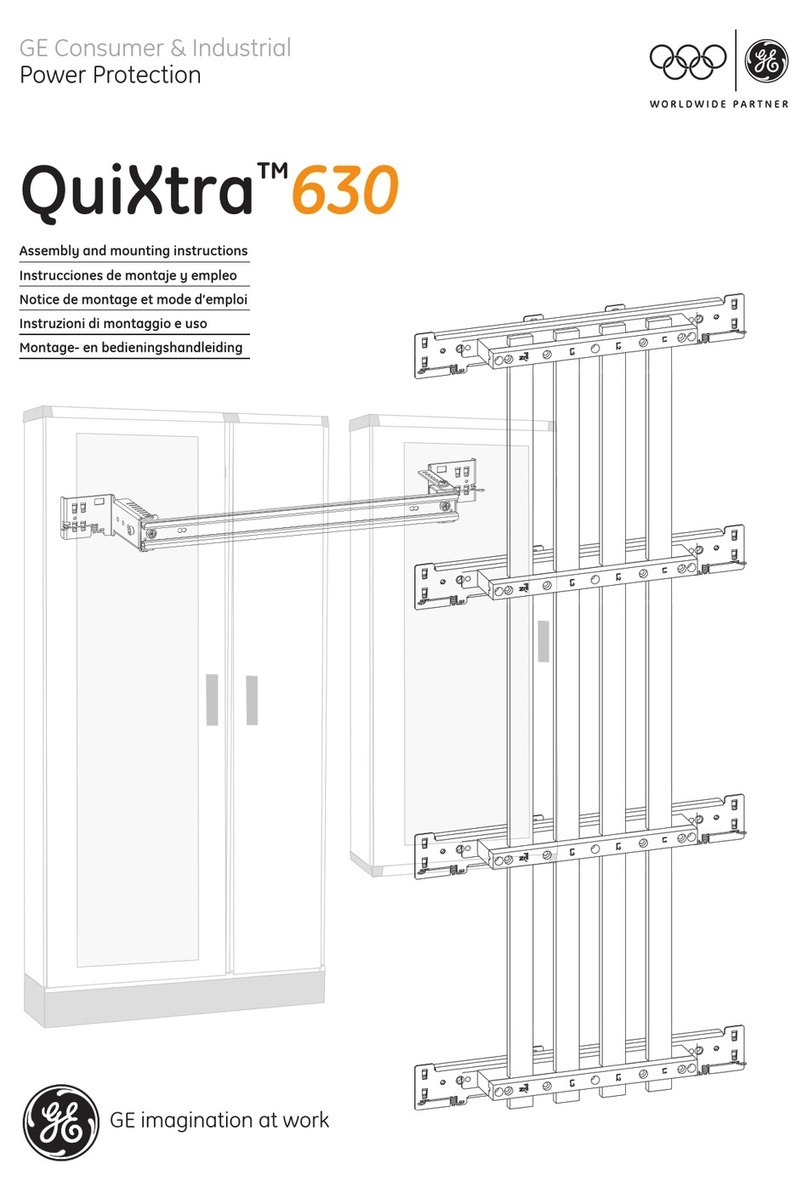
Section 5. EntelliGuard BreakerSection 5. EntelliGuard Breaker
normally open and one normally closed contact.normally open and one normally closed contact.
The position switch is used to indicate the drawoutThe position switch is used to indicate the drawout
position of the position of the
the switch contactsthe switch contacts
change state when the breaker is moved betweenchange state when the breaker is moved between
the CONNECT and the TEST positions. The twothe CONNECT and the TEST positions. The two
contacts on the position switch are wired to thecontacts on the position switch are wired to the
Messenger in the breaker cubicle and provideMessenger in the breaker cubicle and provide
position indication on the position indication on the
Status screen at the HMI. They can also be used inStatus screen at the HMI. They can also be used in
any Flex Logic control scheme.any Flex Logic control scheme.
Spring Charge Indicator SwitchSpring Charge Indicator Switch
The spring charge indicator switch is provided onThe spring charge indicator switch is provided on
all electrically operated EntelliGuard circuit breakersall electrically operated EntelliGuard circuit breakers
and is wired to the Messenger. This contact providesand is wired to the Messenger. This contact provides
status of the circuit breaker closing springs on thestatus of the circuit breaker closing springs on the
Breaker Status screen at the HMI and can also beBreaker Status screen at the HMI and can also be
used in Flex Logic control schemes.used in Flex Logic control schemes.
Remote Close Accessory with One-ShotRemote Close Accessory with One-Shot
Electronic Close CircuitElectronic Close Circuit
The remote close accessory is an electricallyThe remote close accessory is an electrically
operated solenoid which, when energized throughoperated solenoid which, when energized through
the HMI or a Flex Logic control scheme, closes thethe HMI or a Flex Logic control scheme, closes the
EntelliGuard circuit breakerEntelliGuard circuit breaker
“one-shot” electr“one-shot” electr
close circuit, with built-in anti-pump feature, andclose circuit, with built-in anti-pump feature, and
the closing solenoid. The remote close accessorythe closing solenoid. The remote close accessory
is continuously rated and operates as follows.is continuously rated and operates as follows.
Applying control voltage to the close circuit throughApplying control voltage to the close circuit through
the Messenger produces a 250ms pulse to thethe Messenger produces a 250ms pulse to the
closing coil which, in turn, releases the energy storedclosing coil which, in turn, releases the energy stored
in the closing springs. The anti-pump feature preventsin the closing springs. The anti-pump feature prevents
the breaker from repeatedly closing if the closethe breaker from repeatedly closing if the close
signal is maintained. The Messenger provides asignal is maintained. The Messenger provides a
al (1⁄2 second duratial (1⁄2 second durati
whenever the HMI or Flex Logic issues a closewhenever the HMI or Flex Logic issues a close
command. Reset time for the anti-pump circuit iscommand. Reset time for the anti-pump circuit is
approximately 2.5 seconds.approximately 2.5 seconds.
Secondary DisconnectSecondary Disconnect
All EntelliGuard breakers are furnished in drawoutAll EntelliGuard breakers are furnished in drawout
n. The interface between the n. The interface between the
the Entellisys system occurs through a rugged,the Entellisys system occurs through a rugged,
top of the circuit breaker. The secondary disconnecttop of the circuit breaker. The secondary disconnect
is engaged when the breaker is in the CONNECT andis engaged when the breaker is in the CONNECT and
TEST positions and is disengaged when the breakerTEST positions and is disengaged when the breaker
is in the DISCONNECT position. A feedback mecha-is in the DISCONNECT position. A feedback mecha-
nism is provided on the secondary disconnect tonism is provided on the secondary disconnect to
confirm to Entellisys that the secondary disconnectconfirm to Entellisys that the secondary disconnect
is properly engaged. Status of the secondaryis properly engaged. Status of the secondary
disconnect (Connected or Disconnected) is showndisconnect (Connected or Disconnected) is shown
on the Breaker Status screen at the HMI.on the Breaker Status screen at the HMI.
The shunt trip allows remote electrical opening ofThe shunt trip allows remote electrical opening of
the EntelliGuard circuit breaker through the HMIthe EntelliGuard circuit breaker through the HMI
and Flex Logic. The shunt trip is supplied on alland Flex Logic. The shunt trip is supplied on all
electrically operated breakers and is not availableelectrically operated breakers and is not available
on manually operated breakers. The shunt trip coilon manually operated breakers. The shunt trip coil
is rated for intermittent duty and is supplied withis rated for intermittent duty and is supplied with
an auxiliary switch contact that automaticallyan auxiliary switch contact that automatically
removes control power from the coil when theremoves control power from the coil when the
breaker opens.breaker opens.
Spring Charging MotorSpring Charging Motor
The spring charging motor is supplied on all elec-The spring charging motor is supplied on all elec-
trically operated EntelliGuard circuit breakers. Thetrically operated EntelliGuard circuit breakers. The
sing springs sing springs
charged automaticalcharged automatical
when control voltage is when control voltage is
applied to the applied to the
typically occurs when the breaker is racked in totypically occurs when the breaker is racked in to
disconnect engages.disconnect engages.
When the breaker closing springs are fully charged,When the breaker closing springs are fully charged,
cutoff switch de-enercutoff switch de-ener
gizes the charging gizes the charging
The closing springs will recharge automaticallyThe closing springs will recharge automatically
after a breaker closing operation. If control powerafter a breaker closing operation. If control power
is lost during the spring charging cycle, springis lost during the spring charging cycle, spring
charging can be completed using the integralcharging can be completed using the integral
manual pump handle.manual pump handle.
The EntelliGuardThe EntelliGuard
available in available in
2000, 3200, 4000, and 5000 amp frame sizes with2000, 3200, 4000, and 5000 amp frame sizes with
short circuit interrupting ratings from 30kA to 200kA.short circuit interrupting ratings from 30kA to 200kA.
The model number of the breaker indicates itsThe model number of the breaker indicates its
interrupting capacity (IC). EGS indicates “Standardinterrupting capacity (IC). EGS indicates “Standard
indicates “Fused.indicates “Fused.
larger kVA substation transformers as well as inlarger kVA substation transformers as well as in
paralleling applications. Fused circuit breakers haveparalleling applications. Fused circuit breakers have
200kA IC rati200kA IC rati
ng for use in large netng for use in large net
Table 5.1 lists the interrupting capacities (IC) forTable 5.1 lists the interrupting capacities (IC) for
perating voltages.perating voltages.
Catalog NumbersCatalog Numbers
unique catalog unique catalog
number identifies number identifies
breakers. The catalog number contains informationbreakers. The catalog number contains information
on the breaker frame rating (continuous currenton the breaker frame rating (continuous current
and short circuit), the fuse rating (if equipped withand short circuit), the fuse rating (if equipped with