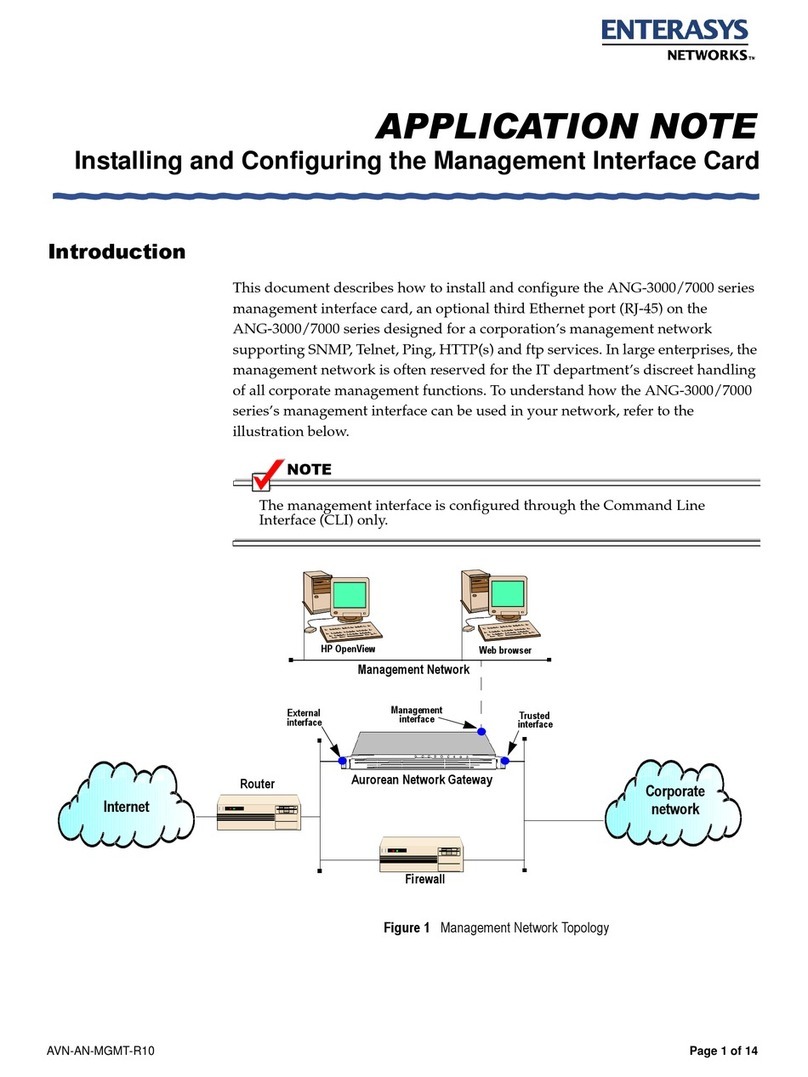
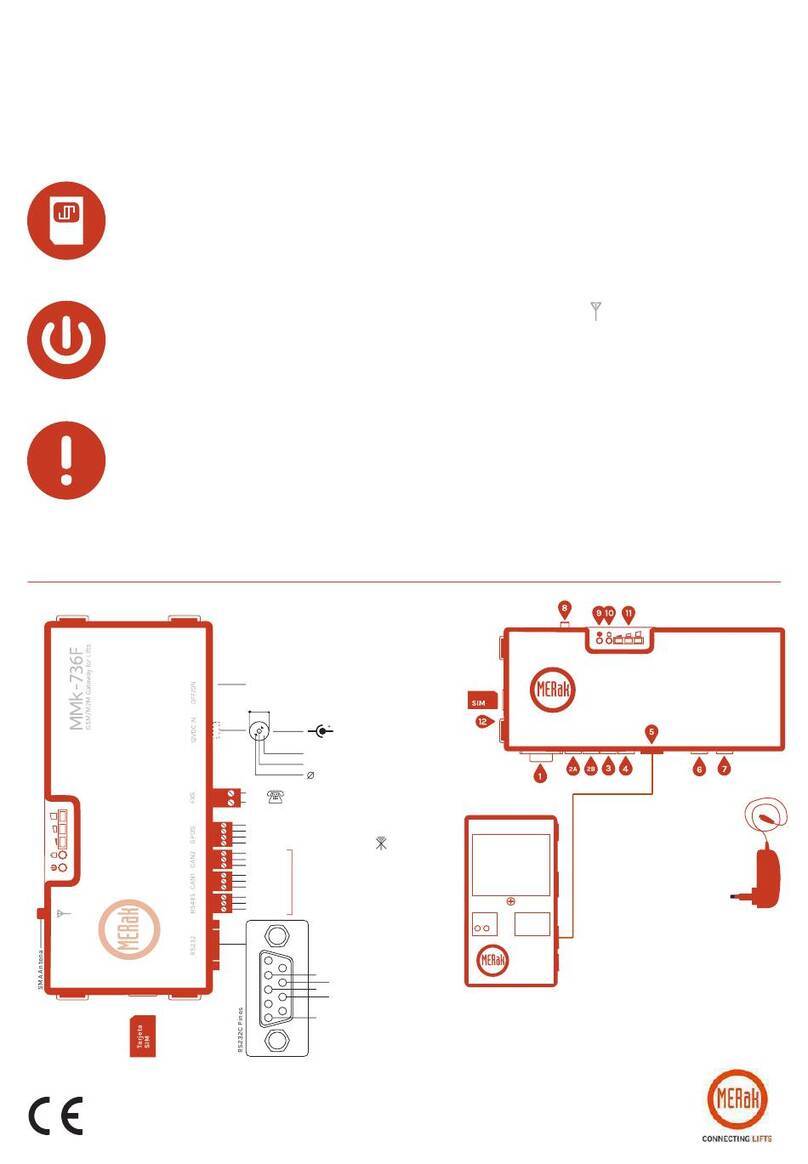
Application Note ANG Configuration Commands
AVN-AN-CLI-R11 Page 9 of 64
-p IP address Set the target (destination) IP address: the destination address of
an ICMP ping.
-i Milliseconds Specify the heartbeat interval - how often pings or LCP echos are
transmitted. The ANG rounds this value up to the nearest multiple
of 250 milliseconds.
-r Retries Specify how many LCP echos or ICMP pings must be transmitted,
without getting a reply, before the heartbeat fails and the tunnel
failed.
-c True or False Determine whether the heartbeat is critical or not.
-l None List the Nth heartbeat object
-h Help Request Help for command variables
-L None List all heartbeat objects
Defaults
!Default - The heartbeat nameddefault is always present and it defines
the heartbeat mechanism used when any other heartbeat, by name,
does not exist. The default heartbeat parameters provide tunnel
timeout detection identical to earlier Aurorean releases.
!IKE, IRPP and PPTP - These defaults define the heartbeats used for
the IKE/IPSec, IRPP/IPSec, and PPTP tunnel protocols, respectively.
Notes
!A single VPN Scope heartbeat will take down the entire VPN if the
addressed ping destination goes down. This may be extreme, so
multiple VPN Scope heartbeats may be defined that all reference
different IP addresses reachable via the trusted interface. If those
heartbeats are not marked as critical then the VPN is not brought
down until every non-critical heartbeat has failed. Note that the VPN
is brought down if any critical heartbeat fails.
!All Tunnel Scope heartbeats are unconditionally considered critical
because only one is used per tunnel and because they only terminate
a single tunnel when the heartbeat fails.
!The Ping Address heartbeat mechanism continues to run even when
the VPN has been disabled after a failure of the trusted interface on
the connected ANG. The VPN will automatically allow new inbound
tunnel connections once the ANG starts getting replies to its ICMP
echo requests.
!Heartbeat time-outs and Retry counts should be the same at both
ends of a site-to-site tunnel.
Applies a tunnel keep-alive interval to the Aurorean Network Gateway. This enables
Uninterrupted Data Session failover between site-to-site tunnels, providing high availability
for mission critical applications.
Usage ircheartbeat -a -d -n <name> -s -m -p -i -r -e -l <arg> -h -L
SW <arg> Definition