ESS Sfoam Dust Suppression 10 20/05/2020
Mechanical Installation
Install the SFoam Junior/Senior at ground level on a level site with good access to
the required services.
The SFoam Junior/Senior unit comes complete with Ø25 mm male screwed BSP
connections for the water and air lines and a Ø12 mm N.B. tube connection for the
chemical line.
It is recommended that the unit be situated as close as practicable to the chemical
storage tank, tote or drum. A flooded suction condition is preferred.
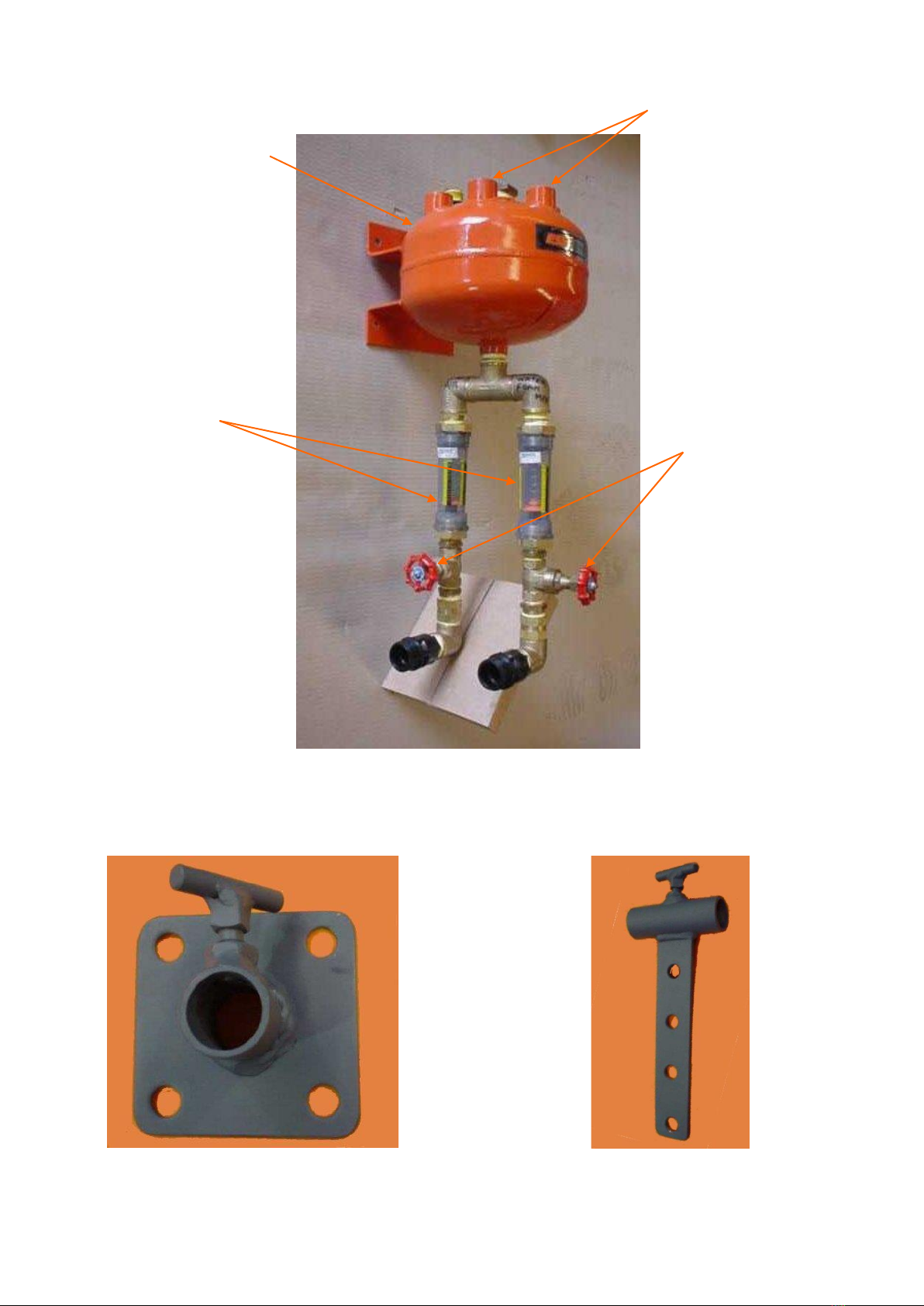
Each expansion chamber should be installed such that the foam delivery lines are
located at the top of the chamber and the solution and air inlets are located at the
bottom of the chamber. The expansion chambers should be located as close as
possible to the dose points.
Install a non-return valve to the air line on the inlet side of the expansion chamber.
When connecting the solution and air supply line to the expansion chambers, ensure
that the air line is connected to the Omega 510 flow meter and the solution line is
connected to the omega 505 flow meter. Note: It is recommended that each inlet
or delivery hose/pipe be a minimum of Ø20mm inside diameter with individual
foam delivery lines to be of lengths less that 15 meters.
Ensure that all pipe/hose lines are secured safely and tidily using weld-on double
pipe clamps or similar.
Connect the SFoam suction tube to the dosing feeder by unscrewing the securing
ferrule. For drums, fit the foot-valve to the end of the tube and place inside the drum.
For Bulki-Bins, a Camlock adapter must be attached to the container outlet and the
suction tube fits over the tail of the adaptor. For suction tube lengths greater than 2
metres, pre-fill the line with chemical to reduce delay at start-up. Note: The
maximum recommended suction tube length is 4 metres.
Select the desired solution concentration by turning the adjusting screw on the
dosing feeder and read the graduated scale. Note: DO NOT ADJUST SOLUTION
CONCENTRATION WHILE THE DOSING FEEDER IS OPERATING, THIS WILL
DAMAGE THE DOSING FEEDER.
Refer to appendix A for details regarding the typical setup of dose points utilising the
various brackets and nozzle types available.
Electrical installation
Note: All electrical installation work should be undertaken by an electrician or
other suitable qualified electrical person.
The SFoam unit will accept 90 to 260Vac single phase power. Refer to the electrical
schematic in Appendix E for further details.
A 24Vdc field switch such as a proximity probe, ultrasonic detector or photoelectric
cell can also be used to automatically start/stop the SFoam unit. Such a device
should be connected across terminals 2 and 6. A volt free N.O. contact may also be
used. Refer to Appendix E for further details.