6
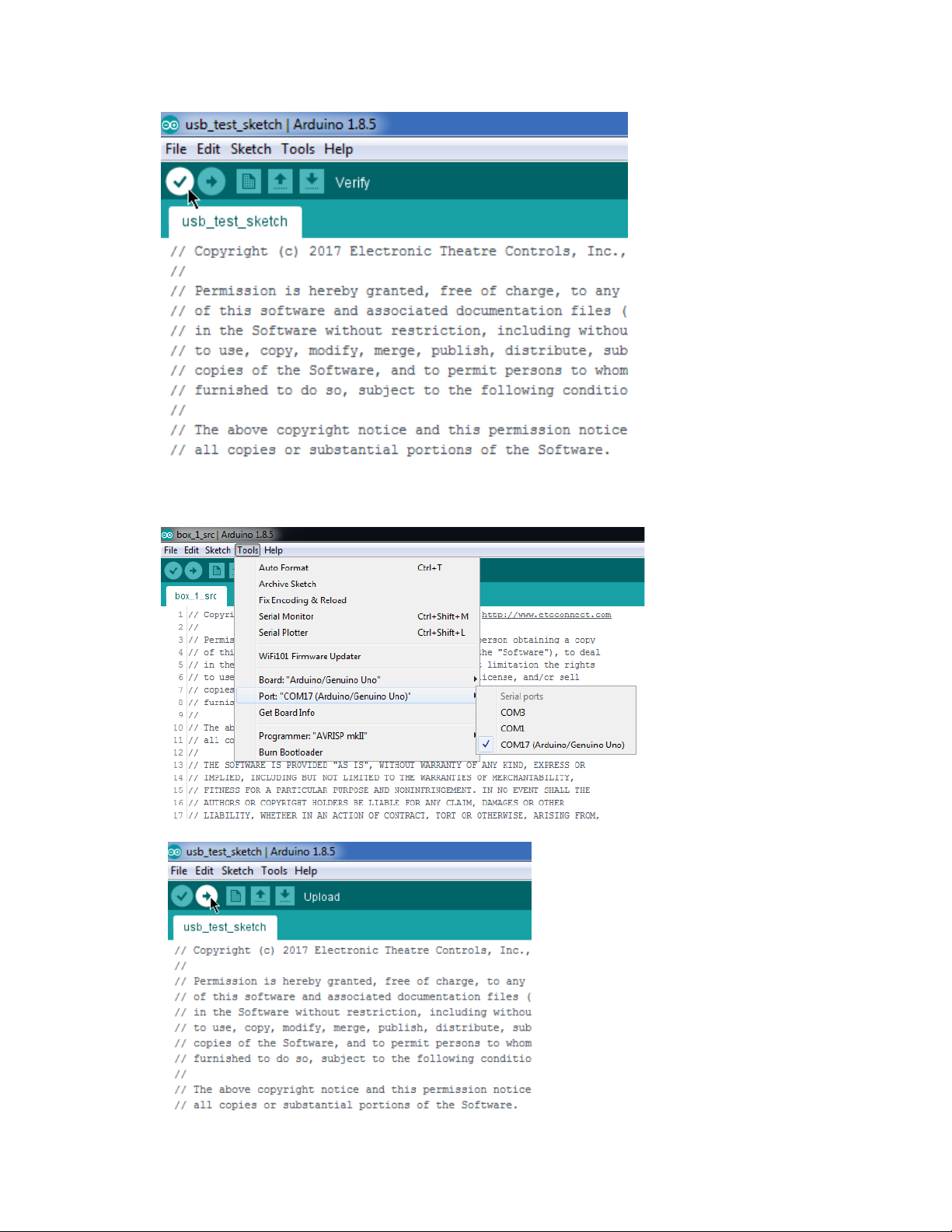
14.After the sketch hasbeen loaded, startEosagain and look for the same Handshake
messages. Note that in this mode, the Arduino doesnot send the repeatingPing
messages, and the Arduino’s TX/RXLEDs will onlyblink once.
If text does notappear, followthe troubleshootingstepsat the end of this document.
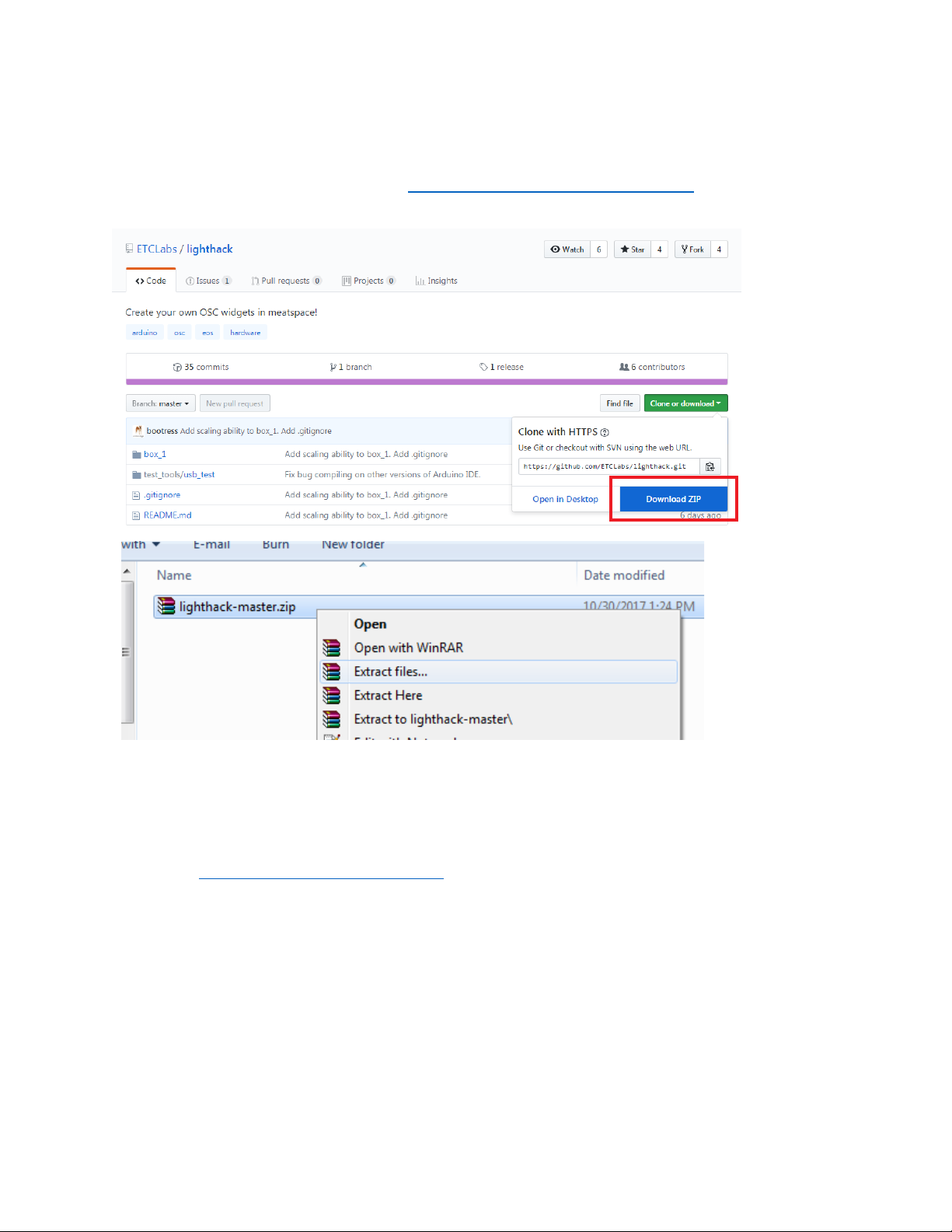
15.Print outthe paper template, making sure to disable any"fit to paper"or scaling options so
that it prints at actualsize. The template isfound at
https://github.com/ETCLabs/lighthack/tree/master/box_1.
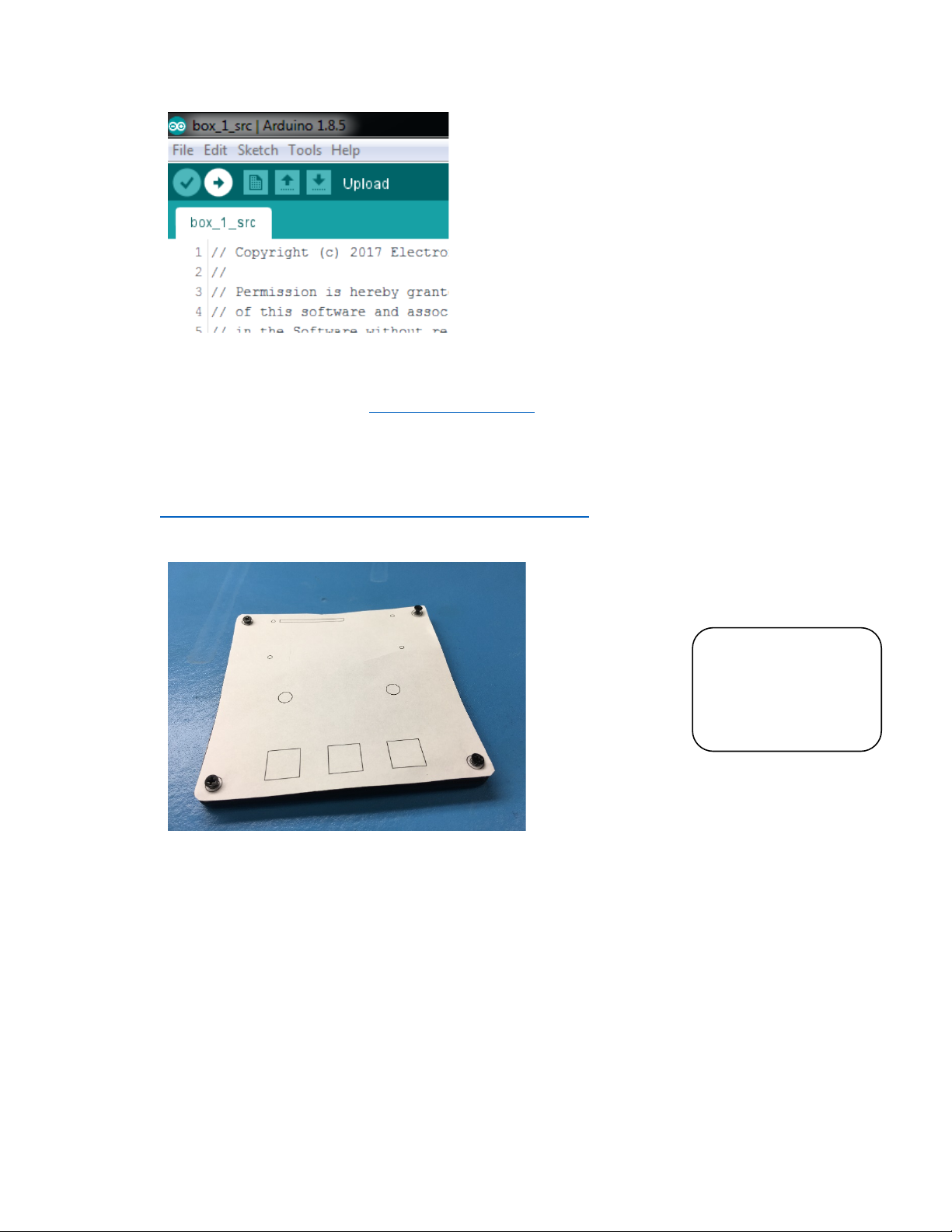
16.Cut out the template and layitover the top of the enclosure lid, using the screwholesor
tape to make sure it doesn't move.
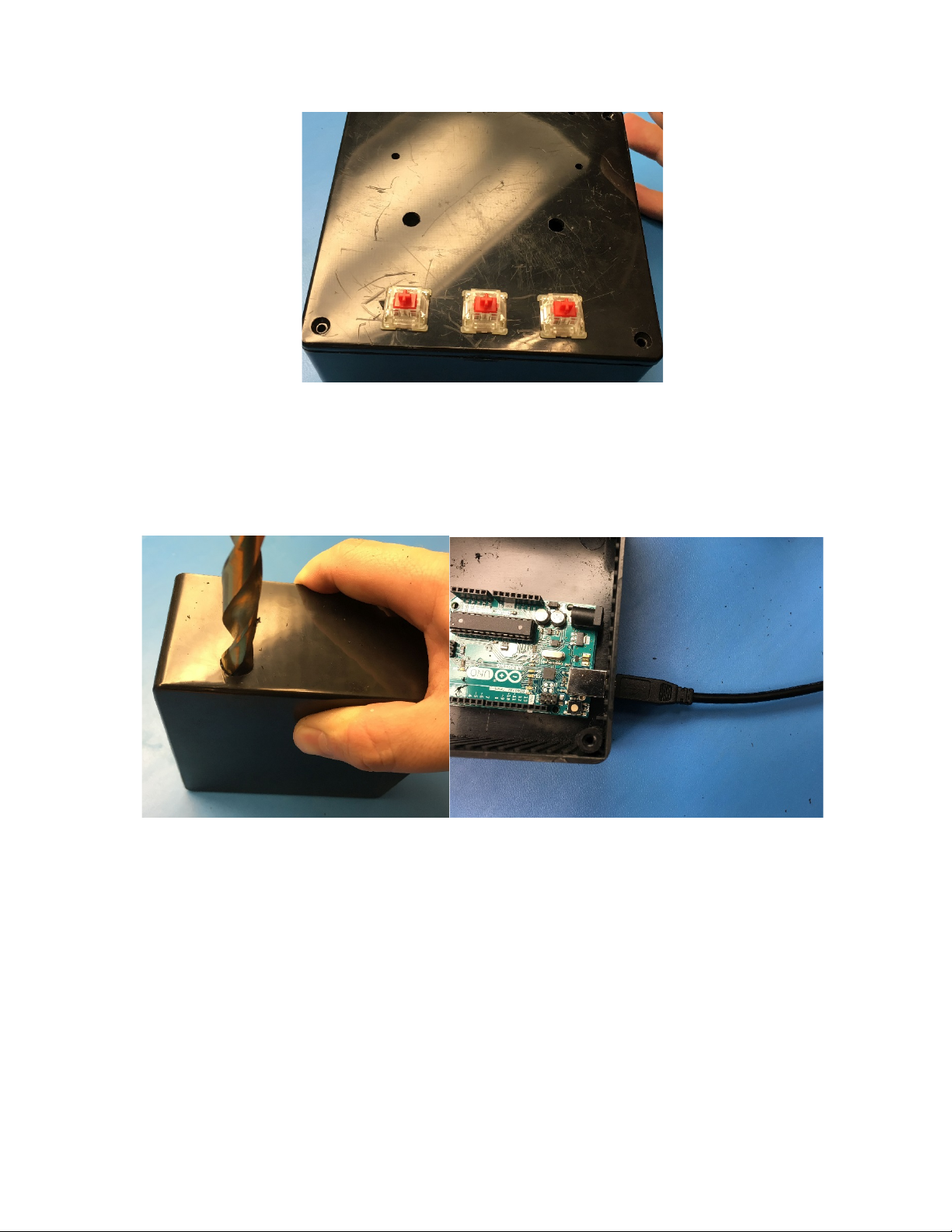
17.Drill outthe holes using the proper size drill bits. Drill starter holes in the square cutouts.
For the long rectangular slot, you may want to drill a few holes right next to each other as a
starting pointfor a file.
18.Using thistemplate, the LCDdisplaywill be mounted to the outside of the lid. Skip to Step
13 if you want to followthe template. If you would like to mount the display to the inside of
the box, cuta rectangular hole in the enclosure lid slightly largerthan the face of the LCD
screen.
TIP: Don't feel like
drilling and filing? Use
the provided 3D
Printer template to
print a "pre-drilled" lid.