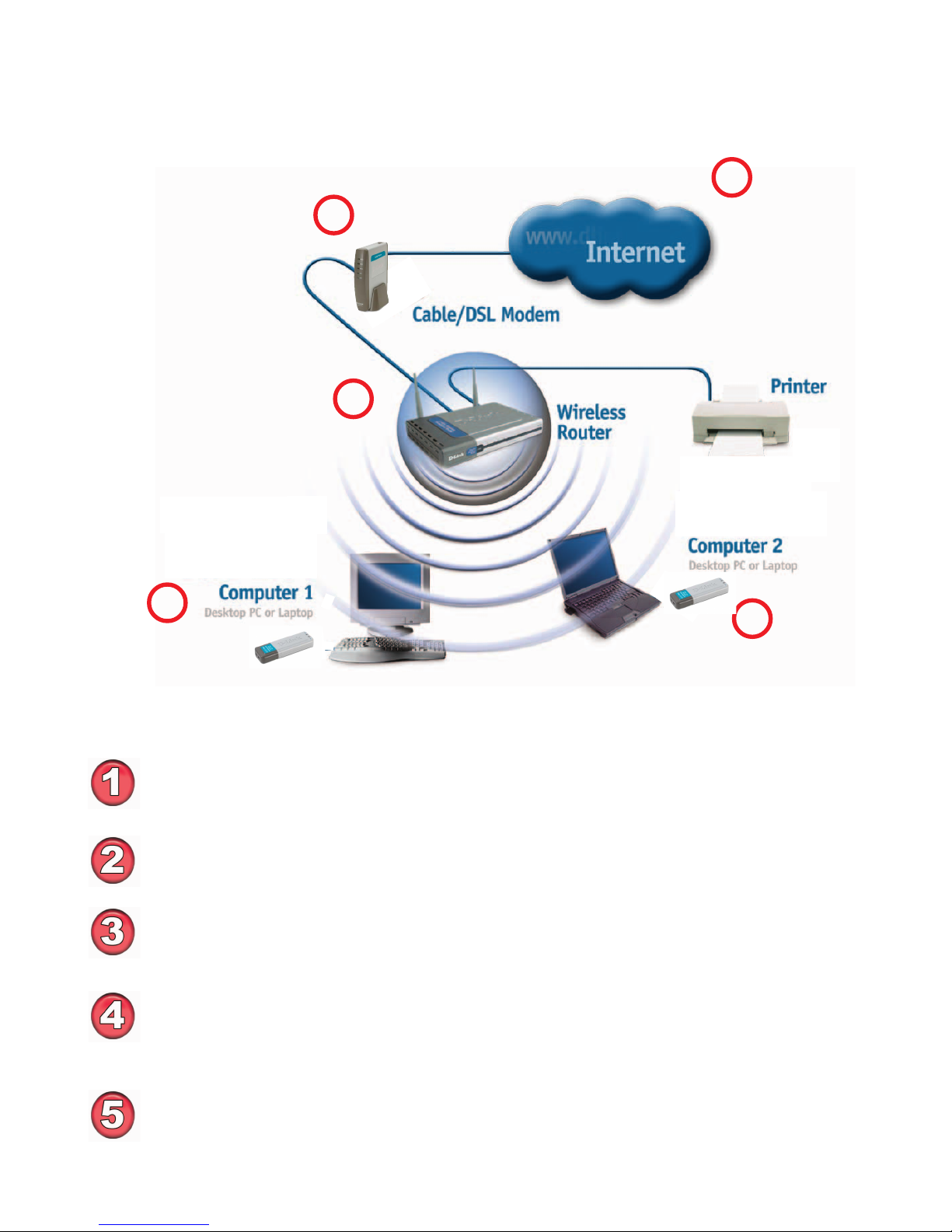
D-Link wireless products are based on industry standards to provide
easy-to-useandcompatible high-speedwirelessconnectivity withinyourhome,
business or public access wireless networks. D-Link wireless products will
allow you access to the data you want, when and where you want it.You will be
able to enjoy the freedom that wireless networking brings.
A wireless local area network (WLAN) is a computer network that transmits
and receives data with radio signals instead of wires. WLANs are used
increasingly in both home and office environments, and public areas such as
airports, coffee shops and universities. Innovative ways to utilize WLAN
technology are helping people to work and communicate more efficiently.
Increased mobility and the absence of cabling and other fixed infrastructure
have proven to be beneficial to many users.
People use WLAN technology for many different purposes:
Mobility - Productivity increases when people have access to data in any
locationwithin theoperatingrange oftheWLAN. Managementdecisionsbased
on real-time information can significantly improve worker efficiency.
Low Implementation Costs - WLANs are easy to set up, manage, change
and relocate. Networks that frequently change can benefit from WLANs ease
ofimplementation.WLANs can operate inlocationswhereinstallation of wiring
may be impractical.
Installation and Network Expansion - Installing a WLAN system can be fast
and easy and can eliminate the need to pull cable through walls and ceilings.
Wireless technology allows the network to go where wires cannot go - even
outside the home or office.
Inexpensive Solution - Wireless network devices are as competitively priced
as conventional Ethernet network devices.
Scalability - WLANs can be configured in a variety of ways to meet the needs
of specific applications and installations. Configurations are easily changed
and range from Peer-to-Peer networks suitable for a small number of users to
larger Infrastructure networks to accommodate hundreds or thousands of
users, depending on the number of wireless devices deployed.