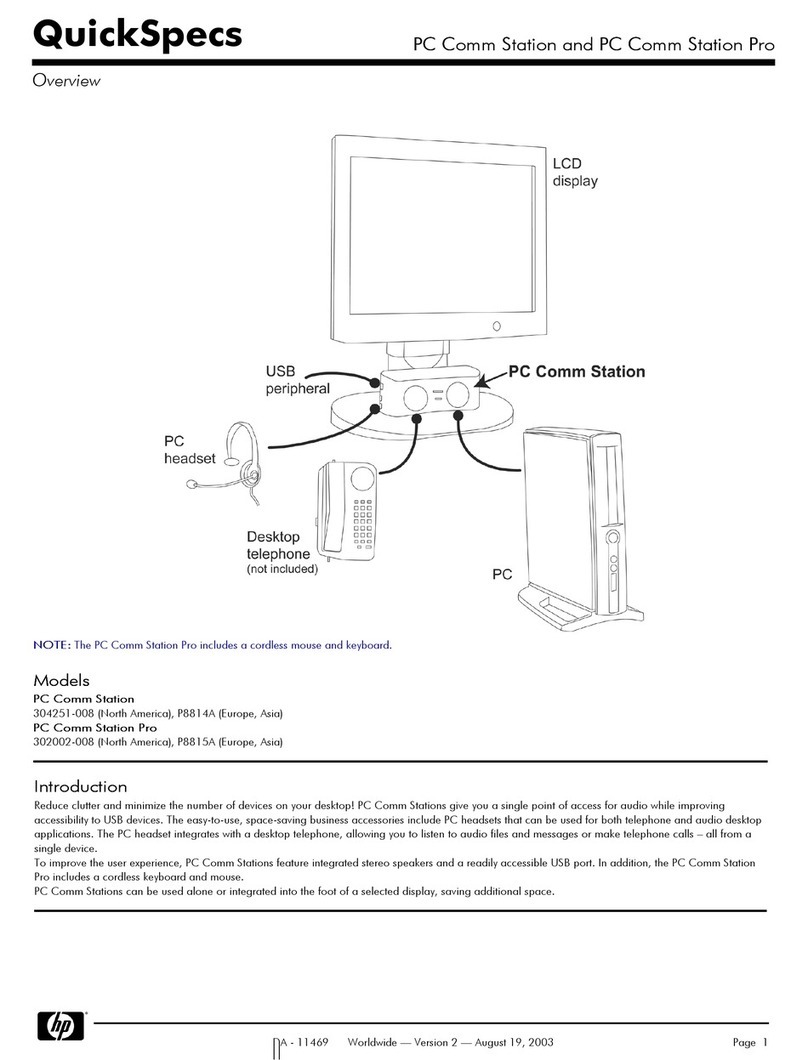
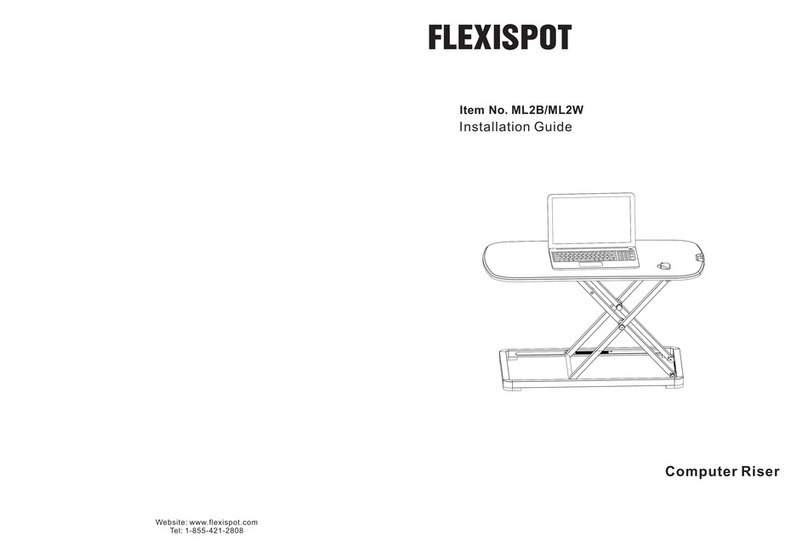
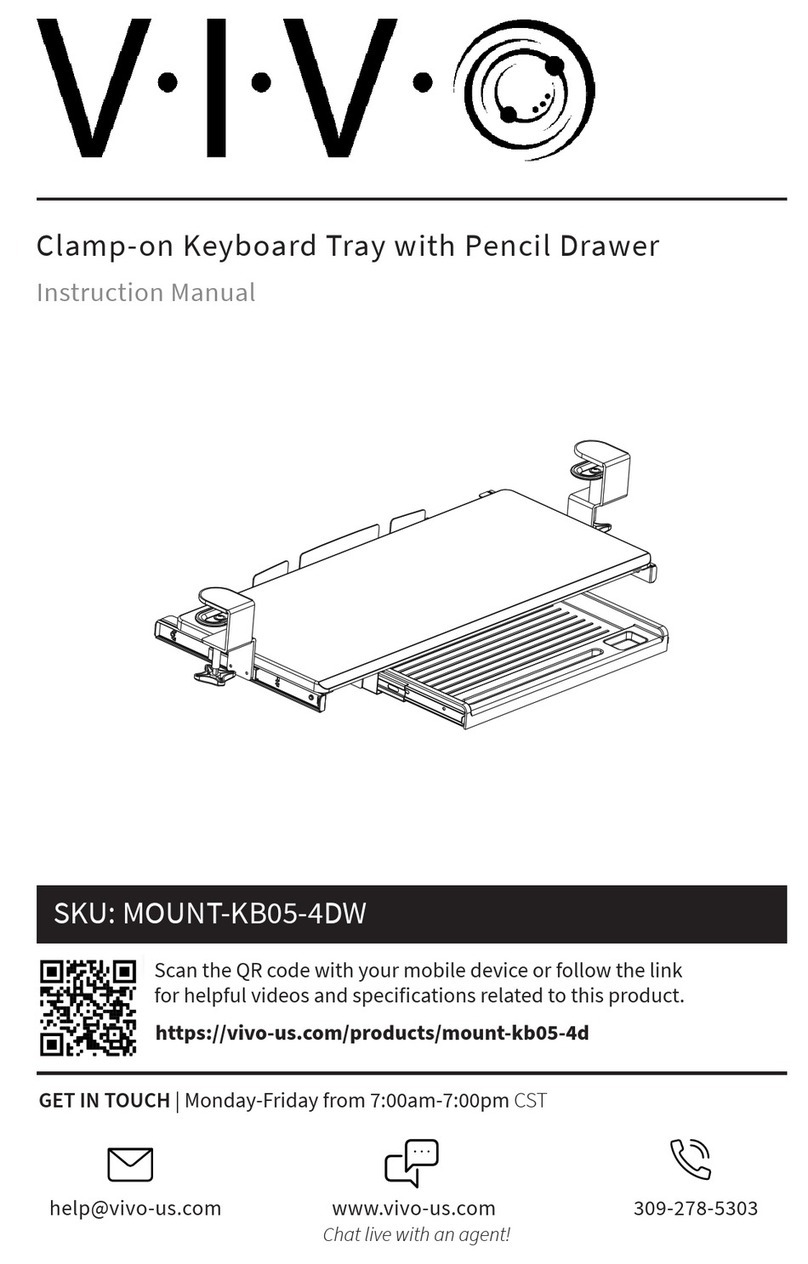
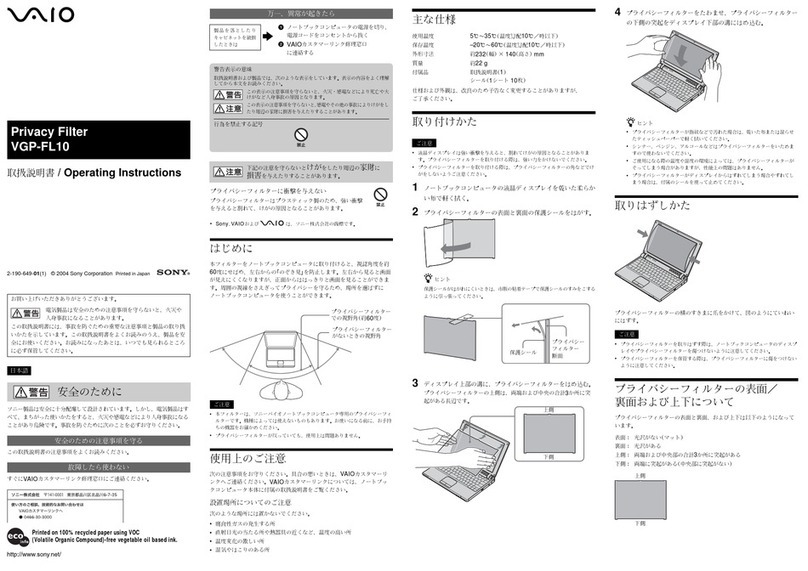
HP 68000 Series User manual
Other HP Computer Accessories manuals

HP
HP GM322AA - Wireless Multimedia Keyboard User manual

HP
HP 5992-3838 User manual

HP
HP Pavilion Slimline s3000 - Desktop PC User manual

HP
HP MINI 1101 User manual

HP
HP MH0GC User manual

HP
HP Integrity cx2600 User manual

HP
HP FQ481AA - Wireless Elite Desktop Keyboard User manual

HP
HP 5219URF Instruction Manual

HP
HP 5219URF Instruction Manual

HP
HP L1510 User manual

HP
HP B1476 68020 User manual

HP
HP EISA/PCI Multiplexer User manual

HP
HP Xw6200 - Workstation - 2 GB RAM User manual

HP
HP Integrity cx2600 User manual

HP
HP P5911A - Cordless Keyboard And Mouse User manual

HP
HP HP Wired Keyboard + Mouse User manual

HP
HP DHN0 Guide

HP
HP P2360AA #ABA User manual

HP
HP Xw4550 - Workstation - 2 GB RAM User manual

HP
HP P5911A - Cordless Keyboard And Mouse User manual