Hypersen Technologies Co., Ltd. HPS-FT-USER V1.8
3/38
Table of Contents
1 Product introduction ........................................................................................................................................5
1.1 Sensor introduction ..................................................................................................................................5
1.1.1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................................5
1.1.2 Product features ................................................................................................................................5
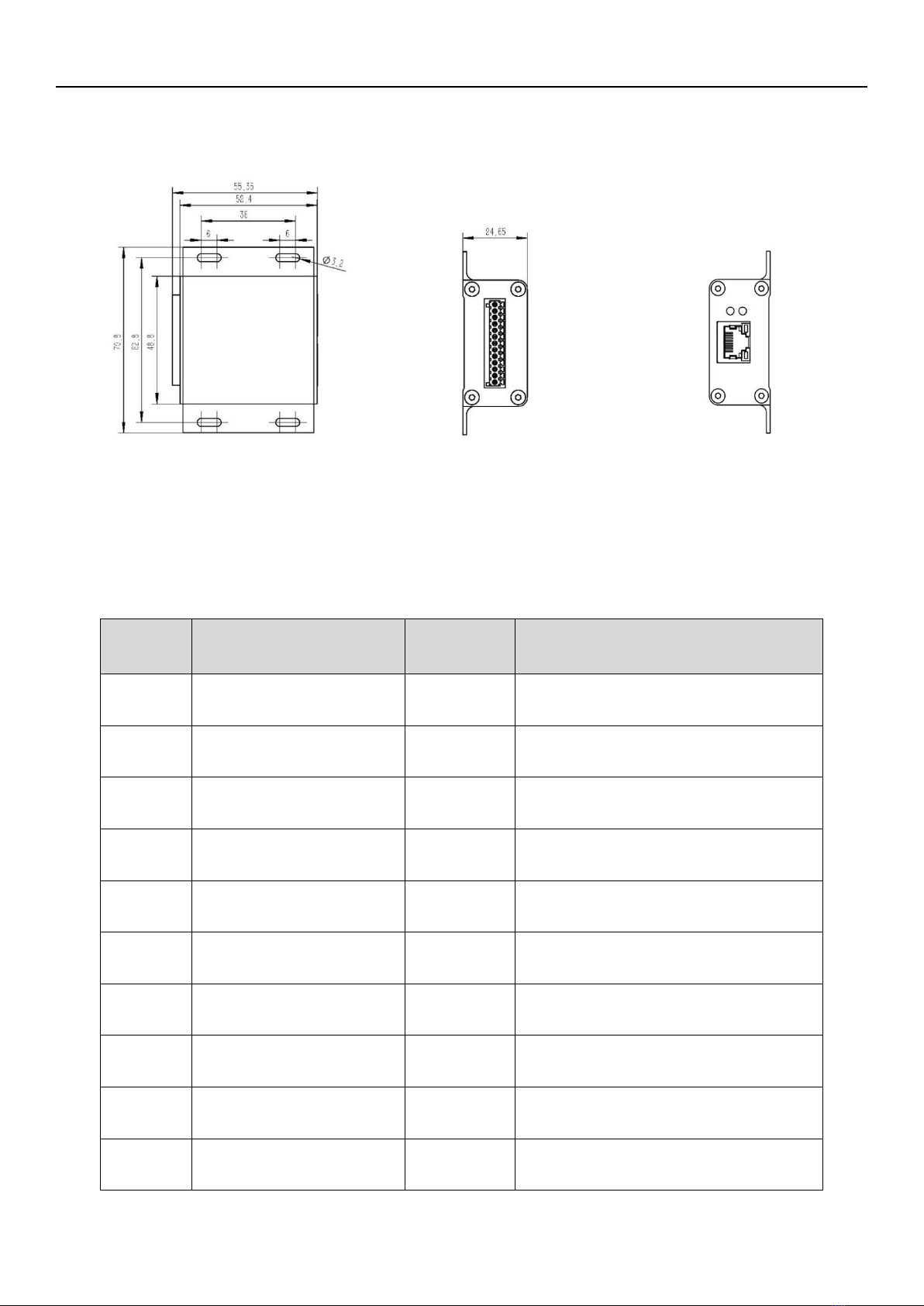
1.1.3 Physical dimensions ..........................................................................................................................6
1.1.4 Cable definition ................................................................................................................................. 8
1.1.5 Packaging information ...................................................................................................................... 8
1.2.1 Product description ........................................................................................................................... 8
1.2.2 Physical dimensions ..........................................................................................................................9
1.2.3 Wiring and indicator light definition ...................................................................................................9
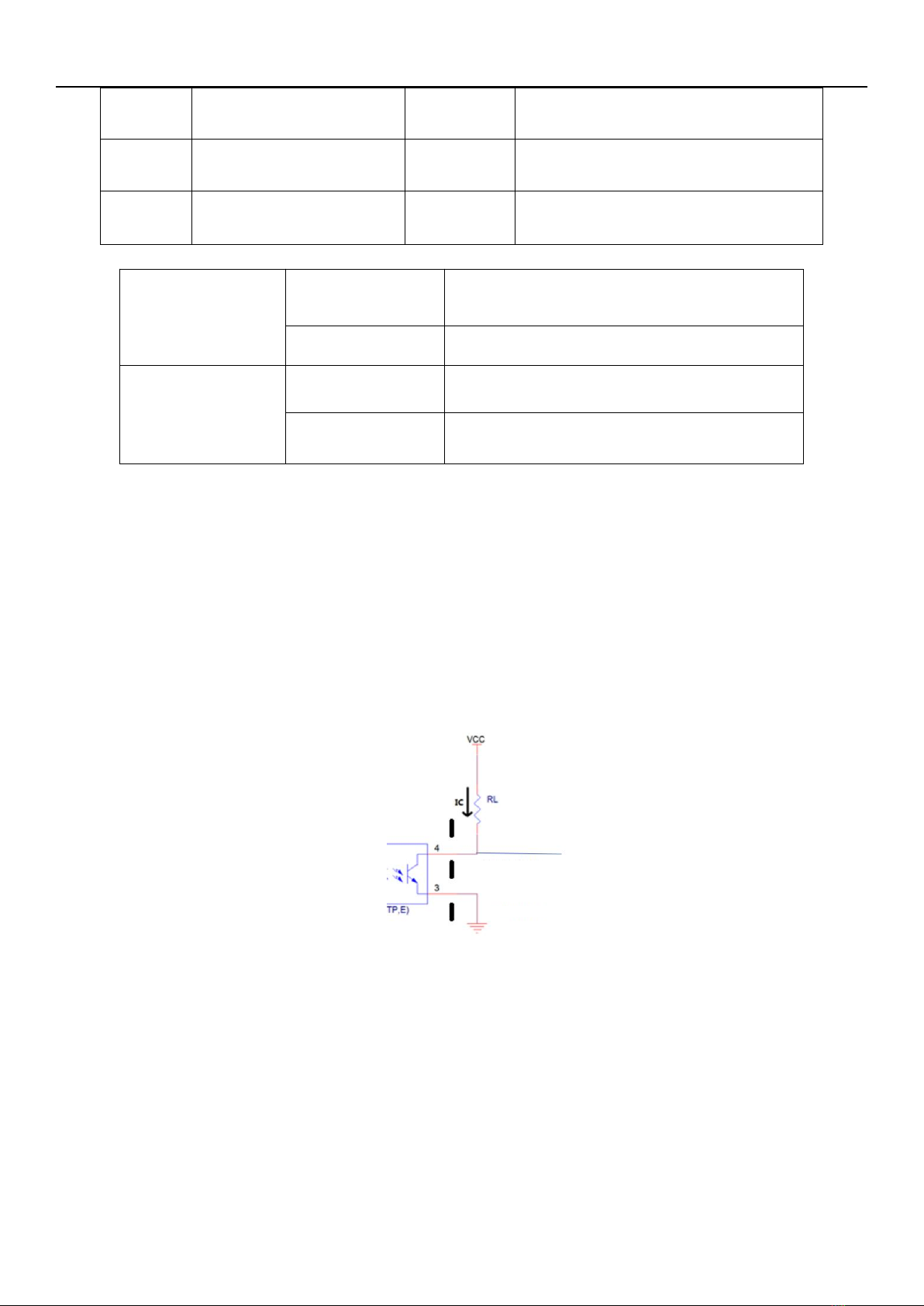
1.2.4 IO protection alarm function ............................................................................................................10
1.2.5 Ethernet bus communication port ...................................................................................................10
2 Precautions for use .......................................................................................................................................11
2.1 Sensor overload protection ....................................................................................................................11
2.1.1 Calculation of the total torque during use .......................................................................................11
2.1.2 Robot emergency stop IO control ...................................................................................................12
2.1.3 Setting of the overload protection threshold ...................................................................................12
2.2 Sensor and robotic arm connection .......................................................................................................13
3 Warranty ....................................................................................................................................................... 13
3.1 Product warranty ....................................................................................................................................13
3.2 Disclaimer .............................................................................................................................................. 14
4 Installation .....................................................................................................................................................14
4.1 Tools and accessories ...........................................................................................................................14
4.2 Mechanical structure installation ........................................................................................................... 15
4.3 Electrical cable installation .................................................................................................................... 17
4.4 IO protection wiring ................................................................................................................................18
4.4.1 Robot emergency stop IO wiring (NPN, no-load IO)......................................................................19
4.4.2 Robot protective stop wiring (NPN, no-load IO) ............................................................................. 19
4.4.3 Setting and enabling of the protection mode of the robot .............................................................. 20
5 Host demonstration software ....................................................................................................................... 21
5.1 Ethernet-based host demonstration software ....................................................................................... 21