Table of Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.1 Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.2 Measuring system . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.3 Measuring principle . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.4 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . 9
2 Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.1 Probes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.2 Silometer installation . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.3 Transmitter wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.4 Probe connection . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.5 Hardware configuration . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.6 Technical data: Silometer FMC 671 Z/676 Z
transmitter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3 Operating elements . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.1 Commutec operating matrix . . . . . . . . 19
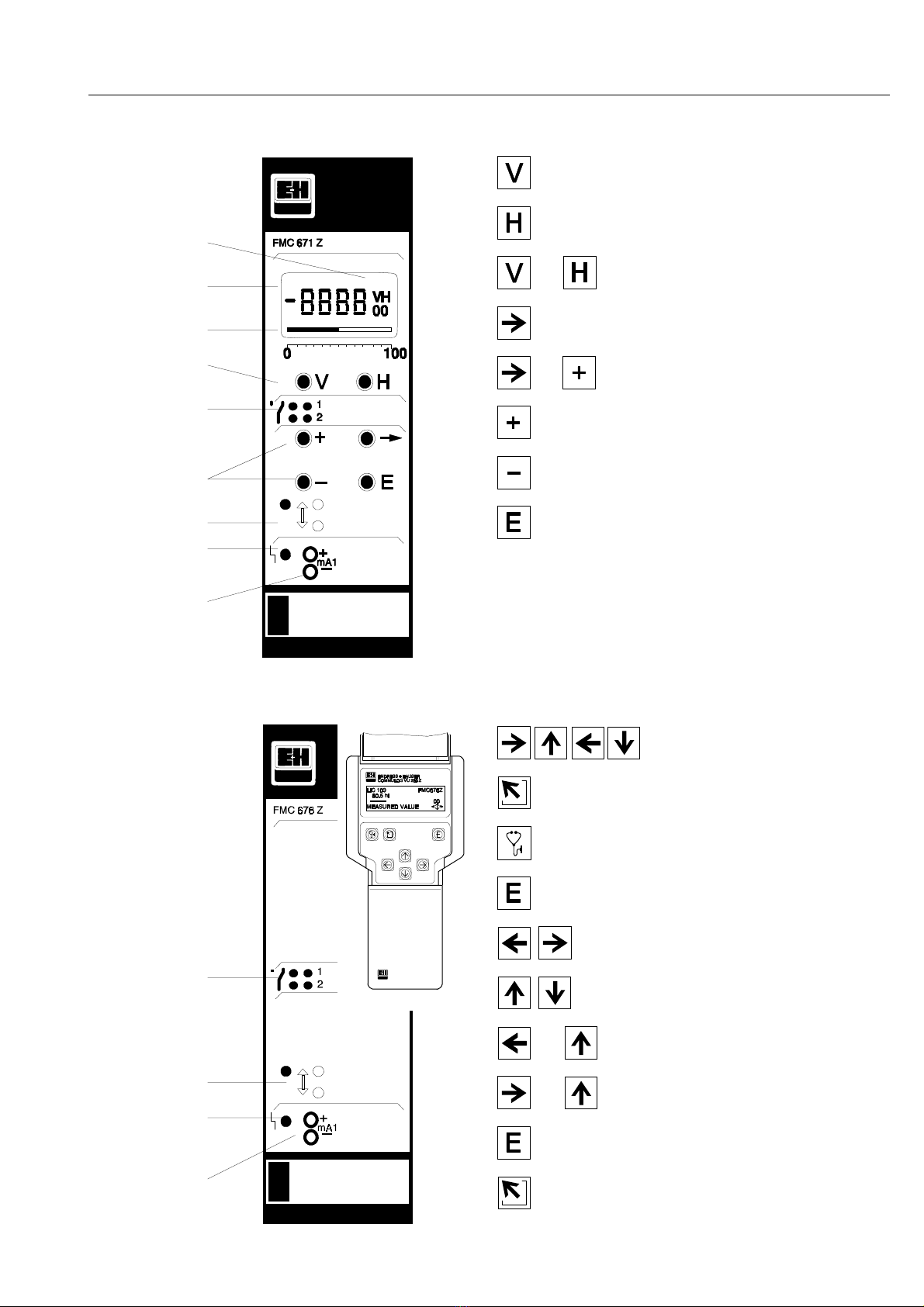
3.2 Operating elements: Silometer FMC 671 Z . . 20
3.3 Operating elements: Silometer FMC 676 Z . . 21
4 Calibration and Operation . . . . . . . 22
4.1 Commissioning of the transmitter . . . . . . 22
4.2 Empty/full calibration for level measurement . 23
4.3 Empty/full calibration for volume measurement 24
4.4 Level offset value . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.5 Measured value display . . . . . . . . . 26
4.6 Locking the parameter matrix . . . . . . . 26
5 Linearization . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
5.1 Linearization for a horizontal cylindrical tank . 28
5.2 Linearization for a tank with conical outlet . . 29
5.3 Other modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
6 Analogue Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . 33
6.1 Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
7 Limit Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
7.1 Relay settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
7.2 Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
8 Other Applications . . . . . . . . . . 41
8.1 »Dry calibration« for continuous level
measurement with Deltapilot probes . . . . 41
8.2 Level limit switching . . . . . . . . . . . 43
8.3 Continuous level measurement with separate
level limit detection . . . . . . . . . . . 46
8.4 Level measurement with automatic calibration
correction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
9 Trouble-Shooting . . . . . . . . . . . 50
9.1 Faults and warnings . . . . . . . . . . . 50
9.2 Simulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
9.3 Exchanging transmitters or probes . . . . . 54
9.4 Repairs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
10 Quick programming guide . . . . . . . 56
10.1 Level measurement with separate level switching,
capacitance probes . . . . . . . . . . . 56
10.2 Continuous volume measurement (linearization) 57
10.3 Level limit switching . . . . . . . . . . . 58
10.4 Level measurement with automatic calibration
correction: two capacitance probes . . . . 59
2
Silometer FMC 671 Z/676 Z Table of Contents