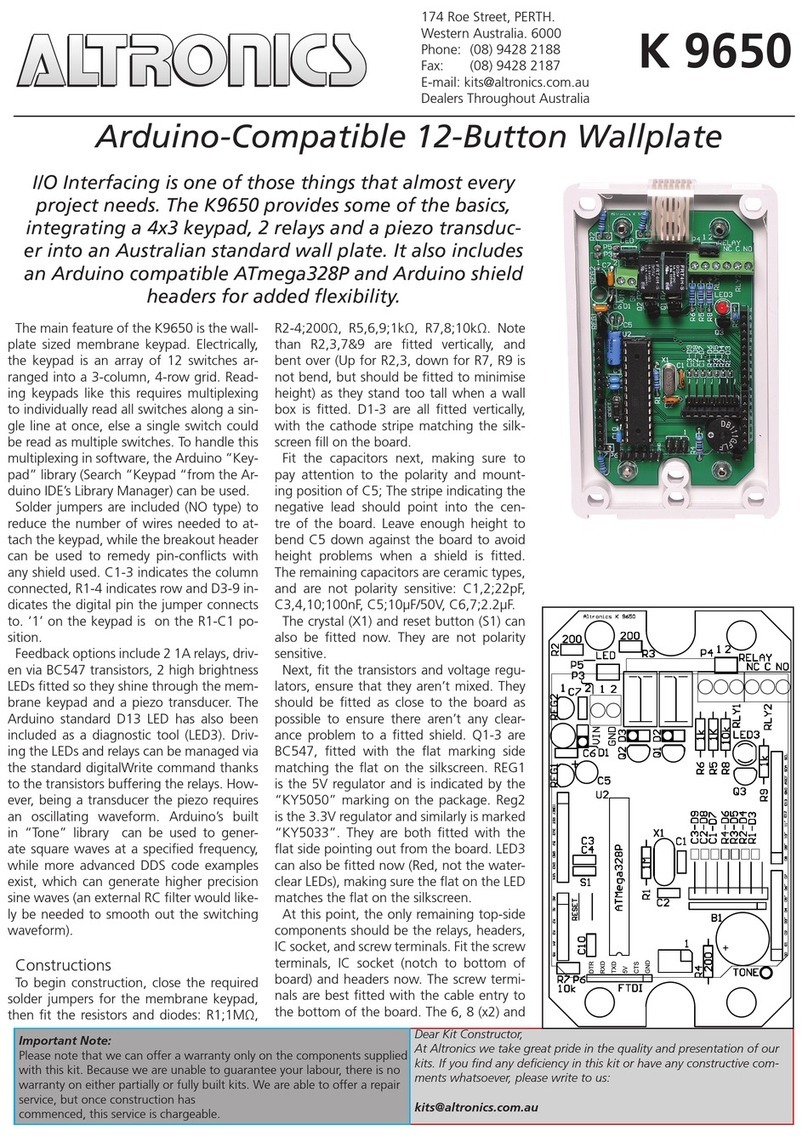
MM200 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE I
Table of Contents
1.COMMUNICATION
S INTERFACES
2.RS485 INTERFACE
(MODBUS RTU)
Modbus Protocol .................................................................................................................................2-1
Electrical Interface ...................................................................................................................................... 2-1
Data Frame Format and Data Rate.................................................................................................... 2-2
Data Packet Format................................................................................................................................... 2-2
Error Checking .............................................................................................................................................. 2-2
CRC-16 Algorithm........................................................................................................................................ 2-3
Timing ............................................................................................................................................................... 2-3
MM200 supported functions.................................................................................................................. 2-4
Modbus Functions ..............................................................................................................................2-4
Function Code 03H..................................................................................................................................... 2-4
Function Code 04H..................................................................................................................................... 2-5
Function Code 05H..................................................................................................................................... 2-5
Function Code 06H..................................................................................................................................... 2-6
Function Code 07H..................................................................................................................................... 2-7
Function Code 08H..................................................................................................................................... 2-8
Function Code 10H..................................................................................................................................... 2-8
Error Responses ........................................................................................................................................... 2-9
Modbus memory map ...................................................................................................................2-10
Format codes.....................................................................................................................................2-19
Performing Commands Using Function Code 10H..........................................................2-25
Using the User Definable Memory Map..........................................................................................2-26
3.FIELDBUS
INTERFACE
Profibus DP.............................................................................................................................................3-1
Profibus power supply configuration................................................................................................. 3-2
Profibus termination .................................................................................................................................. 3-3
Profibus DP-parameterization............................................................................................................... 3-3
Profibus DP-configuration....................................................................................................................... 3-4
Profibus Input Data .................................................................................................................................... 3-6
Profibus Output Data................................................................................................................................. 3-7
Profibus DPV0-Diagnostics ..................................................................................................................... 3-7
Profibus DPV1 ....................................................................................................................................3-16
Profibus DPV1-Acyclic read/write data...........................................................................................3-16
Extended Profibus DPV1 functionality.............................................................................................3-17
Acyclic Read Operation (Modbus functions 03H and 04H) ...................................................3-17
Profibus DPV1-Diagnostics ...................................................................................................................3-18
DeviceNet protocol..........................................................................................................................3-26
DeviceNet power supply configuration ..........................................................................................3-27
DeviceNet setup and configuration (typical) ................................................................................3-28
DeviceNet setup and configuration (ADR) .....................................................................................3-43
DeviceNet Communications ................................................................................................................3-46
Poll data.........................................................................................................................................................3-46
Identity Object (Class Code 01H) ........................................................................................................3-47
Message Router (Class Code 02H).....................................................................................................3-47
DeviceNet Object (Class Code 03H) ..................................................................................................3-48
DeviceNet Connection Object (Class Code 05H).........................................................................3-48
DeviceNet Motor Data - Explicit Object (Class Code A0H)......................................................3-49
DeviceNet Motor Data - Explicit Object (Class Code A1H)......................................................3-51