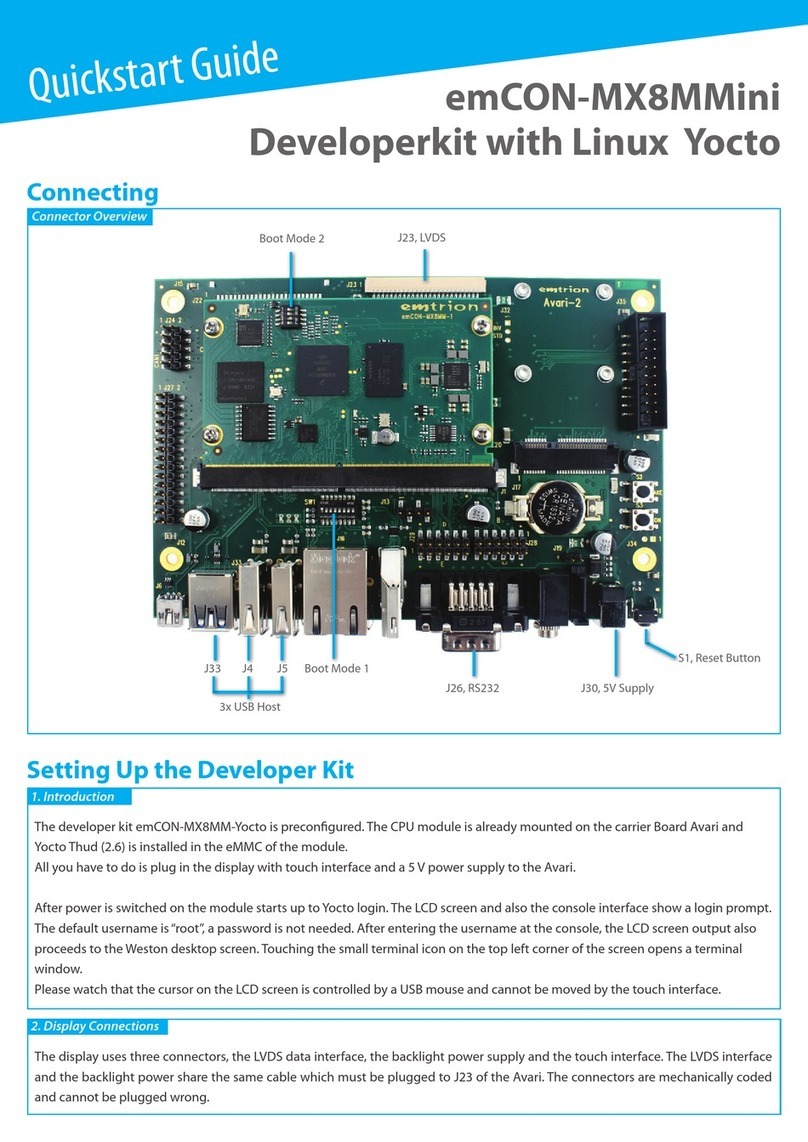
EMTRION emCON-MX8MM User manual

emCON-MX8MM
Hardware Manual
Rev1 / 09.09.2019
emtrion GmbH

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 2/33
© Copyright 2018 emtrion GmbH
All rights reserved. This documentation may not be photocopied or recorded on any electronic
media without written approval. The information contained in this documentation is subject to
change without prior notice. We assume no liability for erroneous information or its consequences.
Trademarks used from other companies refer exclusively to the products of those companies.
Revision: 1 / 09.09.2019
Rev
Date/Signature
Changes
1
09.09.2019/Sch
First revision

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 3/33
Contents
1Introduction........................................................................................................................................................4
2Block Diagram ....................................................................................................................................................5
3Handling Precautions.......................................................................................................................................5
4Functional Description.....................................................................................................................................6
4.1 Processor.....................................................................................................................................................6
4.1.1 Processor Clocks...............................................................................................................................7
4.1.2 Boot Mode/Boot Medium..............................................................................................................7
4.2 NAND Flash.................................................................................................................................................8
4.3 LPDDR4 SDRAM.........................................................................................................................................8
4.4 Ethernet.......................................................................................................................................................8
4.5 USB Host......................................................................................................................................................9
4.6 USB OTG.......................................................................................................................................................9
4.7 Graphic Display....................................................................................................................................... 10
4.7.1 LVDS.................................................................................................................................................. 10
4.8 MIPI CSI-2.................................................................................................................................................. 11
4.9 Audio - Synchronous Audio Interface (SAI)..................................................................................... 11
4.10 Audio - SPDIF........................................................................................................................................... 12
4.11 SD-Card Interface................................................................................................................................... 12
4.12 Serial Ports................................................................................................................................................ 12
4.12.1 IrDA................................................................................................................................................... 12
4.13 I²C- Bus ...................................................................................................................................................... 12
4.14 SPI Interface............................................................................................................................................. 13
4.15 PCI Express............................................................................................................................................... 13
4.16 General Purpose I/Os............................................................................................................................. 13
4.17 PWM........................................................................................................................................................... 14
4.18 Status LED ................................................................................................................................................ 14
4.19 Interrupts.................................................................................................................................................. 14
4.20 Reset .......................................................................................................................................................... 15
4.21 Power Supply .......................................................................................................................................... 15
4.21.1 Signal Description......................................................................................................................... 15
4.21.2 Power Consumption .................................................................................................................... 16
5emCON Interface............................................................................................................................................ 17
6Pin Assignments ............................................................................................................................................. 18
6.1 J1, emCON Connector........................................................................................................................... 18
7Signal Characteristics..................................................................................................................................... 24
7.1 J1, emCON Connector........................................................................................................................... 25
8Technical Characteristics.............................................................................................................................. 31
8.1 Electrical Specifications ........................................................................................................................ 31
8.2 Environmental Specifications............................................................................................................. 31
8.3 Mechanical Specifications.................................................................................................................... 31
9Dimensional Drawing.................................................................................................................................... 32
10 References........................................................................................................................................................ 33

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 4/33
1Introduction
The emCON-MX8MM processor module is based on the i.MX8MM processor from Freescale. It is
one of emtrion's emCON-family CPU boards. The i.MX8MM includes up to 4 ARM Cortex A53 cores
as well as an additional ARM Cortex M4 core for low-power processing.
The emCON-MX8MM processor modules are available with i.MX8MM quad core, dual core or solo
core (every configuration is also available in “lite”-version). Please contact emtrion GmbH for
further information.
The processor cores run up to 1.8 GHz in the customer version and 1.6 GHz in the industrial version.
They comprise a variety of functions which are required for multimedia or industrial applications.
These include video compression standards like VP9, VP8, H.265 and H.264, a 2D/3D graphics
accelerator, two LVDS interfaces, a MIPI-CSI2 camera interface and a SAI and S/PDIF audio interface.
The module is available in various sizes of NAND-Flash and RAM, as well as different amounts of
ARM Cortex A53 cores. The CPU has an internal Ethernet MAC and two USB controllers, which are
used as USB Host and USB Device.
All interfaces are accessible through a 315 pin MXM type III edge connector. The pin assignment is
defined in emtrion's emCON standard, which ensures a pin-to-pin compatibility with all emCON
CPU modules.
Features and interfaces of the emCON-MX8MM processor module are described in the following
table:
emCON-MX8MM
2GB/4GB LPDDR4 SDRAM
up to 32GB eMMC NAND Flash
16MB QSPI NOR Flash
1x 10/100/1000-Mbit Ethernet
1x USB 2.0 Host
1x USB 2.0 Device
1x PCIe (1 lane)
2x LVDS 24-bit max. WUXGA (1920x1200) @ 60Hz
1x MIPI CSI-2 (4 lanes)
1x SAI Audio
1x S/PDIF
4x UART (LVTTL)
1x SD Card
1x SPI
1 x Quad SPI
2x I2C
8x GPIO
1x PWM
RTC, battery buffered
JTAG
Please contact emtrion GmbH for the available processor, NAND Flash and SDRAM configurations.
The module is available in standard temperature range (0°C to 70°C) as well as extended
temperature range (-40°C to 85°C).

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 5/33
2Block Diagram
The following figure shows the emCON-MX8MM block diagram.
3Handling Precautions
Please read the following notes prior to installing the processor module. They apply to all ESD
(electrostatic discharge) sensitive components:
•The module does not need any configurations before installation.
•The module does not provide any on-board ESD protection circuitry –this must be
provided by the product it is used in.
•Before installing the module, it is recommended that you discharge yourself by touching a
grounded object.
•Be sure all tools required for installation are electrostatically discharged as well.
•Before installing (or removing) the module, unplug the power cable from the mains supply.
•Handle the board with care and try to avoid touching its components or tracks.

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 6/33
4Functional Description
4.1 Processor
The emCON-MX8MM processor module uses the i.MX processor i.MX8MM from Freescale [1]. It
includes up to 4 ARM Cortex A53 cores and runs up to 1.8 GHz.
In addition to the CPU core with MMU, FPU and Caches, this processor provides a variety of
features, such as:
•16/32-bit DRAM Controller (LP-DDR4, DDR4, DDR3-L)
•8-bit NAND Flash Controller
•eMMC 5.0 Flash and SPI NOR Flash interfaces
•Ethernet MAC 10/100/1000-Mbit with IEEE1588 support
•2 x USB 2.0 OTG controller with high-speed mode
•3 x Ultra Secure Digital Host Controller (uSDHC) interfaces
•1 x PCI Express (Single Lane)
•Two Image Processing Units, which include:
oVideo input module with camera capturing module
oLCDIF Display Controller (Support up to 1080p60 display through MIPI DSI)
o2D and 3D graphic hardware accelerator
oNEON SIMD media accelerator
•4 UARTs with 2x 32-byte FIFO
•I2C bus interfaces
•SPI interfaces
•IrDA interfaces
•Watchdog timer
•Real time clock
•5 x SAI Sound modules (Supporting I2S, AC97, TDM, codec/DSP and DSD interfaces)
•S/PDIF Sound interface (Input and Output)
•Interrupt controller
•32-bit General Purpose Timer
•JTAG debug interface
Further details of the processor can be found in the i.MX8MM Reference Manual [1].

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 7/33
4.1.1 Processor Clocks
The 24 MHz main clock is generated by a quartz crystal. The internal PLLs multiply the 24 MHz main
clock to the internal clocks. All clocks within the processor are derived from theses frequencies, via
various software configurable dividers.
The core clock can run up to 1,8 GHz. For power management, the core clock can be varied.
It must be considered that the core voltage should be adapted if the core frequency is varied.
More information about the i.MX8MM clock system is described in the CCM chapter of the
i.MX8MM Reference Manual [1].
The RTC_XTALI clock input of the CPU is supplied by a 32,768 kHz clock, generated by the PMIC and
used for the internal low speed clocks. The PMIC generates the clock signal by an external 32,768
kHz quartz crystal.
An additional I²C RTC Chip is used to generate a battery-backed-up Real-Time Clock.
4.1.2 Boot Mode/Boot Medium
The emCON-MX8MM Uboot can be booted either from the onboard eMMC, the NOR Flash, the SD-
Card interface or external via the USB Device interface. To switch between the options, the right
boot mode and boot device has to be configured via some Dip Switches.
The boot mode is configured via two processor pins which are available at the emCON connector.
A dip switch on the carrier board is used to configure the boot mode.
emCON Avari Baseboard (SW1):
SW1
SW2
SW3
SW[4:8]
Boot Mode
Configuration
ON
ON
X
X
Boot from Fuses
-
OFF
ON
X
X
Serial Downloader
USB
ON
OFF
X
X
Internal Boot
eMMC/SDC/NAND/NOR
OFF
OFF
X
X
Reserved
-
emCON Bvari Baseboard (SW4):
SW1
SW2
SW3
SW4
Boot Mode
Configuration
ON
ON
X
X
Boot from Fuses
-
OFF
ON
X
X
Serial Downloader
USB
ON
OFF
X
X
Internal Boot
eMMC/SDC/NAND/NOR
OFF
OFF
X
X
Reserved
-

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 8/33
The Boot medium is configured via a dip switch on the emCON MX8MM module.
emCON MX8MM CPU Module (SW1):
SW1
SW2
SW3
SW4
Configuration
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
eMMC
Na.
Na.
Na.
Na.
SDC
Na.
Na.
Na.
Na.
QSPI
Configurations for other boot devices will be coming soon.
4.2 NAND Flash
To store the operating system and application data, an eMMC-NAND Flash is provided on the
emCON-MX8MM module. It is connected to the uSDHC1 controller of the i.MX8MM.
You can choose a NAND Flash size between 4GB and 32GB, depending on your requirements.
Please contact emtrion GmbH for your required NAND Flash size.
The onboard NAND Flash controller can be reset by a logical “0” on the GPIO1_IO03 Pin.
4.3 LPDDR4 SDRAM
LPDDR4 SDRAM is available as main memory. The RAM memory has a 32-bit width interface, a
density of 4GB and can be clocked up to 1865 MHz (3733 Mb/s).
Please contact emtrion GmbH for your required RAM size.
4.4 Ethernet
The Ethernet interface is realized with the processor internal Media Access Controller (MAC) and an
external Physical Layer Interface (PHY) KSZ9031RNX from Micrel. The RGMII interface is used for
communication between the MAC and the PHY.
The Ethernet interface supports the operating modes 10, 100 and 1000BASE-TX, all half- and full
duplex. HP Auto-MDIX is also supported.
The registers of the Ethernet PHY can be configured via the Media Independent Interface (MII).
The Ethernet signal lines (GBE1_MDIO[0:3]_P, GBE1_MDIO[0:3]_N) as well as two status signals,
indicating the link status and the transfer speed, are connected to the emCON connector. An
appropriate 1:1 transformer with a 100nF capacitor to GND at each center tap pin must be added
externally. The center tap pin shall not be supplied with 3.3V!
The emCON pins GBE1_LED_10_100# and GBE1_LED_1000# are both connected to the LED2 pin of
the Ethernet PHY and indicate if a link is established. (“0” = link). Therefore, the link speed has to be
determined by the software.

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 9/33
The emCON pin GBE1_LED_TRAFFIC# is connected to the LED1 pin of the Ethernet PHY, it indicates
that data is being transferred (“blinking”= traffic).
The RGMII 125MHz Ethernet clock is generated by the PLL of the Ethernet PHY and routed to the
processor’s internal MAC.
The Ethernet Phy can be reset by a logical “0” on the GPIO1_IO09 Pin.
4.5 USB Host
A USB Host interface is used to connect USB devices such as a keyboard, mouse, printer or memory
stick.
The USB host interface is realized by the internal host controller of the i.MX8MM. It complies with
the USB specification Rev. 2.0, supporting data transfers at low-speed (1,5Mbps), full-speed (12
Mbps) and high-speed (480Mbps).
To switch the bus power, the control line USBH_PEN# is connected to the emCON connector. A
logical “0” at the processor’s pin GPIO1_IO14 switches the power on; a logical “1” turns the power
off. The signal USBH_OC# reports an overcurrent at the GPIO1_IO15 (“0” = overcurrent).
The data lines and the two control lines are available at the emCON connector. A USB power switch
must be added externally. The data lines are internally terminated by 15-Kpulldown resistors.
The USBH_VBUS signal on the emCON connector is only an input to detect the VBUS voltage on
the baseboard.
4.6 USB OTG
The USB OTG port can operate in Host or Device mode. The signal USBOTG_ID is used to determine
the mode of the connected device.
The interface is realized by the internal device controller of the i.MX8MM. The interface is USB 2.0
compliant, supporting data transfers at low-speed (1,5Mbps), full-speed (12 Mbps) and high-speed
(480Mbps).
To switch the bus power in USB Host mode the control line USBOTG_PEN# is connected to the
emCON connector. A logical “0” at the processor GPIO1_IO12 switches the power on; a logical “1”
turns the power off. The signal USBH_OC# reports an overcurrent at the GPIO1_IO13 (“0” =
overcurrent).
The USBOTG_VBUS signal on the emCON connector is only an input to detect the VBUS voltage on
the baseboard.

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 10/33
4.7 Graphic Display
The i.MX8MM includes two Graphic Processing Units (GPU) for 2D and 3D acceleration and a Video
Processing Unit (VPU) for Video decoding (H.265, VP9, H.264, VP8). More information about the
Multimedia system is described in the Multimedia, GPU and VPU chapter of the i.MX8MM
Reference Manual [1].
The enhanced Liquid Crystal Display Interface (eLCDIF) on the processor is a general-purpose
display controller which supports a wide range of display devices.
4.7.1 LVDS
The LCD controller of the i.MX8MM supports a 4-lane MIPI DSI port which drives a MIPI DSI to LVDS
Bridge (SN65DSI84 from Texas Instruments) on the CPU module, in order to generate two Single-
Link or one Dual-Link LVDS Interface with four data lanes per link.
The pixel clock is limited to 154 MHz in Single and Dual-Link mode. This results in a maximum
resolution of WUXGA (1920 x 1200 @ 60 Hz).
The SN65DSI84 from Texas Instruments can communicate via the internal I2C3 Interface. The
interrupt output of the device is connected to the GPIO3_IO22 Pin of the processor.
To enable the MIPI DSI to LVDS Bridge, set a logical “1” on the GPIO3_IO24 (pay attention to the
timing specifications of the device in the SN65DSI84 Datasheet [2] Chapter 7.4.1). A logical “0”
disables the device.
The following table describes the signals of the LVDS port 1:
Signal
Description
LVDS1_CLK_P/N
Differential LVDS clock
LVDS1_D[3:0]_P/N
Four differential LVDS data signal pairs
LVDS1_PANEL_EN
Display power enable signal, GPIO3_IO25
LVDS1_BL_EN
Backlight power enable signal, GPIO3_IO23
LVDS1_BL_CTRL
PWM signal to control the backlight, GPIO1_IO01
The following table describes the signals of the LVDS port 2:
Signal
Description
LVDS2_CLK_P/N
Differential LVDS clock
LVDS2_D[3:0]_P/N
Four differential LVDS data signal pairs
The colour mapping can be different, depending of the used display. The LVDS Output formats can
be adjusted in the MIPI DSI to LVDS Bridge registers. Use the SN65DSI84 Datasheet [2] to setup a
specific LVDS format.

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 11/33
The following table shows the colour mapping of a few example output formats:
Single-Link 18-bit
Slot0
Slot1
Slot2
Slot3
Slot4
Slot5
Slot6
LVDS_D0
G0
R5
R4
R3
R2
R1
R0
LVDS_D1
B1
B0
G5
G4
G3
G2
G1
LVDS_D2
DE
VS
HS
B5
B4
B3
B2
LVDS_D3
CTL
B7
B6
G7
G6
R7
R6
Single-Link 24-bit
Slot0
Slot1
Slot2
Slot3
Slot4
Slot5
Slot6
LVDS_D0
G2
R7
R6
R5
R4
R3
R2
LVDS_D1
B3
B2
G7
G6
G5
G4
G3
LVDS_D2
DE
VS
HS
B7
B6
B5
B4
LVDS_D3
CTL
B1
B0
G1
G0
R1
R0
Dual-Link 24-bit
Slot0
Slot1
Slot2
Slot3
Slot4
Slot5
Slot6
LVDS1_D0 (odd)
G0
R5
R4
R3
R2
R1
R0
LVDS1_D1 (odd)
B1
B0
G5
G4
G3
G2
G1
LVDS1_D2 (odd)
DE
VS
HS
B5
B4
B3
B2
LVDS1_D3 (odd)
CTL
B7
B6
G7
G6
R7
R6
LVDS2_D0 (even)
G0
R5
R4
R3
R2
R1
R0
LVDS2_D1 (even)
B1
B0
G5
G4
G3
G2
G1
LVDS2_D2 (even)
DE
VS
HS
B5
B4
B3
B2
LVDS2_D3 (even)
CTL
B7
B6
G7
G6
R7
R6
4.8 MIPI CSI-2
The MIPI CSI-2 interface is a serial interface with differential data pairs, it transports camera data
with a high bandwidth. The i.MX8MM comes with 4 data lanes which support up to 1000 Mbps per
lane and one clock pair.
The following table describes the MIPI CSI-2 signals available at the emCON interface.
Signal
Description
MIPI_CSI-2_D[3:0]_P/N
Four differential data signal pairs
MIPI_CSI-2_CLK_P/N
Differential clock
4.9 Audio - Synchronous Audio Interface (SAI)
The integrated I2S module of the i.MX8MM provides a SAI interface that can be used to send and
receive audio data from external audio codecs.
It supports full duplex serial interfaces with frame synchronisation and allows audio processing in
different audio formats such as I2S, AC97, TDM and codec/DSP.
The interface is connected to the emCON connector, which allows the selection of an external
audio codec.

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 12/33
4.10 Audio - SPDIF
The emCON-MX8MM also supports audio data in SPDIF format. The SPDIF_OUT signal at the
emCON connector has LVTTL level and will need to be configured externally, according to SPDIF
specification.
4.11 SD-Card Interface
The i.MX8MM includes three SD Card interfaces to drive memory- or I/O cards. One of them
(uSDHC2) is used for the 4-bit SD Card interface of the emCON connector. uSDHC2 is used for the
interface SDC1. The SDC2 interface on the emCON connector is not connected.
The card’s detect and write protect signals can be controlled either by the SD card controller or by
the GPIO ports of the i.MX8MM:
Signal
Description
GPIO
emCON SDC port
SDC2_CD#
Low-active card detection signal
GPIO2_IO12
SDC1_CD#
SDC2_WP
high-active write protection signal
GPIO2_IO20
SDC1_WP
4.12 Serial Ports
The emCON-MX8MM has four serial ports. All serial ports are integrated in the processor i.MX8MM
and available as LVTTL level. External transceivers are necessary to use interfaces like RS232 or
RS485.
An overview of the UART interfaces is shown in the following table:
i.MX8MM interface
emCON name
Handshake Signals
UART1
UART_A
-
UART2
UART_B
RTS, CTS
UART3
UART_C
-
UART4
UART_D
-
UART1 is used as a standard debug and communication interface (TERMINAL).
4.12.1 IrDA
Each processor UART port can also be used as a low speed (115200bps) Infrared port (IrDA). The
UART RXD input signal is also the IrDA RXD input signal. The UART TXD output signal is the IrDA
TXD output signal.
4.13 I²C- Bus
There are three I²C bus interfaces available on the emCON-MX8MM module.
The I²C interface (I2C3) is only routed on the emCON-MX8MM module and all onboard I²C devices
on the module are connected to that interface. The interface works with a transmission speed of up
to 400 kb/s. The interface operates as a master.

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 13/33
Three devices are connected to the I2C3 bus on emCON-MX8MM:
Slave
Device
Chip Address (7-bit)
Real Time Clock
RV-1805-C3
0x69
PMIC
BD71847MWV
0x4B
MIPI to LVDS Bridge
SN65DSI84
0x2D
The other I²C interfaces (I2C1, I2C2) are routed to the emCON connector and can be used
exclusively for baseboard functions. The maximum I²C speed is 400kb/s.
The external I²C interfaces can be used either in Master mode (default) or in Slave mode. In Slave
mode, the I²C address can be defined in the i.MX8MM register.
The bus connects to the emCON connector. The SCL and SDA lines are pulled up with 2,2k
resistors to 3,3V.
4.14 SPI Interface
The SPI interface ECSPI1 of the i.MX8MM processor is connected to the SPI2 interface of the
emCON connector. The second slave select signal SPI2_CS1# on the SPI2 interface is connected to
the GPIO5_IO13.
The SPI1 interface of the emCON connector is connected to the QSPI_B interface of the i.MX8MM.
4.15 PCI Express
The i.MX8MM processor includes the following PCI Express cores:
•PCI Express Dual Mode (DM) core
•PCI Express Root Complex (RC) core
•PCI Express Endpoint (EP) core
One PCI Express lane is supported. The required AC coupling (220nF) at the TX pair is done on the
emCON-MX8MM module. More details of the PCI Express controller can be found in the i.MX8MM
Reference Manual [1].
4.16 General Purpose I/Os
The emCON interface supports eight dedicated GPIOs which are directly connected to the CPU.
emCON Signal
i.MX8MM Port
Direction
Features
GPIO_1
GPIO4_IO10
In/Out
GPIO_2
GPIO5_IO02
In/Out
PWM capable
GPIO_3
GPIO3_IO16
In/Out
GPIO_4
GPIO3_IO17
In/Out
GPIO_5
GPIO3_IO04
In/Out
Timer Compare
GPIO_6
GPIO3_IO15
In/Out
Timer Compare
GPIO_7
GPIO3_IO02
In/Out
Timer Capture
GPIO_8
GPIO3_IO18
In/Out
Timer Capture
The signal level of each GPIO pin is 3,3V.

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 14/33
4.17 PWM
The i.MX8MM includes four PWM modules. Three of them are available on the emCON connector:
emCON Signal
PWM Channel
Remark
LVDS1_BL_CTRL
PWM1
Backlight dimming
GPIO_2
PWM4
For general purpose
PWM_FAN
PWM2
Fan control
The signal level of each PWM pin is 3,3V.
4.18 Status LED
Two LEDs are connected to the port pins of the i.MX8MM. A green LED is connected to GPIO5_IO04
and a red LED to GPIO5_IO10. A logical “1” on the respective output turns the LEDs on.
4.19 Interrupts
The processor i.MX8MM has an integrated interrupt controller that analyses all interrupt sources,
prioritizes them and outputs the interrupt with highest priority to the processor.
Generally, each GPIO input can be configured as an interrupt input. On the emCON-MX8MM, some
GPIOs are defined as interrupts. The interrupt sources are shown in the following table:
Signal
Source
i.MX8MM GPIO Port
polarity
IRQ_1
emCON connector
GPIO4-IO11
configurable
IRQ_2
emCON connector
GPIO3-IO21
configurable
IRQ_3
emCON connector
GPIO1-IO05
configurable
IRQ_TOUCH1#
emCON connector
GPIO4-IO01
configurable
IRQ_TOUCH2#
emCON connector
GPIO4-IO00
configurable
IRQ_LVDS
MIPI to LVDS Bridge (SN65DSI84)
GPIO3-IO22
high active
PMIC_IRQ#
PMIC (DA9063)
GPIO3-IO02
low active
POWERFAIL#
emCON connector
GPIO3-IO18
low active
IRQ_1, IRQ_2 and IRQ_3 are general purpose interrupts from the emCON connector. The signal
level of each interrupt is 3,3V.
IRQ_TOUCH1# and IRQ_TOUCH2# are interrupts from the emCON connector reserved for external
touch controllers. The signal level of each interrupt is 3,3V.
The LVDS interrupt can be asserted by the onboard MIPI to LVDS Bridge chip.
The PMIC interrupt can be asserted by the onboard Power Management chip.
The Powerfail interrupt is immediately asserted if the RESI# emCON pin is set to low. With this
interrupt the SW can shut down itself until a hard reset is asserted 1s later.

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 15/33
4.20 Reset
There are several ways for issuing a reset signal:
•A voltage monitor checks the board voltages. If one voltage is out of tolerance, a module
reset is asserted.
•The active low signal RESI# and the signal JTAG_RESI# at the emCON connector can assert a
reset.
•A processor internal SW reset is available at a processor pin. In this case the RESO# pin is
asserted if a SW reset is asserted.
All resets are hardware resets of the whole board. All resets except the internal SW reset issue a
processor cold reset. The internal SW reset issues a processor warm reset.
The duration of the reset signal is min.120ms. For resetting external devices, the reset signal is
available as an output (RESO#) at the emCON connector.
4.21 Power Supply
The typical power consumption is depending on the running software tasks and the external
devices which must be supplied via the emCON connector.
The onboard required voltages for the processor and the other parts are generated on board via a
Power Management (PMIC) chip.
The voltages generated by the PMIC can be configured via the I²C interface. During operation, the
voltages can be varied depending on core frequencies and temperature.
4.21.1 Signal Description
VCC_STANDBY & VCC_5V:
The 5v power supply is divided into two voltage areas. VCC_Stby is used to power up and keep the
PMIC, as well as the most important voltages of the CPU, alive during power down states. +5V0DC
is the main supply and used to supply the board in the running state.
If power management is used, the +5V0DC can be disabled in deep power down states. The
disabling can be done for example with a mosfet circuit at the baseboard. To control the mosfet,
the signal SUSPEND# is available at the emCON interface. Example schematics are also available.
VCC_Stby has to be kept on all the time.
If no power management is needed, VCC_STANDBY and +5V0DC can be both connected to 5V
directly.

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 16/33
POWER_ON_BASE:
During some power down states, the 3.3V areas of the CPU module will be switched off. In this case
all the peripheral chips which are connected to 3.3V referenced signals have to be switched off,
too. Otherwise the CPU will be back-powered via the I/O pins.
The signal POWER_ON_BASE can be used to control a DC/DC converter or a mosfet to switch the
3.3V on the baseboard on and off. Example schematics are available.
POWERFAIL#
The signal POWERFAIL# is an input to signalize a power fail condition. A low will trigger an
interrupt, e.g. to safe data.
ON_OFF# & WAKEUP:
The signals ON-OFF# and Wakeup are used to control the PMIC so it gets up from power down
states.
BAT:
The emCON BAT pin is the battery input pin for the RTC power supply. The typical power
consumption of the RTC via the BAT pin is < 1µA.
4.21.2 Power Consumption
A benchmark document [3] from NXP provides measurements and detailed information about the
power consumption of the i.MX8MM processor itself.

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 17/33
5emCON Interface
All interface signals of the board are available at the emCON connector.
The emCON interface is a 314 pos. MXM connector. These sockets are available from various
manufacturers.
The pin assignment is emtrion specific and matches most interface requirements in actual
embedded designs. Depending on the CPU features, every emtrion CPU module uses different set
of pins on the emCON connector. More details can be found in emtrion's emCON specification.
Usage details of the connector and its electrical and mechanical characteristics can be found
further down in this document.
Notes:
The pin assignment of the emCON connector is ONLY compatible with devices of emtrion's
emCON-family. Insertion into a socket with another pin assignment may damage the emCON-
MX8MM module and the carrier board.
Most of the pins are directly connected to the processor i.MX8MM.

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 18/33
6Pin Assignments
6.1 J1, emCON Connector
Type MXM, 314 pos.
Possible carrierboard connector: Aces 91782-3140M-001
Notes:
The pin assignment of the emCON connector is ONLY compatible with devices of emtrion's
emCON-family. Insertion into a socket with another pin assignment may damage the emCON-
MX8MM module and the carrier board.
Most of the pins are directly connected to the processor i.MX8MM.
Pin
Signal
Interface
Signal
Pin
1E20
GND
Power Supply
VCC_5V
2E20
1E19
GND
VCC_5V
2E19
1E18
GND
VCC_5V
2E18
1E17
GND
VCC_5V
2E17
1E16
GND
VCC_5V
2E16
1E15
GND
VCC_5V
2E15
1E14
GND
VCC_5V
2E14
1E13
GND
VCC_5V
2E13
1E12
GND
VCC_5V
2E12
1E11
GND
VCC_5V
2E11
1E10
BAT
VCC_STANDBY
2E10
1E9
BOOT_MODE_3
Manufacturing
MISC
TAMPER
2E9
1E8
BOOT_MODE_2
POWER_ON_BASE
2E8
1E7
BOOT_MODE_1
IRQ_TOUCH1#
2E7
1E6
JTAG_RESET#
IRQ_TOUCH2#
2E6
1E5
JTAG_MOD
IRQ_1
2E5
1E4
JTAG_TRST#
IRQ_2
2E4
1E3
JTAG_TMS
IRQ_3
2E3
1E2
JTAG_TDO
RESO#
2E2
1E1
JTAG_TDI
RESI#
40

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 19/33
1
JTAG_RTCK
POWERFAIL#
2
3
JTAG_VCC
SUSPEND#
4
5
JTAG_TCK
ON_OFF#
6
7
GND
POWER
WAKEUP#
8
9
UART-A_RXD
UART-A
PWM_FAN
10
11
UART-A_TXD
POWER
GND
12
13
n/c
UART-C
UART-C_RXD
14
15
n/c
UART-C_TXD
16
17
UART-B_RXD
UART-B
UART-D
UART-D_RXD
18
19
UART-B_TXD
UART-D_TXD
20
21
UART-B_RTS
UART-E
UART-E_RXD
22
23
UART-B_CTS
UART-E_TXD
24
25
GND
POWER
GND
26
27
GPIO_1
GPIOs
PCI Express
PCIE_DISABLE#
28
29
GPIO_2
PCIE_RESET#
30
31
GPIO_3
PCIE_CLK1_P
32
33
GPIO_4
PCIE_CLK1_N
34
35
GPIO_5
GND
36
37
GPIO_6
PCIE_RX1_P
38
39
GPIO_7
PCIE_RX1_N
40
41
GPIO_8
PCIE_TX1_P
42
43
GND
POWER
PCIE_TX1_N
44
45
LCD_D23
RGB IF
GND
46
47
LCD_D22
n/c
48
49
LCD_D21
n/c
50
51
LCD_D20
n/c
52
53
LCD_D19
n/c
54
55
LCD_D18
GND
56
57
LCD_D17
n/c
58
59
LCD_D16
n/c
60
61
LCD_D15
RGB IF
PCI Express
GND
62

emCON-MX8MM - Hardware Manual (Rev1) 20/33
63
LCD_D14
n/c
64
65
LCD_D13
n/c
66
67
LCD_D12
n/c
68
69
GND
n/c
70
71
LCD_D11
GND
72
73
LCD_D10
n/c
74
75
LCD_D9
n/c
76
77
LCD_D8
n/c
78
79
LCD_D7
n/c
80
81
LCD_D6
POWER
GND
82
83
LCD_D5
n/c
84
85
LCD_D4
n/c
86
87
LCD_D3
CPI 2 Camera
Input
CPI2_CLK
88
89
LCD_D2
CPI2_HSYNC
90
91
LCD_D1
CPI2_VSYNC
92
93
LCD_D0
CPI2_D0
94
95
LCD_PIXCLK
CPI2_D1
96
97
LCD_HSYNC
CPI2_D2
98
99
LCD_VSYNC
CPI2_D3
100
101
LCD_DISP
CPI2_D4
102
103
LCD_BL_CTRL
CPI2_D5
104
105
LCD_BL_EN
CPI2_D6
106
107
LCD_PANEL_EN
CPI2_D7
108
109
CAN2_RX
CAN 2
CAN 1
CAN1_RX
110
111
CAN2_TX
CAN1_TX
112
113
GND
POWER
POWER
GND
114
115
SPI1_SCK
SPI 1
SPI 2
n/c
116
117
SPI1_CS0#
n/c
118
119
SPI1_MOSI/D0
n/c
120
121
SPI1_MISO/D1
n/c
122
123
SPI1_CS1#/D2
n/c
124
125
n/c
The pins 126 - 132 are used for mechanical coding and not available as electrical pins.
Table of contents
Other EMTRION Microcontroller manuals
Popular Microcontroller manuals by other brands

Eurotech
Eurotech DuraCOR DRCR4400 quick start
Silicon Laboratories
Silicon Laboratories C8051F02 Series user guide
Renesas
Renesas Synergy Promotion Kit S5D9 user manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments LM26EVM user guide
Lattice Semiconductor
Lattice Semiconductor HM01B0 UPduino Shield user guide
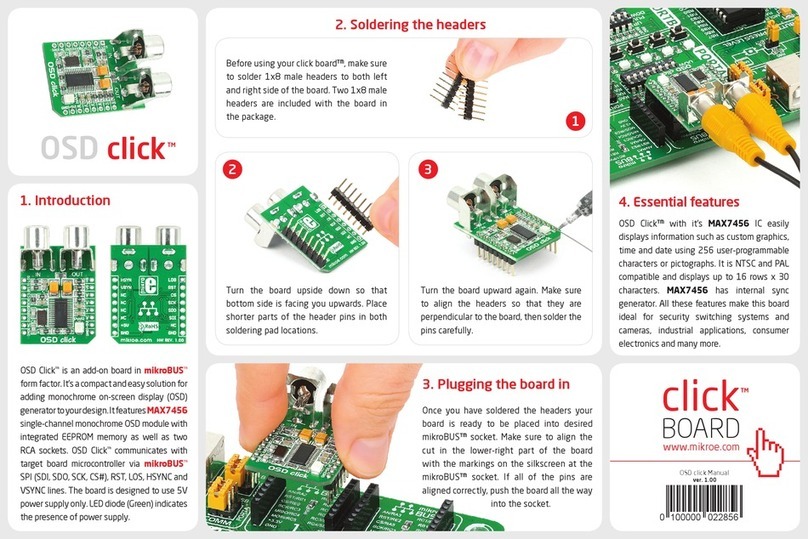
MicroElektronika
MicroElektronika click OSD quick start guide