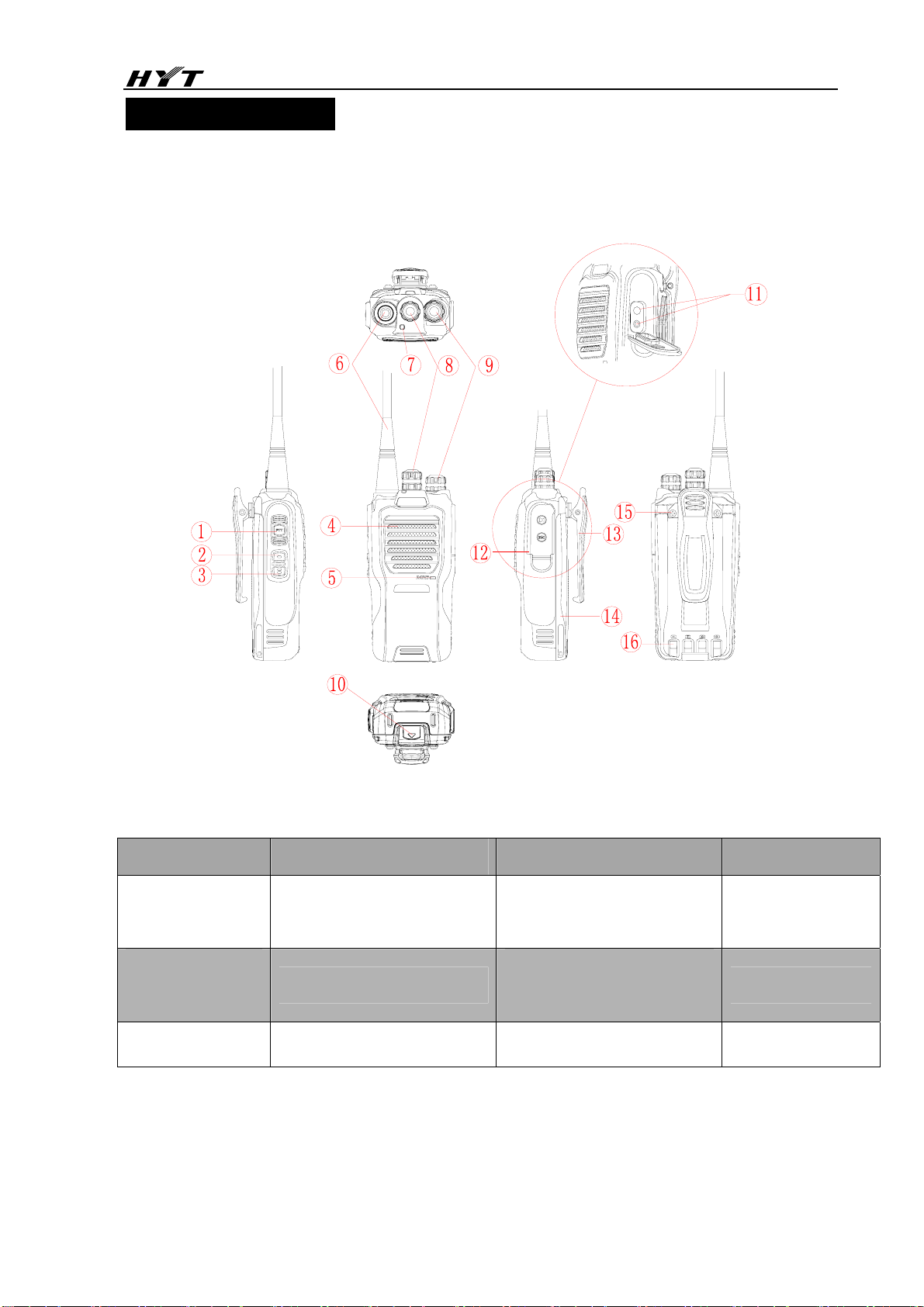
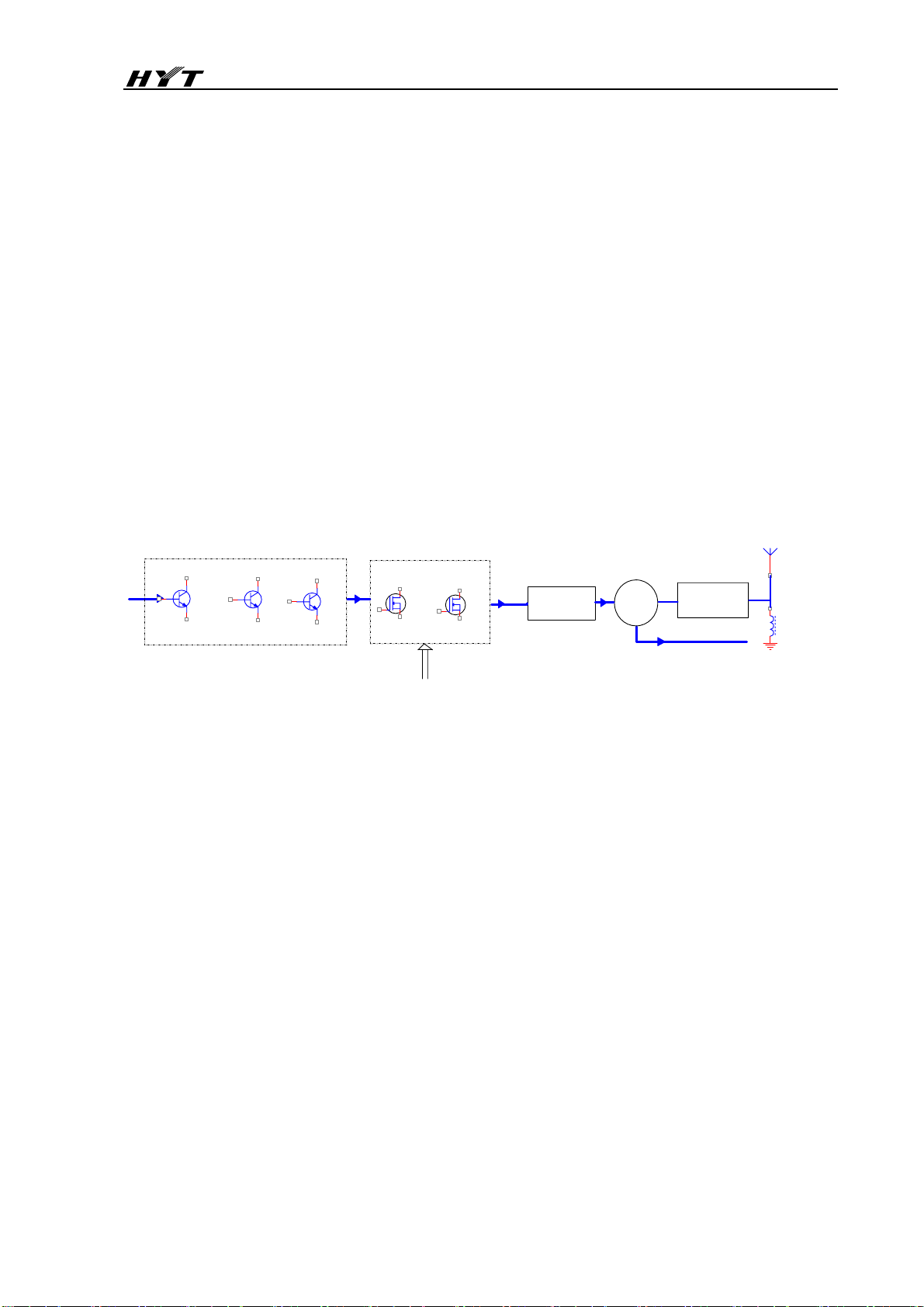
3
General
Manual Scope
This manual is intended for use by experienced technicians familiar with similar types of
communication equipment. It contains all service information required for the equipment and is
current as of the publication date.
Safety and General Information
The following general safety precautions as would normally apply, should be observed during all
phases of operation, service and repair of this equipment.
zThis equipment should be serviced by qualified technicians only.
zDO NOT operate the transmitter of radio unless all RF connectors are secure and any open
connectors are properly terminated.
zDo not modify the radio for any reason.
zUse only HYT original batteries and chargers.
zUse only the supplied or an approved antenna.
zDo not use any portable radio that has a damaged antenna. If a damaged antenna comes into
contact with your skin, a minor burn can result.
zFor vehicles with an air bag, do not place a radio in the area over an air bag or in the air bag
deployment area. Air bags inflate with great force. If a radio is placed in the air bag deployment
area and the air bag inflates, the radio may be propelled with great force and cause serious
injury to occupants of the vehicle.
zTurn off your radio prior to entering any area with a potentially explosive atmosphere.
zDo not charge your battery in a potentially explosive atmosphere.
zTo avoid possible interference with blasting operations, turn off your radio when you are near
electrical blasting caps, in a blasting area, or in areas posted: “Turn off two-way radio.” Obey
all signs and instructions.
zDo not expose the radio to direct sunlight over a long time, nor place it close to heating source.
zWhen using your radio, hold the radio in a vertical position with the microphone 3 to 4
centimeters away from your lips.
zIf you wear a radio on your body when transmitting, ensure that the radio and its antenna are at
least 2.5cm away from your body.