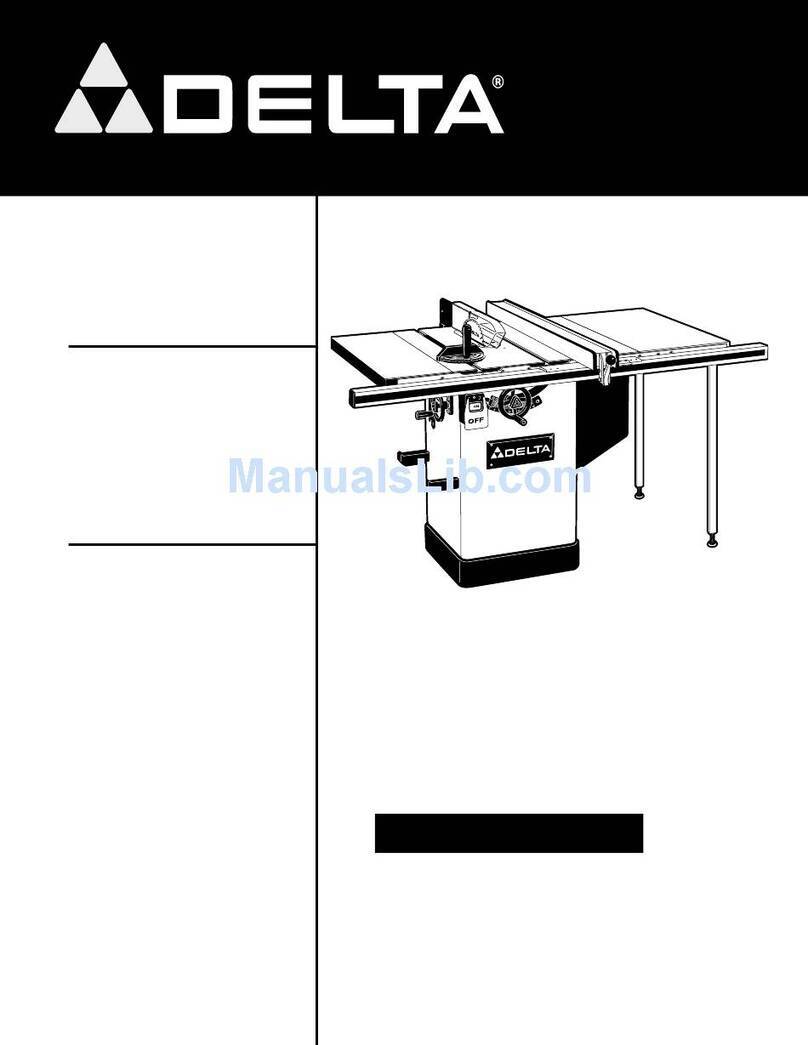
5
ADDITIONAL SAFETY RULES FOR MITER SAWS
Refer to them often
and use them to instruct others.
FAILURE TO FOLLOW THESE RULES MAY RESULT IN SERIOUS INJURY.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS.
1. DO NOT OPERATE THIS MACHINE until it is completely
assembled and installed according to the instructions. A
machine incorrectly assembled can cause serious injury.
2. OBTAIN ADVICE from your supervisor, instructor, or
another qualified person if you are not thoroughly familiar
with the operation of this machine. Knowledge is safety.
3. FOLLOW ALL WIRING CODES and recommended
electrical connections to prevent shock or electrocution.
4. SECURE THE MACHINE TO A SUPPORTING SURFACE.
Vibration can possibly cause the machine to slide, walk,
or tip over, causing serious injury.
5. USE ONLY CROSSCUT SAW BLADES. Use only zero-
degree or negative hook angles when using carbide-
tipped blades. Do not use blades with deep gullets.
These can deflect and contact the guard, and can cause
damage to the machine and/or serious injury.
6. USE ONLY BLADES OF THE CORRECT SIZE AND
TYPE specified for this tool to prevent damage to the
machine and/or serious injury.
7. USE A SHARP BLADE. Check the blade to see if it runs
true and is free from vibration. A dull blade or a vibrating
blade can cause damage to the machine and/or serious
injury.
8. INSPECT BLADE FOR CRACKS or other damage prior
to operation. A cracked or damaged blade can come
apart and pieces can be thrown at high speeds, causing
serious injury. Replace cracked or damaged blades
immediately.
9. CLEAN THE BLADE AND BLADE FLANGES prior to
operation. Cleaning the blade and flanges allows you to
check for any damage to the blade or flanges. A cracked
or damaged blade or flange can come apart and pieces
can be thrown at high speeds, causing serious injury.
10. USE ONLY BLADE FLANGES specified for this tool to
prevent damage to the machine and/or serious injury.
11. CLEAR THE AREA OF FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS and/or
gas prior to operation. Sparks can occur that would
ignite the liquids and cause a fire or an explosion.
12. CLEAN THE MOTOR AIR SLOTS of chips and sawdust.
Clogged motor air slots can cause the machine to
overheat, damaging the machine and possibly causing a
short which could cause serious injury.
13. TIGHTEN THE TABLE CLAMP HANDLE and any other
clamps prior to operation. Loose clamps can cause parts
or the workpiece to be thrown at high speeds.
14. NEVER START THE TOOL with the blade against the
workpiece. The workpiece can be thrown, causing
serious injury.
15. KEEP ARMS, HANDS, AND FINGERS away from the
blade to prevent severe cuts. Clamp all workpieces that
would cause your hand to be in the “Table Hazard Zone”
(within the red lines).
16. WHEN CUTTING WITH A COMPOUND SLIDING
MITER SAW, PUSH THE SAW FORWARD (AWAY
FROM YOU) and toward the fence. Pulling the saw
toward you can cause the saw to kick upward and
toward you.
17. WHEN USING A SLIDING MITER SAW AS A REGULAR
MITER SAW, LOCK THE SLIDE MECHANISM IN PLACE.If
the slide mechanism is not locked, the saw can kick
back toward you.
18. ALLOW THE MOTOR TO COME TO FULL SPEED prior
to starting cut. Starting the cut too soon can cause
damage to the machine or blade and/or serious injury.
19. NEVER REACH AROUND or behind the saw blade. A
moving blade can cause serious injury.
20. NEVER CUT FERROUS METALS or masonry. Either of
these can cause the carbide tips to fly off the blade at
high speeds causing serious injury.
21. NEVER CUT SMALL PIECES. Cutting small pieces can
cause your hand to move into the blade, resulting in
serious injury.
22. NEVER LOCK THE SWITCH in the “ON” position.
Setting up the next cut could cause your hand to move
into the blade, resulting in severe injury.
23. NEVER APPLY LUBRICANT to a running blade.
Applying lubricant could cause your hand to move into
the blade, resulting in serious injury.
24. DO NOT PERFORM FREE-HAND OPERATIONS. Hold
the work firmly against the fence and table. Free-hand
operations on a miter saw could cause the workpiece to
be thrown at high speeds, causing serious injury. Use
clamps to hold the work when possible.
25. PROPERLY SUPPORT LONG OR WIDE WORK-
PIECES. Loss of control of the workpiece can cause
serious injury.
26. AFTER COMPLETING CUT, release power switch and
wait for coasting blade to come to a complete stop
before returning saw to raised position. A moving blade
can cause serious injury.
27. TURN OFF THE MACHINE and allow the blade to come
to a complete stop prior to cleaning the blade area or
removing debris in the path of the blade. A moving blade
can cause serious injury.
28. TURN OFF MACHINE and allow the blade to come to a
complete stop before removing or securing workpiece,
changing workpiece angle, or changing the angle of the
blade. A moving blade can cause serious injury.
29. PROPERLY SUPPORT LONG OR WIDE WORK-
PIECES. Loss of control of the workpiece can cause injury.
30. NEVER PERFORM LAYOUT, ASSEMBLY, OR SET-UP
WORK on the table/work area when the machine is
running. A sudden slip could cause a hand to move into
the blade. Severe injury can result.
31. TURN THE MACHINE “OFF”, disconnect the machine
from the power source, and clean the table/work area
before leaving the machine. LOCK THE SWITCH IN THE
“OFF” POSITION to prevent unauthorized use.
Someone else might accidentally start the machine and
cause injury to themselves.
32. BEFORE OPERATING THE SAW, check and securely
lock the bevel, miter, and sliding fence adjustments.
33. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION regarding the safe and
proper operation of power tools (i.e. a safety video) is
available from the Power Tool Institute, 1300 Sumner
Avenue, Cleveland, OH 44115-2851 (www.powertool
institute.com). Information is also available from the
National Safety Council, 1121 Spring Lake Drive, Itasca,
IL 60143-3201. Please refer to the American National
Standards Institute ANSI 01.1 Safety Requirements for
Woodworking Machines and the U.S. Department of
Labor regulations.